Movement That Tips The Soles Laterally
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
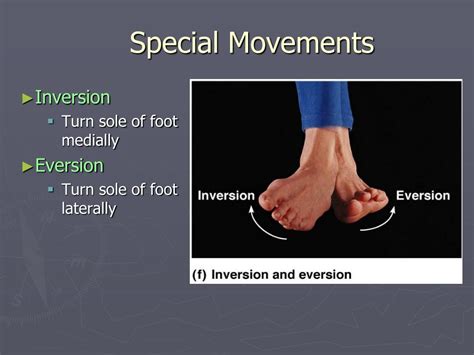
Table of Contents
Lateral Sole Tipping Movements: A Comprehensive Guide
Lateral sole tipping, a movement often overlooked in discussions of gait and biomechanics, refers to the tilting of the sole of the foot outward, away from the midline of the body. This subtle yet significant movement plays a crucial role in various aspects of human movement, from maintaining balance and stability to facilitating efficient locomotion and shock absorption. Understanding the mechanisms, contributing factors, and potential implications of lateral sole tipping is essential for professionals in fields such as physiotherapy, podiatry, and athletic training. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this movement, exploring its biomechanics, associated conditions, and strategies for assessment and intervention.
Biomechanics of Lateral Sole Tipping
Lateral sole tipping, also known as eversion, is a complex movement involving multiple joints and muscle groups in the lower limb. It’s not an isolated action but rather a component of the overall foot and ankle complex motion during gait and other activities. The movement primarily involves the subtalar joint, which is situated between the talus and calcaneus bones. Subtalar eversion, a key component of lateral sole tipping, is accompanied by abduction (movement away from the midline) and dorsiflexion (bending the foot upward) of the foot.
Muscles Involved in Lateral Sole Tipping
Several muscle groups contribute to this movement:
- Tibialis posterior: This deep posterior compartment muscle is crucial for inversion (opposite of eversion). While not directly responsible for causing eversion, its proper function is vital for controlling and limiting excessive eversion. Weakness or dysfunction here can lead to increased lateral tipping.
- Peroneal muscles (Peroneus longus and Peroneus brevis): These lateral compartment muscles are the primary evertors of the foot. They play a critical role in stabilizing the foot during stance phase and assist in propulsion during gait. Overactivity or tightness in these muscles can contribute to excessive lateral sole tipping.
- Extensor digitorum longus and Extensor hallucis longus: These muscles contribute to dorsiflexion, which often accompanies eversion.
- Intrinsic foot muscles: These smaller muscles within the foot contribute to the fine-tuning of foot position and arch support, indirectly influencing lateral sole tipping.
Factors Influencing Lateral Sole Tipping
Various factors can influence the degree and pattern of lateral sole tipping:
- Foot structure: Individuals with certain foot types, such as pes planus (flat feet) or pes cavus (high arches), may exhibit different patterns of lateral sole tipping due to variations in arch support and bone structure.
- Muscle imbalances: Muscle weakness or tightness in the muscles surrounding the ankle and foot, as mentioned above, can significantly affect lateral sole tipping. This is a key area to investigate during biomechanical assessments.
- Gait patterns: Different gait patterns, influenced by factors such as running style, footwear, and underlying neurological conditions, will impact the extent of lateral sole tipping.
- Ground reaction forces: The nature of the surface being walked or run on influences the forces applied to the foot and thus the degree of lateral sole tipping. Uneven surfaces or inclines can increase the amount of eversion required for balance.
- Joint laxity: Excessive laxity in the subtalar and other ankle joints can contribute to increased lateral sole tipping.
Clinical Implications of Excessive Lateral Sole Tipping
Excessive or uncontrolled lateral sole tipping can contribute to a variety of musculoskeletal problems:
- Ankle sprains: Repeated or forceful eversion can lead to injury of the lateral ankle ligaments, resulting in sprains. This is a common injury among athletes and individuals with inadequate proprioception (awareness of body position).
- Plantar fasciitis: The plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue on the bottom of the foot, can become inflamed due to excessive strain from abnormal foot mechanics, including excessive eversion.
- Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD): Weakness or dysfunction of the tibialis posterior muscle, responsible for inversion, can lead to increased eversion and eventually PTTD, a condition that often results in flat feet and pain.
- Metatarsalgia: Pain in the ball of the foot can be related to abnormal weight distribution and loading patterns, which can be exacerbated by excessive lateral sole tipping.
- Knee pain: Excessive lateral sole tipping can disrupt the kinetic chain, impacting the alignment of the knee and potentially leading to knee pain.
- Hip and back pain: The effects of poor foot mechanics can propagate upwards, affecting hip and back alignment and contributing to pain in these areas.
Assessment and Diagnosis of Lateral Sole Tipping
Identifying excessive lateral sole tipping requires a thorough assessment, involving several methods:
- Observational gait analysis: Observing an individual's gait pattern can reveal excessive eversion, often characterized by outward rolling of the foot during the stance phase.
- Foot and ankle examination: Palpating the muscles of the lower leg and foot can reveal muscle imbalances or tenderness. Assessing range of motion in the ankle and subtalar joints is also important.
- Postural assessment: Analyzing posture can reveal compensatory mechanisms related to foot mechanics.
- Static and dynamic foot posture analysis: Assessing the foot's position in both static (non-moving) and dynamic (moving) situations allows for a more comprehensive evaluation.
- Specialized imaging: In some cases, X-rays or other imaging techniques may be used to assess the structural integrity of the bones and joints.
Interventions for Lateral Sole Tipping
Management of excessive lateral sole tipping involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific needs:
- Therapeutic exercises: Strengthening exercises targeting the tibialis posterior and other inverters, while stretching the peroneal muscles, can help restore muscle balance and improve foot stability.
- Proprioceptive training: Exercises focused on improving balance and proprioception can help enhance awareness of foot position and control during movement. These might include balance boards or exercises performed on unstable surfaces.
- Foot orthotics: Custom-made orthotics can provide support to the arch and control excessive eversion, reducing strain on the foot and ankle. These devices are often used in conjunction with therapeutic exercises.
- Taping techniques: Kinesiology taping or other taping methods can provide temporary support and improve muscle activation.
- Manual therapy: Physical therapists may use manual techniques to address joint restrictions and improve tissue mobility.
- Footwear modifications: Choosing appropriate footwear with adequate support and cushioning can reduce stress on the foot and improve alignment. Avoidance of high heels or footwear lacking adequate arch support is often advised.
Footwear Considerations for Lateral Sole Tipping
The type of footwear worn significantly impacts lateral sole tipping. Inappropriate footwear can exacerbate existing problems or even contribute to the development of excessive eversion.
- Supportive footwear: Footwear that provides adequate arch support, cushioning, and a stable base is crucial for minimizing excessive eversion.
- Avoidance of high heels: High heels significantly alter foot mechanics, promoting increased eversion and strain on the foot and ankle.
- Proper fit: Ensure footwear fits correctly, avoiding shoes that are too tight or too loose. A proper fit allows for optimal foot function and reduces the risk of injury.
- Consideration of foot type: Footwear choices should be tailored to individual foot type, with those having flat feet requiring greater arch support than those with high arches.
Conclusion
Lateral sole tipping is a complex movement with significant implications for human movement and musculoskeletal health. Understanding the biomechanics, contributing factors, and potential consequences of this movement is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to optimize their physical performance and well-being. A comprehensive approach to assessment and intervention, addressing both structural and functional components, is essential for effective management of excessive lateral sole tipping. Through a combination of targeted exercises, appropriate footwear, and potentially orthotic intervention, individuals can improve their foot stability, reduce pain, and enhance their overall musculoskeletal health. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on managing lateral sole tipping.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Laker Company Reported The Following January
Mar 17, 2025
-
Quantitative Analysis Of Vinegar Via Titration
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Interest Rate A Company Pays On 1 Year 5 Year
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Shape Of An Atomic Orbital Is Associated With
Mar 17, 2025
-
Parallelism In Writing Can Reflect Which Of The Following
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Movement That Tips The Soles Laterally . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
