Which Statement Summarizes The Main Idea Of Reciprocal Determinism
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
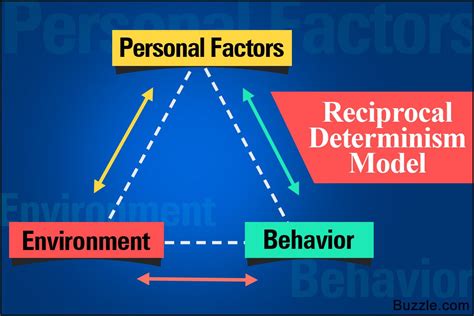
Table of Contents
Which Statement Summarizes the Main Idea of Reciprocal Determinism?
Albert Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory (SCT) is a prominent framework in psychology that explains human behavior as a dynamic interplay between personal factors, environmental factors, and behavior itself. Central to this theory is the concept of reciprocal determinism. Understanding this concept is crucial for comprehending how individuals learn, develop, and interact with their surroundings. But what exactly is reciprocal determinism, and which statement best captures its essence? Let's delve deep into this fascinating psychological principle.
Understanding Reciprocal Determinism: A Three-Way Street
Reciprocal determinism posits that personal factors, environmental factors, and behavior influence one another in a continuous, cyclical fashion. It's not a simple linear cause-and-effect relationship; rather, it's a complex interplay where each element acts as both a cause and an effect. Think of it as a three-way street, with constant traffic flowing in all directions.
Let's break down each component:
1. Personal Factors: The Internal World
Personal factors encompass an individual's internal attributes, including:
- Cognitive processes: This includes thoughts, beliefs, expectations, self-efficacy (belief in one's ability to succeed), and self-concept. For example, believing you're a good public speaker (high self-efficacy) will influence your behavior when giving a presentation.
- Emotional states: Feelings like anxiety, excitement, or confidence directly impact behavior. Feeling anxious before a test might lead to poor performance, while feeling confident might enhance it.
- Biological factors: Genetics, temperament, and physical health contribute to individual differences in how people behave and interact with their environment. A predisposition to anxiety, for instance, can influence social interactions and overall behavior.
2. Environmental Factors: The External World
Environmental factors refer to the external stimuli that surround an individual, such as:
- Physical environment: This includes the physical setting, climate, and available resources. Living in a noisy, crowded environment might lead to stress and different behaviors than living in a quiet, peaceful setting.
- Social environment: This encompasses social interactions, cultural norms, and the influence of significant others. Peer pressure, family dynamics, and societal expectations profoundly shape an individual's behavior.
- Cultural factors: Cultural norms and values influence what behaviors are considered acceptable or unacceptable. Different cultures have different expectations about communication styles, personal space, and social interactions.
3. Behavior: The Observable Actions
Behavior refers to observable actions and responses. This is the outcome of the interaction between personal and environmental factors. It is also a crucial factor that shapes both personal factors and the environment. For example:
- A student consistently studies diligently (behavior) which reinforces their belief in their ability to succeed (personal factor). This can lead them to seek out more challenging courses (changing the environment).
- A person's shy behavior (behavior) might lead them to avoid social gatherings (changing the environment), which reinforces their negative self-perception (personal factor).
Illustrative Examples of Reciprocal Determinism in Action
Let's look at some concrete examples to better grasp the concept:
Example 1: Learning to Ride a Bicycle
A child's attempt to learn to ride a bicycle illustrates reciprocal determinism perfectly.
- Personal Factors: The child's self-efficacy (belief in their ability to learn), previous experiences, and physical coordination all play a role.
- Environmental Factors: The availability of a bicycle, a safe place to practice, and parental encouragement or instruction are crucial environmental influences.
- Behavior: The child's practice, their attempts at balancing, and their persistence in learning are the observable behaviors. Success in balancing and riding reinforces the child's self-efficacy, leading them to practice more (and change their environment by seeking out more challenging terrains). Conversely, repeated failures might decrease their self-efficacy, causing them to give up (changing the behavior and, potentially, the environment by avoiding the bike).
Example 2: Developing a Healthy Diet
The adoption of a healthy diet also involves reciprocal determinism.
- Personal Factors: One's knowledge about nutrition, self-discipline, and health goals significantly influence dietary choices.
- Environmental Factors: Accessibility to healthy food options, social norms around eating habits, and family traditions shape dietary behavior.
- Behavior: The individual's actual food choices, the frequency of healthy eating, and their adherence to a meal plan represent their behavior. Success in maintaining a healthy diet reinforces positive self-efficacy related to health and might lead the individual to further explore healthy recipes and join fitness groups (changing the environment).
Example 3: Overcoming Social Anxiety
Overcoming social anxiety showcases the cyclical nature of reciprocal determinism.
- Personal Factors: Negative self-perception, fear of judgment, and low self-esteem contribute to social anxiety.
- Environmental Factors: Previous negative social experiences, lack of supportive relationships, and exposure to critical social settings influence the development and maintenance of social anxiety.
- Behavior: Avoiding social situations, exhibiting anxious behaviors during social interactions, and experiencing high levels of distress in social settings are the observable behaviors. Successfully navigating a social interaction might lead to increased self-efficacy and a willingness to engage in more social situations (changing behavior and environment), while continued avoidance reinforces the negative self-perception and anxiety.
Statements Summarizing Reciprocal Determinism: Which is Best?
Now, let's consider several statements that attempt to summarize the main idea of reciprocal determinism and evaluate their accuracy:
Statement A: "Behavior is solely determined by environmental factors." Incorrect. This statement ignores the significant role of personal factors.
Statement B: "Personal factors are the primary drivers of behavior." Incorrect. This statement ignores the influence of environmental factors and the feedback loop between behavior and the environment.
Statement C: "Behavior, personal factors, and environmental factors mutually influence one another in a continuous process." Correct. This accurately captures the essence of reciprocal determinism.
Statement D: "Environmental factors shape behavior, which in turn influences personal factors, but not the other way around." Incorrect. This statement describes a linear, not a cyclical, relationship.
Therefore, Statement C, "Behavior, personal factors, and environmental factors mutually influence one another in a continuous process," is the best summary of the main idea of reciprocal determinism. It accurately emphasizes the dynamic interplay and cyclical nature of the relationship between these three elements.
Implications and Applications of Reciprocal Determinism
The understanding of reciprocal determinism has significant implications across various fields, including:
- Education: Teachers can use this knowledge to create learning environments that support students' self-efficacy and motivation. Creating a supportive classroom environment (environmental factor) can encourage participation and engagement (behavior), which in turn enhances a student's belief in their capabilities (personal factor).
- Therapy: Therapists utilize reciprocal determinism in therapeutic interventions. By modifying either the environment or personal factors (through cognitive restructuring or behavioral techniques), they can facilitate changes in behavior. For example, a therapist might help a patient with social anxiety identify and challenge negative thoughts (personal factor) and create opportunities for positive social interactions (environmental factor) to reduce avoidance behaviors.
- Health Promotion: Promoting healthy behaviors requires addressing both environmental factors (access to healthy food and exercise facilities) and personal factors (self-efficacy and motivation). By providing support and resources, healthcare professionals can increase the likelihood of successful behavior change.
- Organizational Behavior: Understanding reciprocal determinism is crucial for managing and motivating employees. Creating a supportive and rewarding work environment (environmental factor) can foster job satisfaction and productivity (behavior), which in turn strengthens employees' self-efficacy and commitment (personal factor).
Conclusion: The Ongoing Dance of Reciprocal Influence
Reciprocal determinism offers a powerful and nuanced perspective on human behavior, highlighting the ongoing dance of reciprocal influence between personal factors, environmental factors, and behavior. By understanding this intricate interplay, we can better understand ourselves, others, and the world around us. This understanding empowers us to design interventions and strategies aimed at promoting positive change and achieving desired outcomes in various aspects of life. It is not merely a theory; it's a framework for understanding the complexity of human experience and a tool for creating more effective strategies for personal growth and societal improvement. The accurate statement summarizing the main idea underscores the dynamic, cyclical, and mutually influential nature of this crucial psychological concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Definition Best Describes The Term Activation Energy
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Political Business Cycle Refers To The Possibility That
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Job Cost Sheet Contains Blank The Job
Mar 18, 2025
-
An Example Of A Control Statement Is
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Budget Is A Formal Financial
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement Summarizes The Main Idea Of Reciprocal Determinism . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
