Which Of The Following Accurately Describes A Supply Chain Map
Holbox
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
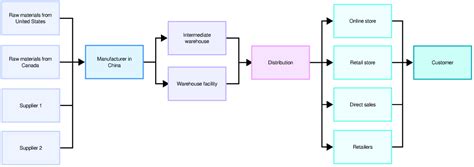
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Accurately Describes A Supply Chain Map
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following Accurately Describes a Supply Chain Map? A Deep Dive
- Understanding the Core Function of a Supply Chain Map
- Evaluating Descriptions of a Supply Chain Map: Accuracy and Completeness
- The Importance of Accuracy in Supply Chain Mapping
- Creating an Accurate Supply Chain Map: Best Practices
- Conclusion: The Value of a Comprehensive Supply Chain Map
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following Accurately Describes a Supply Chain Map? A Deep Dive
A supply chain map is more than just a pretty picture; it's a powerful tool for understanding and optimizing the flow of goods and services from origin to end consumer. But what exactly is a supply chain map, and what makes it accurate? This article will explore the multifaceted nature of supply chain mapping, examining different descriptions and clarifying what constitutes an accurate and effective representation.
Understanding the Core Function of a Supply Chain Map
Before diving into specific descriptions, let's establish the fundamental purpose of a supply chain map. At its core, a supply chain map visually represents the entire process involved in getting a product or service to the market. This includes all the key players, activities, and information flows within the supply chain. An effective map doesn't just list components; it shows the relationships and dependencies between them, highlighting potential bottlenecks, risks, and areas for improvement.
Key elements typically included in a comprehensive supply chain map:
- Suppliers: Tier 1, Tier 2, and even beyond, illustrating the complex network of suppliers providing raw materials and components.
- Manufacturers: Highlighting the processes involved in transforming raw materials into finished goods.
- Distributors: Showcasing the channels used to move products from manufacturers to retailers or end-users.
- Retailers: The points of sale where consumers acquire the final product.
- Transportation Methods: Identifying the modes of transportation (e.g., trucking, shipping, air freight) used at each stage.
- Warehousing and Storage: Illustrating the storage facilities and their roles in managing inventory.
- Information Flows: Showing the movement of data and communication between different stages of the supply chain.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Incorporating relevant metrics to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of each stage.
Evaluating Descriptions of a Supply Chain Map: Accuracy and Completeness
Now, let's evaluate some possible descriptions of a supply chain map, assessing their accuracy and completeness. A truly accurate description will encompass all the key aspects mentioned above. An incomplete description might focus on only one aspect, omitting crucial elements that contribute to a holistic understanding of the supply chain.
Description 1: A simple list of suppliers and manufacturers involved in producing a product.
Accuracy: Low. This description is highly limited. While listing suppliers and manufacturers is a starting point, it lacks critical information about the processes, flows, relationships, and performance metrics that form the core of a supply chain map. It's merely a partial component of a complete map.
Description 2: A flowchart depicting the sequential steps involved in manufacturing a product.
Accuracy: Moderate. This description is more accurate than the first but still falls short. While a flowchart shows the steps, it typically neglects crucial aspects such as supplier relationships, distribution channels, and the movement of information. It often focuses solely on internal manufacturing processes and ignores the broader supply chain ecosystem.
Description 3: A visual representation of all the entities involved in getting a product from raw materials to the end consumer, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, along with the flow of goods and information.
Accuracy: High. This description is much more comprehensive and accurately captures the essence of a supply chain map. It explicitly mentions all the key entities and the crucial flow of both goods and information, which are fundamental elements of a complete and useful supply chain map.
Description 4: A detailed schematic showing the physical locations of all warehouses, factories, and distribution centers involved in the supply chain.
Accuracy: Moderate. This description focuses on the geographical aspect but overlooks other equally important elements, such as the flow of goods, information, and the relationships between different entities. A map focusing solely on physical locations may be a component of a broader supply chain map but is insufficient on its own.
Description 5: A dynamic model that simulates different scenarios to assess the impact of disruptions and optimize supply chain performance.
Accuracy: High. This description recognizes the evolving and dynamic nature of supply chains. While a static map is valuable, a dynamic model offers far greater insight into potential vulnerabilities and opportunities for improvement. It goes beyond simply representing the current state and allows for scenario planning and optimization.
Description 6: A spreadsheet listing all the costs associated with each stage of the supply chain.
Accuracy: Low. A spreadsheet detailing costs is a useful tool for cost analysis, but it's not a supply chain map. A true supply chain map provides a visual representation of the entire chain, not merely a financial summary of its various components. While cost data can be incorporated into a supply chain map to highlight areas of inefficiency, the cost data alone is not the map itself.
The Importance of Accuracy in Supply Chain Mapping
The accuracy of a supply chain map is paramount for its effectiveness. An inaccurate or incomplete map can lead to:
- Misunderstanding of the supply chain: A poorly designed map can obscure critical relationships and dependencies, hindering a comprehensive understanding of the entire system.
- Inefficient decision-making: Poorly understood processes lead to suboptimal strategies and decisions regarding inventory management, logistics, and risk mitigation.
- Missed opportunities for improvement: An incomplete map won't reveal bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas where optimization can significantly reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Increased vulnerability to disruptions: Without a clear picture of the supply chain's intricacies and dependencies, the organization is more susceptible to disruptions and their cascading effects.
Creating an Accurate Supply Chain Map: Best Practices
Creating an accurate supply chain map requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices:
- Define clear objectives: Start by identifying the specific goals of the mapping exercise. What aspects of the supply chain need to be optimized? What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) to be tracked?
- Identify key stakeholders: Engage with all relevant parties, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, to gather accurate data and perspectives.
- Choose the right mapping tool: Select a software or platform that allows for easy visualization, data integration, and collaboration.
- Use standardized symbols and notations: Maintain consistency in the use of symbols and notations to ensure clarity and readability.
- Regularly update the map: Supply chains are dynamic systems. The map should be updated regularly to reflect changes in suppliers, processes, and market conditions.
- Integrate data analysis: Use data analytics to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach enhances the accuracy and effectiveness of the map.
- Incorporate risk assessment: Identify potential disruptions and vulnerabilities within the supply chain and develop mitigation strategies.
Conclusion: The Value of a Comprehensive Supply Chain Map
An accurate supply chain map is an indispensable tool for any organization seeking to improve efficiency, mitigate risks, and gain a competitive advantage. It is not a simple list or a flowchart, but a comprehensive visual representation of the entire flow of goods, services, and information, incorporating key entities, processes, relationships, and performance metrics. By adhering to best practices and focusing on accuracy and completeness, organizations can leverage supply chain maps to optimize their operations and achieve strategic objectives. The descriptions that most accurately capture this comprehensive understanding are those that emphasize the holistic nature of the supply chain, including the flow of goods and information across multiple entities, and the use of dynamic modeling for scenario planning and optimization. Only with such depth of understanding can a truly effective and insightful supply chain map be created.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Complete The Subscripts On The Following Equations
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Monopolist Faces A Downward Sloping Demand Curve Because
Mar 28, 2025
-
Choose The Correct Name For The Following Compound
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is Unusual About Glutathiones Structure
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Significant Weakness Of The Ordinal Scale Is
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Accurately Describes A Supply Chain Map . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
