What Is The Conjugate Base Of Nh3
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
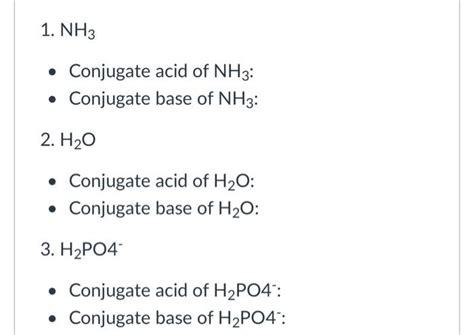
Table of Contents
What is the Conjugate Base of NH₃? A Comprehensive Guide
Ammonium (NH₄⁺) and ammonia (NH₃) are crucial in chemistry, particularly in acid-base reactions. Understanding their relationship, especially concerning conjugate acid-base pairs, is fundamental to grasping acid-base equilibrium and calculations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the concept of conjugate bases, focusing specifically on the conjugate base of ammonia (NH₃). We'll explore its properties, reactions, and significance in various chemical contexts.
Understanding Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
The Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory defines an acid as a proton (H⁺) donor and a base as a proton acceptor. A crucial concept within this theory is the conjugate acid-base pair. When an acid donates a proton, it forms its conjugate base. Conversely, when a base accepts a proton, it forms its conjugate acid. These pairs differ by only one proton (H⁺).
Key characteristics of conjugate acid-base pairs:
- They differ by a single proton (H⁺).
- They are related through a reversible reaction.
- The strength of the acid is inversely related to the strength of its conjugate base (a strong acid has a weak conjugate base, and vice versa).
Identifying the Conjugate Base of NH₃
Ammonia (NH₃), a weak base, readily accepts a proton (H⁺) from an acid. When it does so, it forms the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺). Therefore, to find the conjugate base, we need to consider the reverse reaction.
The reaction demonstrating the conjugate acid-base pair is:
NH₃(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ NH₄⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
In this reversible reaction:
- NH₃ acts as a base, accepting a proton from water.
- H₂O acts as an acid, donating a proton to ammonia.
- NH₄⁺ is the conjugate acid of NH₃.
- OH⁻ is the conjugate base of H₂O.
However, the question focuses specifically on the conjugate base of NH₃ itself. Since NH₃ is a base, it does not have a conjugate base in the traditional sense. To have a conjugate base, a molecule must first act as an acid, donating a proton. Ammonia, in its neutral state, does not have a proton to donate.
Therefore, NH₃ does not have a conjugate base. Instead, it has a conjugate acid, which is NH₄⁺.
The Role of NH₃ and NH₄⁺ in Acid-Base Equilibrium
The equilibrium between NH₃ and NH₄⁺ is crucial in many chemical systems, often playing a role in buffering solutions. The position of the equilibrium depends on the pH of the solution.
-
Low pH (acidic conditions): In acidic solutions, the high concentration of H⁺ ions drives the equilibrium to the right, favoring the formation of NH₄⁺. More ammonia molecules will accept protons from the surrounding solution.
-
High pH (basic conditions): In basic solutions, the low concentration of H⁺ ions shifts the equilibrium to the left, favoring the formation of NH₃. Ammonium ions will donate protons to the surrounding solution.
This equilibrium is vital in controlling pH, particularly in buffer solutions. A buffer solution containing a weak acid (or base) and its conjugate base (or acid) resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. A common example of an ammonia-based buffer system involves a solution of ammonia (NH₃) and ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl).
Properties of the Ammonium Ion (NH₄⁺)
While not the conjugate base, understanding the properties of the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺), the conjugate acid of ammonia, is essential.
-
Charge: NH₄⁺ carries a +1 charge, resulting from the acceptance of a proton by NH₃.
-
Shape: It has a tetrahedral geometry, with the nitrogen atom at the center and four hydrogen atoms bonded to it.
-
Acidity: NH₄⁺ is a weak acid. It can donate a proton to a stronger base, returning to NH₃. The strength of NH₄⁺ as an acid is determined by its Kₐ value.
-
Solubility: Ammonium salts (salts containing NH₄⁺) are generally soluble in water.
-
Reactions: NH₄⁺ can participate in various reactions, such as acid-base reactions (as discussed above) and reactions involving its decomposition, which can produce ammonia gas upon heating with strong bases.
Applications of Ammonia and Ammonium Salts
Both ammonia and ammonium salts have wide-ranging applications across various industries:
-
Agriculture: Ammonia is a crucial component of fertilizers, providing nitrogen, essential for plant growth. Ammonium salts are also utilized in fertilizers.
-
Cleaning products: Ammonia is a common ingredient in household cleaners due to its ability to dissolve grease and grime.
-
Industrial processes: Ammonia is used in the production of various chemicals, including nitric acid and urea. Ammonium salts are also essential in various industrial processes.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Ammonium salts are used in certain pharmaceuticals.
-
Food industry: Ammonium salts are used as leavening agents in baking and as food preservatives.
Conclusion
While ammonia (NH₃) does not possess a conjugate base in the conventional sense, its conjugate acid, the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺), is crucial in understanding its behavior in acid-base reactions and its equilibrium with water. The relationship between ammonia and the ammonium ion is fundamental to several chemical processes and applications, particularly within the contexts of acid-base chemistry, buffer solutions, and various industrial processes. Understanding their properties and interactions is essential for anyone working in chemistry, related fields, or anyone interested in the fascinating world of acid-base reactions. The importance of this conjugate acid-base pair extends across numerous scientific and practical applications, highlighting its critical role in chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Balance Sheet Should Be Prepared
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Product S Would Form Under The Conditions Given Below
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Electron Transport Chain Is Blank
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Backup Of Sewage In The Operations Storeroom Is Considered
Mar 14, 2025
-
One Drawback That Is Particuaty Relevent To
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Conjugate Base Of Nh3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
