A Backup Of Sewage In The Operation's Storeroom Is Considered
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
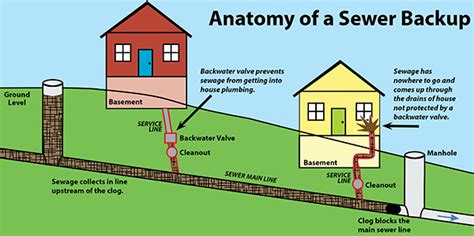
Table of Contents
Sewage Backup in the Operations Storeroom: A Comprehensive Guide to Prevention, Response, and Remediation
A sewage backup in an operations storeroom is a serious event, posing significant risks to health, safety, and business operations. This isn't just a messy cleanup; it's a potential breeding ground for harmful bacteria, a hazard to employees, and a costly disruption to your business. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, consequences, and crucial steps for prevention, response, and remediation of a sewage backup in this critical area of your facility.
Understanding the Severity of a Sewage Backup
The severity of a sewage backup in an operations storeroom is amplified by several factors:
-
Contamination Risk: Storerooms often contain valuable equipment, inventory, and materials. Sewage contamination can render these items unusable, leading to significant financial losses. Furthermore, the risk of exposure to pathogens like E. coli, Salmonella, and other harmful bacteria presents a serious health threat to employees.
-
Operational Disruption: A sewage backup necessitates immediate action, disrupting workflows and potentially halting operations until the area is thoroughly cleaned and sanitized. This downtime translates to lost productivity and revenue.
-
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Depending on your location and industry, you may be subject to strict environmental regulations regarding sewage disposal and wastewater management. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions.
-
Insurance Claims: While your insurance policy might cover cleanup costs, proving the extent of the damage and adhering to their claims procedures can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Identifying Potential Causes of Sewage Backup
Before addressing prevention, it's crucial to understand the potential causes of a sewage backup in your operations storeroom. These can include:
1. Clogged Sewer Lines: This is the most common cause. Grease buildup, foreign objects (e.g., rags, debris), tree roots intruding into pipes, and general wear and tear on the aging infrastructure can all contribute to blockages.
2. Failing Septic System: If your facility relies on a septic system, a malfunctioning system (due to age, improper maintenance, or overloading) can lead to sewage backup.
3. Heavy Rainfall and Flooding: Excessive rainfall can overwhelm the municipal sewer system, causing backups in lower-lying areas, including your storeroom.
4. Improper Plumbing Installation: Faulty plumbing installations, including incorrect pipe slopes or improperly sealed connections, can create points of failure leading to sewage backups.
5. Ground Shifting: Ground movement due to soil erosion or seismic activity can damage sewer lines, causing leaks and backups.
Proactive Measures: Preventing Sewage Backups
Preventing a sewage backup is far more cost-effective and efficient than dealing with the consequences. Implement these proactive measures:
1. Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular inspections of sewer lines and plumbing systems. This includes visual inspections, pressure testing, and potentially using a sewer camera to detect blockages or damage early on.
2. Grease Trap Maintenance: If your operations involve the use of grease or oils, ensure regular cleaning and maintenance of your grease trap to prevent buildup and clogging.
3. Preventative Plumbing: Regularly check for leaks, cracks, or corrosion in your plumbing system. Address minor issues before they escalate into major problems.
4. Proper Waste Disposal: Educate your employees about proper waste disposal practices. This includes avoiding flushing inappropriate items down toilets (e.g., sanitary products, rags) and properly disposing of grease and oils.
5. Stormwater Management: Implement measures to manage stormwater effectively, diverting it away from your building and preventing it from overwhelming the sewer system. This might include installing proper drainage systems and gutters.
6. Regular Septic Tank Pumping (if applicable): If your facility uses a septic system, schedule regular pumping and inspection to ensure its proper functioning and prevent overflows.
7. Tree Root Control: Aggressively manage tree roots that could potentially infiltrate and damage your sewer lines. This may involve root cutting or chemical treatments.
8. Building a Strong Emergency Plan: Create a detailed emergency plan outlining procedures for responding to a sewage backup, including identifying responsible personnel, contact information for emergency services, and cleanup protocols.
Responding to a Sewage Backup: Immediate Actions
If a sewage backup occurs, swift and decisive action is paramount:
1. Immediate Evacuation: Immediately evacuate the affected area to prevent exposure to contaminated sewage. Prioritize the safety of your employees.
2. Emergency Services: Contact emergency services (plumbers, sanitation services) to address the immediate blockage and initiate cleanup.
3. Containment: If possible, contain the spill to prevent further spreading of the sewage. Use absorbent materials to soak up the liquid and prevent its spread to other areas.
4. Documentation: Thoroughly document the event, including photographs, video footage, and records of any communication with emergency services and insurance providers. This documentation will be vital for insurance claims and regulatory compliance.
5. Employee Safety: Ensure the safety of your employees by providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, boots, eye protection, and respirators.
Remediation and Cleanup: A Comprehensive Approach
The cleanup and remediation process after a sewage backup is critical to restoring the storeroom to a safe and functional state:
1. Professional Cleanup: Engage professional biohazard remediation specialists. They possess the expertise, equipment, and safety protocols to safely and effectively clean and disinfect the affected area. This includes removing contaminated materials, disposing of them properly, and thoroughly cleaning and sanitizing all surfaces.
2. Water Extraction: The professionals will use specialized equipment to extract standing water and remove moisture from the affected area. This is crucial to prevent mold growth and further damage.
3. Drying and Dehumidification: After water extraction, specialized equipment will be used to dry the area thoroughly and reduce humidity levels. This prevents mold growth and structural damage.
4. Disinfection and Sanitization: A thorough disinfection and sanitization process is essential to eliminate harmful bacteria and viruses from surfaces and materials. This process should follow industry best practices and utilize approved disinfectants.
5. Odor Removal: Sewage backups often leave behind unpleasant odors. Professional remediation specialists employ advanced odor removal techniques to eliminate lingering smells.
6. Restoration and Repair: Following cleanup and sanitation, any damaged materials or structures need to be repaired or replaced. This might include replacing flooring, drywall, or other affected elements.
7. Inventory Assessment: Assess the condition of stored inventory and equipment. Determine which items can be salvaged and which need to be discarded. This will play a crucial role in determining financial losses.
8. Mold Prevention: Implement measures to prevent mold growth in the future. This might include improving ventilation, addressing moisture issues, and monitoring humidity levels.
Post-Remediation: Prevention and Monitoring
After remediation, implement ongoing preventative measures to minimize the risk of future backups:
1. Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections of the plumbing and sewer lines to detect any issues early.
2. Maintenance Schedule: Maintain a rigorous maintenance schedule for all plumbing fixtures and the sewer system.
3. Employee Training: Regularly train employees on proper waste disposal and hygiene practices to prevent future clogs.
4. Environmental Monitoring: Consider implementing environmental monitoring to detect any signs of potential contamination or water damage.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Prevention and Preparedness
A sewage backup in an operations storeroom is a costly and disruptive event with potential legal and health ramifications. By prioritizing preventative measures, developing a robust emergency response plan, and understanding the comprehensive remediation process, businesses can minimize the impact of such incidents and ensure the safety and well-being of their employees. Remember that proactive maintenance, employee education, and professional assistance are crucial in mitigating the risk and swiftly addressing a sewage backup should it occur. The cost of prevention is significantly less than the cost of reacting to a crisis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Visit A Huge City With Millions
Mar 15, 2025
-
National Income Accountants Can Avoid Multiple Counting By
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Rationing Function Of Prices Refers To The
Mar 15, 2025
-
Select Cell D13 And Paste The Range Names
Mar 15, 2025
-
Identify Each Statement As True Or False
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Backup Of Sewage In The Operation's Storeroom Is Considered . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
