Label The Photomicrograph Of Spongy Bone.
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
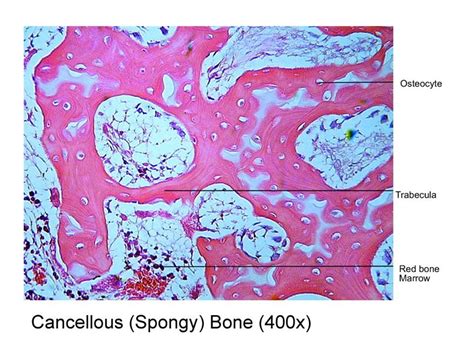
Table of Contents
- Label The Photomicrograph Of Spongy Bone.
- Table of Contents
- Labeling a Photomicrograph of Spongy Bone: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is Spongy Bone?
- Key Structures to Label in a Spongy Bone Photomicrograph
- 1. Trabeculae: The Bony Struts
- 2. Bone Marrow: The Blood Cell Factory
- 3. Osteocytes: The Bone Cells
- 4. Lacunae: Housing for Osteocytes
- 5. Canaliculi: The Communication Network
- 6. Endosteum: The Inner Lining
- Tips for Accurate Labeling
- Applications of Spongy Bone Knowledge
- Advanced Considerations for Labeling
- Conclusion: Mastering Spongy Bone Photomicrograph Labeling
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Labeling a Photomicrograph of Spongy Bone: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the microscopic structure of bone is crucial for anyone studying biology, anatomy, histology, or related fields. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough of how to accurately label a photomicrograph of spongy bone (also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone), covering key structural features and their functions. We'll delve into the details, ensuring you can confidently identify and label the various components.
What is Spongy Bone?
Spongy bone, unlike its compact counterpart, is characterized by its porous, honeycomb-like structure. This structure is not randomly arranged; rather, it's a precisely organized network of thin, bony struts called trabeculae. These trabeculae create a lattice-like framework that is surprisingly strong, given its seemingly delicate appearance. The spaces within this framework are filled with bone marrow, a crucial component of the hematopoietic system responsible for blood cell production.
The arrangement of trabeculae isn't haphazard. It's precisely oriented along lines of stress, maximizing strength and minimizing weight. This architectural marvel allows spongy bone to efficiently support weight and withstand forces applied to it.
Key Structures to Label in a Spongy Bone Photomicrograph
Identifying and labeling the following structures will complete a comprehensive annotation of your spongy bone photomicrograph:
1. Trabeculae: The Bony Struts
Trabeculae are the defining feature of spongy bone. These are thin, interconnected bony spicules or plates that form the three-dimensional network. When labeling, clearly indicate the trabeculae and highlight their interconnected nature. Note their irregular shapes and varying thicknesses. Their orientation often reflects the stresses experienced by the bone.
Important Note: The trabeculae themselves are composed of lamellae, similar to compact bone, though they are generally thinner and less organized. While you might not be able to resolve individual lamellae at lower magnifications, understanding their presence within the trabeculae is essential.
2. Bone Marrow: The Blood Cell Factory
The spaces between the trabeculae are occupied by bone marrow. This is a soft tissue that houses hematopoietic stem cells, responsible for the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In your photomicrograph, the bone marrow will appear as a less dense, often reddish or pinkish area contrasted against the darker trabeculae. Clearly mark the bone marrow and label it appropriately. Remember to distinguish it from the trabeculae.
3. Osteocytes: The Bone Cells
Within the trabeculae reside osteocytes, mature bone cells. These are responsible for maintaining the bone matrix. At high magnification, you might be able to see these cells within the lacunae (small spaces) within the bone matrix of the trabeculae. While individually identifying osteocytes can be challenging at lower magnifications, indicating their general location within the trabeculae is sufficient.
4. Lacunae: Housing for Osteocytes
Lacunae are small, hollow spaces within the bone matrix of the trabeculae. These spaces house the osteocytes. They are interconnected by a network of tiny canals called canaliculi. While you might not see individual canaliculi clearly, indicating the presence of lacunae within the trabeculae helps demonstrate understanding of osteocyte placement and nutrient delivery.
5. Canaliculi: The Communication Network
Canaliculi are microscopic canals that connect lacunae to each other and to the bone marrow spaces. They facilitate nutrient exchange and waste removal for the osteocytes, which are somewhat isolated within the bone matrix. Although difficult to visualize clearly at lower magnifications, mentioning canaliculi in your labeling helps demonstrate a complete understanding of bone structure and cell functionality.
6. Endosteum: The Inner Lining
The trabeculae are covered by a thin layer of connective tissue called the endosteum. This membrane contains osteoprogenitor cells, which can differentiate into osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and participate in bone remodeling. Identifying the endosteum might be challenging depending on the quality and magnification of the photomicrograph, but recognizing its potential presence is beneficial for a complete labeling.
Tips for Accurate Labeling
- Use a Sharp Pencil or Digital Annotation Tool: Ensure your labels are clear and easy to read. Avoid messy or overlapping labels.
- Use Arrows or Lines: Direct arrows or lines from your labels to the specific structures they identify. This improves clarity and prevents ambiguity.
- Keep Labels Concise: Use short, descriptive labels (e.g., "Trabeculae," "Bone Marrow"). Avoid lengthy explanations directly on the photomicrograph.
- Maintain Scale: Be mindful of the scale of the image and adjust your labeling size accordingly.
- Check for Artifacts: Be aware of potential artifacts or staining inconsistencies that might be mistaken for actual bone structures.
- Consult Reliable Resources: If unsure about identifying a specific structure, consult histological textbooks or online resources with high-quality images of spongy bone.
Applications of Spongy Bone Knowledge
Understanding the structure and function of spongy bone is critical in various fields:
- Medicine: Diagnosing bone diseases like osteoporosis, which affects bone density and strength.
- Orthopedics: Designing implants and prosthetics that integrate effectively with the bone's structure.
- Biomaterials Engineering: Developing biomaterials that promote bone regeneration and repair.
- Forensic Science: Analyzing bone fragments to determine age, sex, and other identifying factors.
- Paleontology: Studying fossilized bones to understand extinct organisms.
Advanced Considerations for Labeling
For advanced studies, your labeling might also include:
- Different types of bone marrow: Distinguishing between red and yellow bone marrow (if visible). Red marrow is hematopoietic, while yellow marrow is primarily adipose tissue.
- Blood vessels: Identifying blood vessels within the bone marrow spaces, highlighting their role in nutrient and waste transport.
- Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts: At higher magnifications, you may be able to distinguish osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and osteoclasts (bone-resorbing cells) involved in bone remodeling. These are crucial for bone maintenance and repair.
By incorporating these advanced considerations, you demonstrate a thorough understanding of bone biology and its complexities. The level of detail needed will depend on your educational level and the specific assignment requirements.
Conclusion: Mastering Spongy Bone Photomicrograph Labeling
Accurately labeling a photomicrograph of spongy bone requires a solid grasp of its histological features and their functions. This comprehensive guide equips you with the necessary knowledge and practical tips to confidently label all key structures, from the trabeculae to the bone marrow and osteocytes. Remember, practice is key; analyzing multiple photomicrographs from various sources and magnification levels will enhance your identification skills. By carefully following these steps, you'll be well-prepared to navigate the intricacies of spongy bone histology and master the art of accurate labeling.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
An Annuity Is A Series Of Blank Deposits
Mar 29, 2025
-
Todos Los Siguientes Son Opciones De No Caducidad Excepto
Mar 29, 2025
-
Two Cables Are Tied Together At C
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Determines Market Price And Equilibrium Output In A Market
Mar 29, 2025
-
Draw The Major E2 Reaction Product Formed When Cis 1 Chloro
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Label The Photomicrograph Of Spongy Bone. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
