An Aircraft Component Is Fabricated From An Aluminum Alloy
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
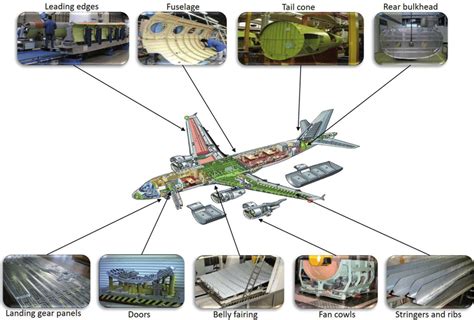
Table of Contents
An Aircraft Component Fabricated from an Aluminum Alloy: A Deep Dive into Material Selection, Fabrication, and Performance
The aerospace industry demands materials that exhibit exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum alloys, with their unique combination of properties, have become a mainstay in aircraft construction, finding application in everything from fuselage panels to engine components. This article delves into the multifaceted world of aluminum alloy application in aircraft components, focusing on material selection, fabrication techniques, performance characteristics, and the ongoing quest for lighter, stronger, and more durable materials.
Selecting the Right Aluminum Alloy: A Balancing Act
The selection of a specific aluminum alloy for a given aircraft component is a critical decision, driven by a complex interplay of factors. The desired properties, manufacturing process, and operating environment all influence the final choice. Hundreds of aluminum alloys exist, each with its own unique characteristics. Some key considerations include:
Strength and Stiffness
-
Yield Strength: This property represents the stress at which a material begins to deform permanently. Higher yield strength is crucial for components subjected to high loads. Alloys like 7075-T6 and 2024-T3 are known for their high yield strengths and are frequently used in highly stressed structural components.
-
Tensile Strength: This indicates the maximum stress a material can withstand before fracturing. Similar to yield strength, high tensile strength is vital for ensuring structural integrity.
-
Stiffness (Young's Modulus): This property describes a material's resistance to deformation under load. High stiffness is important for maintaining the shape and structural integrity of the aircraft component under stress.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum's inherent resistance to corrosion is a significant advantage. However, different alloys exhibit varying degrees of corrosion resistance depending on their alloying elements and the environmental conditions. Anodization, a surface treatment process, further enhances corrosion resistance. Marine environments or areas with high humidity require alloys with superior corrosion protection.
Fatigue Resistance
Aircraft components experience cyclical loading throughout their lifespan. Fatigue resistance, the ability to withstand repeated stress cycles without failure, is paramount. Careful alloy selection and design considerations are crucial to mitigating fatigue-related failures. Heat treatments, such as solution heat treating and aging, play a critical role in enhancing fatigue life.
Weldability
For many aircraft components, welding is the preferred joining method. Certain aluminum alloys are more readily weldable than others. The choice of alloy often depends on the specific welding technique (e.g., gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW)) and the required weld quality.
Machinability
The ease with which an alloy can be machined influences manufacturing costs and efficiency. Some alloys are more easily machined than others, impacting the overall production cost and time.
Cost
The cost of the aluminum alloy itself is a significant factor, especially for large-scale production. Balancing performance requirements with cost-effectiveness is essential in the decision-making process.
Fabrication Techniques: Shaping Aluminum for Aerospace Applications
Once the appropriate aluminum alloy has been selected, various fabrication techniques are employed to shape the material into the desired component. These techniques include:
Casting
Casting is a process where molten aluminum alloy is poured into a mold, solidifying into the desired shape. This method is particularly suitable for complex shapes that would be difficult or expensive to produce using other techniques. However, cast components generally exhibit lower mechanical properties than wrought components. Die casting and investment casting are commonly used in aircraft component fabrication.
Forging
Forging involves shaping the metal by applying compressive forces. This process enhances the mechanical properties of the alloy, increasing its strength and fatigue resistance. Forging is often used for critical components requiring high strength and reliability. This includes hammer forging and press forging.
Extrusion
Extrusion involves forcing a heated aluminum billet through a die to create long, continuous profiles. This is an efficient method for producing components with uniform cross-sections, such as spars, beams, and stringers.
Rolling
Rolling involves passing the aluminum billet through a series of rollers to reduce its thickness and create sheets or plates. This is a common method for producing fuselage skins, wing panels, and other large, flat components.
Machining
Machining involves using cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. This is a versatile technique used for creating both simple and complex shapes, particularly for smaller components. CNC machining is widely employed in the aerospace industry for precision and efficiency.
Sheet Metal Forming
Sheet metal forming techniques such as bending, drawing, and stamping are used to shape thin sheets of aluminum into curved or complex shapes. This method is frequently employed for producing fuselage panels and other aerodynamic components.
Performance Characteristics and Considerations
The performance of an aluminum alloy aircraft component is governed by several critical factors:
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Aluminum alloys offer a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to many other materials, making them ideal for aerospace applications. This contributes significantly to fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance.
Fatigue and Crack Propagation
Aircraft components are subjected to cyclic loading throughout their operational lifespan, making fatigue resistance crucial. Careful material selection, design, and manufacturing processes are essential to mitigating fatigue-related failures. Understanding crack propagation behavior in different alloys is also essential for ensuring component safety.
Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
Different atmospheric conditions, including salinity and humidity, significantly impact the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys. Protective coatings and surface treatments are often necessary to safeguard components from corrosion, particularly in harsh environments.
Thermal Properties
Aluminum alloys exhibit good thermal conductivity, which can be advantageous in certain applications such as heat exchangers. However, high temperatures can affect the mechanical properties of some alloys. Understanding thermal behavior is important for designing components that operate in high-temperature environments.
Joining Methods
The chosen joining method significantly impacts the structural integrity and performance of the component. Methods such as welding, riveting, bonding, and mechanical fastening are employed, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages depending on the component and material.
Ongoing Developments and Future Trends
The aerospace industry is continuously striving for lighter, stronger, and more durable materials. Research and development efforts focus on:
Advanced Aluminum Alloys
The development of new aluminum alloys with enhanced properties, such as higher strength, improved fatigue resistance, and superior corrosion protection, is an ongoing area of research. Alloying with elements like scandium and lithium leads to enhanced performance.
Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs)
MMCs, combining aluminum alloys with reinforcing materials such as ceramic fibers, offer significant improvements in strength, stiffness, and temperature resistance. These are being explored for high-performance applications where lightweight and high-strength properties are critical.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing techniques offer the potential for creating complex shapes and geometries previously unachievable using traditional methods. This technology allows for lighter components with improved structural efficiency, as well as the creation of customized parts with unique designs.
Surface Treatments and Coatings
Advanced surface treatments and coatings are continuously being developed to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and other performance characteristics of aluminum alloy aircraft components. These coatings can provide additional protection from environmental factors and improve the overall lifespan of the component.
Conclusion
Aluminum alloys are indispensable in modern aircraft construction, providing a balance between high strength, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness. The careful selection of the appropriate alloy, coupled with advanced fabrication techniques and ongoing research and development efforts, ensures that aircraft components continue to meet the stringent demands of the aerospace industry. The quest for improved performance and efficiency drives innovation in material science, fabrication processes, and design, leading to safer, more reliable, and fuel-efficient aircraft. The future of aluminum in aerospace is bright, with ongoing research and development pushing the boundaries of what's possible.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When The Wash Sale Rules Apply The Realized Loss Is
Mar 19, 2025
-
Fixed Costs Expressed On A Per Unit Basis
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Companys Strategic Plan Consists Of
Mar 19, 2025
-
Once The Estimated Depreciation Expense For An Asset Is Calculated
Mar 19, 2025
-
During Lewins Changing Stage Managers Should
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Aircraft Component Is Fabricated From An Aluminum Alloy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
