Once The Estimated Depreciation Expense For An Asset Is Calculated:
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
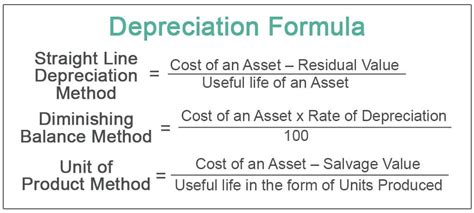
Table of Contents
Once the Estimated Depreciation Expense for an Asset is Calculated: A Comprehensive Guide
Depreciation is a crucial accounting concept that reflects the gradual decrease in an asset's value over its useful life. Once the estimated depreciation expense is calculated, several important steps follow, ensuring accurate financial reporting and effective asset management. This comprehensive guide delves into these post-calculation procedures, covering everything from recording the expense to its impact on financial statements and tax implications.
Understanding Depreciation Methods and Their Impact
Before diving into post-calculation procedures, it's crucial to briefly revisit the various depreciation methods. The choice of method significantly impacts the annual depreciation expense and, consequently, the subsequent financial reporting. Common methods include:
-
Straight-Line Depreciation: This method evenly distributes the asset's cost over its useful life. The formula is simple: (Asset Cost - Salvage Value) / Useful Life. It's straightforward and easy to understand, making it a popular choice.
-
Declining Balance Depreciation: This accelerated method assigns higher depreciation expense in the early years of an asset's life and lower expense in later years. It reflects the faster rate of obsolescence often experienced by certain assets. A common variant is the double-declining balance method, which doubles the straight-line rate.
-
Units of Production Depreciation: This method links depreciation expense to the actual use of the asset. The formula involves calculating depreciation per unit and multiplying it by the number of units produced during the year. It's ideal for assets whose value is directly tied to their output.
-
Sum-of-the-Years' Digits Depreciation: This accelerated method uses a fraction based on the remaining useful life of the asset to calculate annual depreciation. The denominator is the sum of the years' digits, while the numerator is the remaining useful life.
The choice of depreciation method affects the reported net income and the asset's book value. Accelerated methods result in higher depreciation expenses in the early years, leading to lower net income initially, but higher net income later in the asset's life. Conversely, straight-line depreciation provides a more consistent pattern of expense recognition.
Recording Depreciation Expense: Journal Entries and General Ledger
After calculating the depreciation expense using the chosen method, the next step is to record it in the company's accounting system. This typically involves making journal entries. The basic journal entry to record depreciation expense is:
Debit: Depreciation Expense Credit: Accumulated Depreciation
-
Depreciation Expense: This is an expense account that reflects the cost of using the asset during the period. It increases the debit balance, reducing net income.
-
Accumulated Depreciation: This is a contra-asset account that reduces the asset's book value. It has a credit balance. It's crucial to remember that accumulated depreciation doesn't represent a cash outflow; rather, it reflects the cumulative depreciation expense recorded over the asset's life.
Example: If the calculated depreciation expense for a machine is $10,000, the journal entry would be:
Debit: Depreciation Expense $10,000 Credit: Accumulated Depreciation $10,000
These entries are posted to the general ledger, updating the balances of the relevant accounts. The general ledger provides a comprehensive record of all the company's financial transactions.
Reflecting Depreciation on Financial Statements
Depreciation expense and accumulated depreciation significantly impact a company's financial statements, namely the income statement and the balance sheet.
Income Statement: Depreciation expense is reported on the income statement as an operating expense, reducing the company's net income. This reflects the cost of utilizing the asset during the accounting period. A higher depreciation expense will lead to lower net income, potentially impacting key financial ratios like profitability margins.
Balance Sheet: The asset's book value is reflected on the balance sheet. The book value is calculated as the asset's original cost minus accumulated depreciation. This shows the asset's net value after accounting for the accumulated depreciation. Accumulated depreciation appears as a reduction of the asset's gross value. The balance sheet presents a snapshot of the company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
Statement of Cash Flows: It's essential to note that depreciation expense is a non-cash expense. This means it doesn't involve an actual cash outflow. Therefore, it doesn't directly impact the statement of cash flows. However, depreciation can indirectly influence the statement of cash flows through its impact on net income, which is used in the indirect method of calculating cash flow from operating activities.
Tax Implications of Depreciation
Depreciation plays a crucial role in tax calculations. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows businesses to deduct depreciation expense on their tax returns, reducing their taxable income and, consequently, their tax liability. The IRS provides guidelines on acceptable depreciation methods and useful lives for various asset classes. The choice of depreciation method for tax purposes can significantly influence a company's tax obligations, with accelerated methods offering greater tax benefits in the early years.
However, it is crucial to understand that tax depreciation might differ from the depreciation method used for financial reporting purposes. Companies might use different methods for book and tax purposes to optimize their tax liability while adhering to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Careful consideration of both book and tax depreciation is essential for compliance and tax planning.
Reviewing and Adjusting Depreciation Estimates
The useful life and salvage value of an asset are estimations at the time of purchase. Over time, these estimates may need to be reviewed and adjusted based on factors like technological advancements, changes in usage patterns, or unexpected wear and tear. If significant changes occur, the company must revise the depreciation expense calculation and make appropriate adjustments to reflect the updated estimates. This requires recalculating depreciation for the remaining useful life of the asset, ensuring accurate financial reporting and tax compliance.
This adjustment process usually involves a change in the annual depreciation expense, impacting the income statement and balance sheet. Proper documentation of these adjustments is crucial for maintaining clear and transparent accounting records. The change in the depreciation expense will reflect in the financial statements of the period in which the revision is made.
Disposal of Depreciated Assets
When an asset reaches the end of its useful life or is disposed of before the end of its useful life, the accumulated depreciation must be considered. Upon disposal, the asset's book value (original cost less accumulated depreciation) is compared to the proceeds from disposal. The difference between the book value and the proceeds determines whether a gain or loss is recognized.
-
Gain on Disposal: If the proceeds exceed the book value, a gain is recognized. This is reported on the income statement and increases net income.
-
Loss on Disposal: If the book value exceeds the proceeds, a loss is recognized. This is reported on the income statement and decreases net income.
The journal entries related to asset disposal are complex and vary based on the circumstances. They typically involve removing the asset and its accumulated depreciation from the balance sheet and recognizing any gain or loss on disposal.
Importance of Accurate Depreciation Calculations
Accurate depreciation calculations are crucial for several reasons:
-
Financial Reporting: Accurate depreciation ensures the reliable presentation of financial statements, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions.
-
Tax Compliance: Correct depreciation calculations are vital for accurate tax filings and avoiding potential penalties.
-
Asset Management: Tracking depreciation helps businesses monitor the value of their assets and plan for replacements.
-
Investment Decisions: Depreciation figures are essential for evaluating the profitability of investments in fixed assets.
-
Creditworthiness: Accurate depreciation contributes to a company's financial health and creditworthiness, influencing access to financing.
Ignoring or miscalculating depreciation can lead to inaccurate financial statements, underpayment of taxes, poor asset management decisions, and overall financial instability.
Conclusion
Once the estimated depreciation expense for an asset is calculated, a series of critical steps must be followed, encompassing recording the expense, its impact on financial statements, tax considerations, and asset disposal. Understanding these processes ensures accurate financial reporting, effective tax planning, and sound asset management. Regular review and adjustment of depreciation estimates are equally important for maintaining the accuracy and reliability of financial information. By diligently following these procedures, businesses can ensure financial stability, compliance, and informed decision-making. The careful consideration of each aspect – from the initial calculation to final disposal – is paramount for the financial health and success of any organization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Equity Is Composed Of Contributed Capital And
Mar 19, 2025
-
Modeling Population Growth Rabbits Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
Write Short Answers To The Following Questions
Mar 19, 2025
-
Social Support Can Lead To All Of The Following Except
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Tuff And Tough
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Once The Estimated Depreciation Expense For An Asset Is Calculated: . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
