Which Type Of Molecule Never Contains A Phosphate Group
Holbox
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
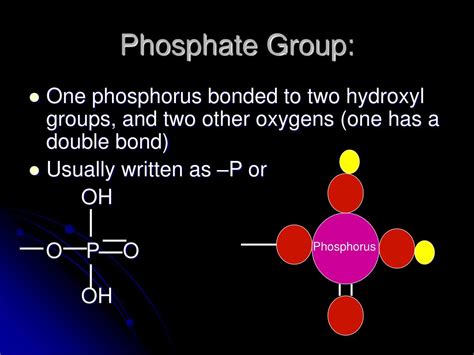
Table of Contents
Which Type of Molecule Never Contains a Phosphate Group?
The presence or absence of a phosphate group significantly impacts a molecule's structure and function within a biological system. While phosphate groups are ubiquitous in many crucial biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and ATP, some molecular classes categorically exclude them. This article delves deep into exploring which types of molecules consistently lack phosphate groups, examining their structure, function, and the implications of this absence. Understanding this fundamental difference aids in comprehending the intricate workings of life at a molecular level.
Understanding Phosphate Groups and their Biological Roles
Before diving into specific molecule types that lack phosphate groups, let's briefly review the significance of phosphates in biological systems. A phosphate group, denoted as PO₄³⁻, is a negatively charged polyatomic ion. Its central phosphorus atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms, resulting in a tetrahedral structure. This structure facilitates the formation of strong covalent bonds with other molecules.
The key biological roles of phosphate groups are numerous and vital:
-
Energy Transfer: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells, relies heavily on the high-energy phosphate bonds. Hydrolysis of these bonds releases energy that fuels various cellular processes.
-
Signal Transduction: Phosphate groups play a pivotal role in signal transduction cascades. Phosphorylation, the addition of a phosphate group to a protein, often acts as a molecular switch, activating or deactivating enzymes and other proteins.
-
DNA and RNA Structure: The backbone of DNA and RNA molecules contains a phosphate group linking adjacent sugar molecules, forming the characteristic phosphodiester bonds.
-
Cell Membrane Structure: Phospholipids, the primary components of cell membranes, possess a phosphate group in their hydrophilic head, contributing to the membrane's structural integrity and selective permeability.
-
Enzyme Regulation: Many enzymes require the presence of a phosphate group for their activity. The addition or removal of this group regulates the enzyme’s catalytic activity.
Molecule Types that Never Contain Phosphate Groups: A Comprehensive Overview
Several classes of molecules consistently lack phosphate groups in their structures. These molecules have evolved distinct functionalities and roles based on their unique chemical compositions. This lack of phosphate, while seemingly simple, dictates their physical and chemical properties and their biological functions.
1. Simple Carbohydrates (Monosaccharides and Disaccharides)
Simple carbohydrates, including monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose) and disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), are fundamental energy sources for living organisms. Their structures primarily consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms arranged in specific ring or linear configurations. Crucially, they lack phosphorus, and therefore phosphate groups are absent. Their function is primarily energy storage and providing immediate energy. Their lack of phosphate makes them readily available for energy metabolism. The absence of charged phosphate groups also impacts their solubility and ability to cross cell membranes.
2. Most Lipids (excluding Phospholipids)
Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules essential for energy storage, cell membrane structure, and hormone production. While phospholipids contain phosphate groups in their polar head, many other lipid types, such as triglycerides, fatty acids, and steroids, do not contain phosphate groups. Triglycerides, for instance, are composed of glycerol and three fatty acids, all carbon-based chains. Steroids, such as cholesterol and various hormones, possess a characteristic four-ring structure, lacking phosphorus entirely.
The absence of phosphate groups in these lipids contributes to their hydrophobic nature. This characteristic allows them to form lipid bilayers in cell membranes and act as efficient energy storage molecules. The lack of charge also facilitates their mobility within cells.
3. Many Amino Acids (in their standard form)
Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, typically consist of an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (R group) all attached to a central carbon atom. In their standard forms, the vast majority of amino acids lack phosphate groups. However, it’s crucial to note that post-translational modifications can sometimes add phosphate groups to specific amino acid residues, particularly serine, threonine, and tyrosine. These modifications are crucial for regulating protein activity, but the unmodified amino acids themselves lack phosphate.
The diverse nature of amino acid side chains dictates the protein’s overall structure and function. The absence of phosphate groups in most amino acids affects the protein’s overall charge, solubility, and interactions with other molecules.
4. Certain Vitamins
Several vitamins lack phosphate groups. For instance, vitamin A (retinol), a fat-soluble vitamin crucial for vision, and vitamin E (tocopherol), an antioxidant, are organic molecules with carbon-based structures that don't include phosphorus. Vitamin K, another fat-soluble vitamin vital for blood clotting, also lacks phosphate groups. The specific structures and functions of these vitamins are entirely independent of phosphate groups.
The absence of phosphate significantly influences their absorption, transport, and overall biological activity, enabling these vitamins to fulfill their unique roles within the body's metabolic pathways. Their lipophilic nature allows for efficient absorption from the digestive tract.
5. Simple Alcohols
Simple alcohols, such as methanol, ethanol, and propanol, are organic molecules comprising a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to a carbon atom. These molecules inherently lack phosphorus and therefore, phosphate groups. They find use as solvents and in various industrial applications, demonstrating the wide range of molecular structures that exist without the need for phosphate groups. Their simple structure and lack of phosphate make them relatively chemically inert in many contexts.
Implications of the Absence of Phosphate Groups
The absence of a phosphate group in these molecular classes has significant implications for their structure, function, and interactions within biological systems:
-
Hydrophobicity: Many molecules lacking phosphate groups are hydrophobic (water-repelling), influencing their solubility and location within cells and tissues. This is crucial for lipids in cell membranes.
-
Charge Distribution: The absence of the negatively charged phosphate group impacts the overall charge distribution of the molecule, affecting its interactions with other charged molecules.
-
Metabolic Pathways: Molecules without phosphate groups follow unique metabolic pathways compared to phosphorylated molecules. Their metabolic fates vary significantly.
-
Regulatory Mechanisms: The lack of phosphorylation sites prevents regulation through this crucial mechanism, resulting in unique regulatory pathways compared to other biomolecules.
Conclusion: A Diverse Molecular World Beyond Phosphate
While phosphate groups are undeniably vital for many critical biological processes, numerous molecules function effectively without them. This article has explored several major classes of molecules, including simple carbohydrates, many lipids, most amino acids (in their unmodified form), some vitamins, and simple alcohols, which never contain phosphate groups. Their absence doesn't diminish their biological importance; rather, it highlights the incredible diversity of molecular structures and their specialized roles in maintaining life's complexity. The contrasting properties arising from the presence or absence of phosphates provide a powerful illustration of how subtle chemical differences can lead to vast functional variations in biological systems. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending the intricacies of biochemistry and the mechanisms that sustain life. Further exploration into the detailed chemistry and functional roles of these non-phosphate-containing molecules continues to unveil deeper insights into the fundamental workings of cellular processes and their overall impact on biological systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Wang Company Accumulates The Following Adjustment
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Do I Sell My Textbooks
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Uses Of Removable Media Is Allowed
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Developing Person Through The Lifespan
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Relationship Between Sales And Profits Can Be Written As
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Type Of Molecule Never Contains A Phosphate Group . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
