The Relationship Between Sales And Profits Can Be Written As
Holbox
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
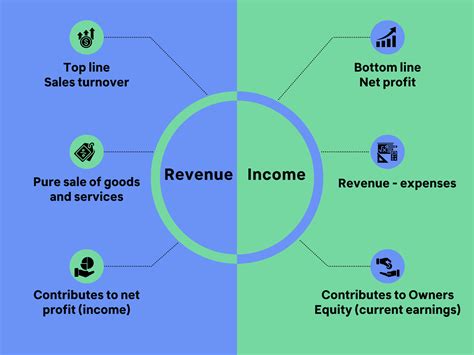
Table of Contents
- The Relationship Between Sales And Profits Can Be Written As
- Table of Contents
- The Intimate Dance of Sales and Profits: A Deep Dive into Their Complex Relationship
- Beyond the Obvious: Unveiling the Nuances of Sales and Profitability
- Optimizing the Relationship: Strategies for Enhanced Profitability
- The Long-Term Perspective: Building a Sustainable Sales and Profit Model
- Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Sales and Profit Optimization
- Conclusion: The Enduring Dance of Sales and Profits
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Intimate Dance of Sales and Profits: A Deep Dive into Their Complex Relationship
The relationship between sales and profits is often simplified to a straightforward equation: more sales equal more profits. While this holds true in a rudimentary sense, the reality is far more nuanced and intricate. Understanding this complex interplay is crucial for businesses of all sizes, from startups to multinational corporations. This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted connection between sales and profits, examining the key factors that influence their relationship and providing actionable strategies to optimize both.
Beyond the Obvious: Unveiling the Nuances of Sales and Profitability
The simplistic "more sales = more profits" mantra ignores several critical elements. While increased sales contribute significantly to higher profits, they are not the sole determinant. Profitability hinges on a delicate balance between revenue generation (sales) and cost management. A business can generate high sales volume yet remain unprofitable if its costs outweigh its revenue.
Key Factors Influencing the Sales-Profit Relationship:
-
Pricing Strategy: This is arguably the most significant factor. While higher prices can lead to higher profit margins per unit, they can also deter customers and reduce sales volume. Finding the optimal price point that balances profitability and sales is crucial. This involves careful market research, understanding customer price sensitivity, and considering competitor pricing.
-
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This encompasses all direct costs associated with producing or acquiring goods sold. Efficient inventory management, negotiating favorable supplier contracts, and optimizing production processes are vital for keeping COGS low and boosting profit margins. Reducing waste and improving operational efficiency are paramount.
-
Operating Expenses: These are all indirect costs involved in running the business, including salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative expenses. Controlling operating expenses without sacrificing quality or customer service is crucial for maximizing profitability. Streamlining processes, leveraging technology, and negotiating favorable contracts are effective strategies.
-
Sales Efficiency: This refers to the effectiveness of sales efforts in generating revenue. A high sales efficiency means generating high revenue with minimal sales cost. This can be improved through targeted marketing campaigns, effective sales training, and improved sales processes.
-
Sales Mix: The proportion of different products or services sold significantly impacts profitability. High-margin products contribute more to profits than low-margin ones. Analyzing the sales mix and focusing on selling more high-margin items can significantly improve overall profitability.
-
Market Demand and Competition: External factors like market trends, economic conditions, and competitive pressures can significantly impact sales volume and, consequently, profitability. Businesses need to adapt their strategies to respond effectively to these external forces.
Optimizing the Relationship: Strategies for Enhanced Profitability
Turning the intricate relationship between sales and profits into a synergistic partnership requires a multi-pronged approach:
1. Data-Driven Decision Making:
-
Sales Analytics: Tracking key sales metrics (e.g., conversion rates, average order value, customer lifetime value) provides crucial insights into sales performance and areas for improvement.
-
Cost Analysis: Regularly analyzing cost structures identifies areas where expenses can be reduced without compromising quality or customer service.
-
Profitability Analysis: By analyzing the profitability of individual products, services, or customer segments, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic focus.
2. Strategic Pricing:
-
Value-Based Pricing: Focusing on the perceived value of your product or service rather than simply cost-plus pricing can justify higher prices and improve profit margins.
-
Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting prices based on factors like demand, seasonality, and competition can optimize revenue generation.
-
Price Bundling: Offering bundled products or services at a discounted price can incentivize purchases and increase the average order value.
3. Enhancing Sales Efficiency:
-
Sales Force Automation (SFA): Utilizing CRM software and other sales tools can streamline sales processes, improve sales team productivity, and enhance customer relationship management.
-
Targeted Marketing: Focusing marketing efforts on specific customer segments with tailored messaging can improve campaign effectiveness and reduce wasted marketing spend.
-
Sales Training: Investing in comprehensive sales training equips sales teams with the skills and knowledge to effectively sell products and services and build strong customer relationships.
4. Cost Optimization:
-
Process Optimization: Streamlining business processes, eliminating redundancies, and automating repetitive tasks can significantly reduce operating expenses.
-
Negotiating Better Deals: Negotiating favorable contracts with suppliers, landlords, and other vendors can lower costs.
-
Inventory Management: Implementing efficient inventory management systems minimizes storage costs, reduces waste, and prevents stockouts.
5. Product Portfolio Management:
-
Analyzing Product Profitability: Identifying and focusing on high-margin products while phasing out low-margin ones can significantly improve overall profitability.
-
Product Innovation: Developing new products or services that address unmet customer needs can generate new revenue streams and enhance profitability.
-
Product Diversification: Offering a diverse range of products or services can reduce reliance on any single product and mitigate risk.
The Long-Term Perspective: Building a Sustainable Sales and Profit Model
Building a truly successful business isn't about short-term sales spikes; it's about creating a sustainable model that balances revenue generation with cost management for consistent long-term profitability. This requires a strategic approach that encompasses:
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Fostering strong customer relationships through exceptional service and personalized communication builds loyalty, leading to repeat business and increased lifetime customer value.
-
Brand Building: Investing in building a strong brand reputation attracts customers, enhances perceived value, and justifies premium pricing.
-
Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluating and improving sales and operational processes ensures long-term efficiency and profitability.
-
Adaptability: The business environment is constantly evolving. Businesses must remain agile and adapt their strategies to respond effectively to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Sales and Profit Optimization
While specific data for proprietary business strategies is often confidential, several general case studies illustrate how the concepts above play out in practice:
Example 1: A Retail Business Optimizing Inventory Management. A retail business experiencing high inventory costs implemented a new inventory management system. This system optimized stock levels, reduced waste from expired goods, and improved order fulfillment times. The result? Lower storage costs, increased cash flow, and ultimately, higher profits despite relatively stable sales figures.
Example 2: A SaaS Company Implementing Value-Based Pricing. A Software as a Service (SaaS) company shifted from a simple subscription-based pricing model to a value-based model. By highlighting the ROI of its software, it was able to justify a significant price increase. While some customers churned, the overall increase in revenue from the remaining higher-paying customers outweighed the loss, significantly boosting profitability.
Example 3: A Manufacturing Company Improving Operational Efficiency. A manufacturing company identified bottlenecks in its production process through data analysis. By streamlining these processes and automating certain tasks, it was able to reduce production costs without sacrificing output. This led to higher profit margins despite maintaining a similar sales volume.
Conclusion: The Enduring Dance of Sales and Profits
The relationship between sales and profits is a dynamic and intricate dance. It's not a simple equation but a multifaceted interplay of factors that require careful consideration and strategic management. By implementing data-driven decision-making, optimizing pricing strategies, enhancing sales efficiency, controlling costs, and fostering strong customer relationships, businesses can achieve a harmonious balance between sales and profits, paving the way for sustained growth and long-term success. The journey requires continuous learning, adaptation, and a commitment to improving processes and strategies over time. It's a continuous improvement cycle, not a destination.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Relationship Between Sales And Profits Can Be Written As . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.