Which Of These Is A Banking Activity Of The Fed
Holbox
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
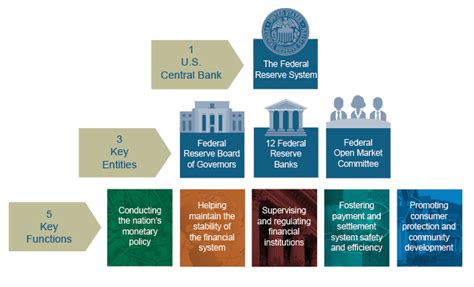
Table of Contents
- Which Of These Is A Banking Activity Of The Fed
- Table of Contents
- Decoding the Fed's Banking Activities: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Fed's Core Banking Functions: A Closer Look
- 1. Serving as a Banker's Bank:
- 2. Regulating and Supervising Banks:
- 3. Influencing Monetary Policy:
- Distinguishing Banking Activities from Other Fed Functions
- The Impact of the Fed's Banking Activities
- Conclusion: The Fed as a Central Bank and Banker's Bank
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Decoding the Fed's Banking Activities: A Comprehensive Guide
The Federal Reserve (Fed), the central bank of the United States, plays a multifaceted role in the nation's financial system. While many understand its influence on interest rates and monetary policy, the Fed's direct involvement in banking activities often remains less clear. This article delves deep into the various banking activities undertaken by the Fed, clarifying its functions and impact on the broader economy. We'll explore which actions constitute banking activities and which fall outside its purview, providing a comprehensive understanding of the Fed's role in maintaining financial stability.
The Fed's Core Banking Functions: A Closer Look
The Fed's banking activities are crucial for maintaining a healthy and stable financial system. These functions are not simply administrative; they are actively shaping the landscape of American finance. Let's explore some key areas:
1. Serving as a Banker's Bank:
This is perhaps the most fundamental banking activity of the Fed. It acts as the central bank, providing crucial services to commercial banks and other depository institutions. This includes:
-
Holding Reserves: Commercial banks are required to hold a certain percentage of their deposits as reserves. The Fed provides a secure and reliable place for these reserves to be held, ensuring the banking system's liquidity. This is a cornerstone of maintaining financial stability; without it, banks would be far more vulnerable to runs.
-
Clearing Checks and Electronic Payments: The Fed facilitates the efficient clearing and settlement of checks and electronic payments between banks. This smooths the flow of funds throughout the economy, preventing bottlenecks and delays. The modern, high-volume payment systems we rely on depend critically on the Fed's infrastructure.
-
Providing Discount Window Lending: When banks face temporary liquidity shortages, they can borrow funds from the Fed's discount window. This acts as a lender of last resort, preventing bank failures during periods of stress. Access to this facility is carefully managed to prevent its overuse and maintain appropriate financial discipline.
-
Managing the Payment System: The Fed's responsibility extends to overseeing and regulating the nation's payment systems, ensuring their security and efficiency. This includes overseeing aspects like ACH (Automated Clearing House) transfers and wire transfers. This activity ensures the reliability and integrity of the payments system which is the lifeblood of the US economy.
2. Regulating and Supervising Banks:
The Fed's regulatory and supervisory powers are essential in maintaining the soundness of the banking system. These activities are directly related to its banking functions, as a healthy banking sector is vital for the overall health of the economy. Specifically, the Fed:
-
Overseeing Bank Holding Companies: The Fed directly regulates and supervises bank holding companies, large financial institutions that own or control multiple banks. This oversight includes rigorous stress tests to assess their resilience to economic shocks. This is proactive risk management on a large scale, protecting the system from systemic failures.
-
Monitoring Bank Capital and Liquidity: The Fed sets capital requirements for banks, ensuring they have sufficient resources to absorb potential losses. It also monitors their liquidity positions, ensuring they can meet their obligations to depositors. This is essential for preventing bank runs and maintaining stability.
-
Enforcing Banking Regulations: The Fed enforces a wide range of banking regulations, ensuring compliance with federal laws and guidelines. This includes regulations related to lending practices, risk management, and consumer protection. This ensures fair and ethical banking practices across the board.
-
Conducting Bank Examinations: The Fed regularly conducts examinations of banks to assess their financial health, identify potential risks, and enforce compliance with regulations. This involves detailed reviews of financial statements, risk management processes and overall bank operations.
3. Influencing Monetary Policy:
While not directly a "banking" activity in the traditional sense, the Fed's monetary policy actions significantly impact the banking sector and its activities. These actions are closely intertwined with the Fed’s role as a banker’s bank:
-
Setting Reserve Requirements: By adjusting the reserve requirements that banks must maintain, the Fed influences the amount of money available for lending and investment. Lower requirements stimulate lending, while higher requirements have a contractionary effect.
-
Setting the Federal Funds Rate: The federal funds rate is the target rate for overnight lending between banks. The Fed influences this rate through open market operations, buying or selling government securities to increase or decrease the money supply. This directly impacts the cost of borrowing for banks and consequently influences lending rates across the economy.
-
Open Market Operations: The buying and selling of government securities in the open market is a powerful tool used by the Fed to influence the money supply and interest rates. This directly affects the liquidity available to banks and influences their lending capacity.
Distinguishing Banking Activities from Other Fed Functions
It's crucial to differentiate the Fed's banking activities from its other critical roles. While all contribute to economic stability, some are more directly related to banking operations. Here’s a breakdown:
-
Monetary Policy: While profoundly impacting banks, the setting of interest rates and management of the money supply isn't a direct banking activity. It's a macro-economic management tool with implications for the banking sector.
-
Financial Regulation (Beyond Banks): The Fed plays a significant role in regulating other financial institutions beyond banks, such as investment banks and securities firms. While important for overall financial stability, it’s a separate area of focus distinct from its core banking functions.
-
Consumer Protection: Although related to banking activities, the Fed's consumer protection efforts, such as enforcing the Truth in Lending Act, are primarily focused on consumer rights rather than direct banking operations.
-
Economic Research and Analysis: The Fed conducts extensive economic research and provides analysis to policymakers and the public. While crucial for informed decision-making, this is an analytical rather than a direct operational banking activity.
The Impact of the Fed's Banking Activities
The Fed's banking activities have a profound and wide-ranging impact on the US economy. These activities are vital for:
-
Maintaining Financial Stability: The Fed’s role as a lender of last resort, regulator, and supervisor is crucial for preventing bank failures and maintaining the stability of the financial system. This stability is vital for economic growth and confidence.
-
Facilitating Economic Growth: By influencing monetary policy and ensuring the smooth functioning of the payment system, the Fed contributes to economic growth. A healthy banking system underpins investment, lending, and overall economic activity.
-
Protecting Consumers: The Fed's regulatory oversight and consumer protection efforts ensure fair banking practices and protect consumers from predatory lending and other abuses.
-
Promoting International Financial Stability: Through its international collaborations and involvement in global financial institutions, the Fed plays a role in promoting stability in the global financial system. This interconnectedness necessitates active international participation for overall stability.
Conclusion: The Fed as a Central Bank and Banker's Bank
The Federal Reserve’s role in the US banking system is complex and multifaceted. While it undertakes many activities beyond direct banking, its core functions as a banker’s bank – holding reserves, clearing payments, providing discount window lending, and regulating and supervising banks – are undeniably central to its mission. These activities are interwoven with its monetary policy functions to create a robust and resilient financial system. Understanding this interplay is crucial for grasping the Fed's influence on the American economy and its crucial role in maintaining financial stability and fostering economic growth. The Fed is much more than a central bank; it’s the backbone of the US financial system, actively shaping the landscape of American finance through its carefully managed banking activities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Predict The Major Organic Product Of The Following Reaction
Apr 01, 2025
-
Label The Floors Of The Hotel
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Possible R Value
Apr 01, 2025
-
Record The Adjusting Entry For Uncollectible Accounts
Apr 01, 2025
-
Como Se Llama El Padre De Sara
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of These Is A Banking Activity Of The Fed . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
