Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Vicarious Punishment
Holbox
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
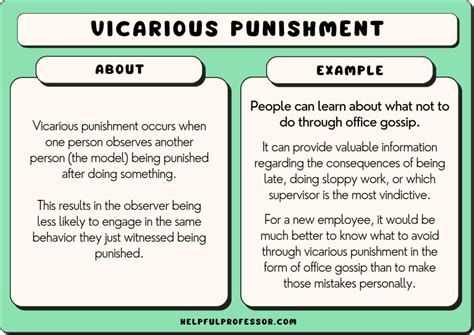
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Vicarious Punishment
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following is an Example of Vicarious Punishment? Understanding Observational Learning and its Consequences
- What is Vicarious Punishment?
- Examples of Vicarious Punishment in Different Contexts
- 1. Childhood Development:
- 2. Workplace Scenarios:
- 3. Social Contexts:
- Distinguishing Vicarious Punishment from Other Learning Processes
- Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Vicarious Punishment
- Potential Drawbacks of Vicarious Punishment
- Applying Vicarious Punishment Effectively
- Conclusion: The Power and Limitations of Vicarious Punishment
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following is an Example of Vicarious Punishment? Understanding Observational Learning and its Consequences
Observational learning, a cornerstone of social learning theory, posits that we learn by watching others. This learning extends beyond simply mimicking actions; it also encompasses understanding the consequences of those actions. A crucial aspect of observational learning is vicarious reinforcement and, conversely, vicarious punishment. While vicarious reinforcement involves learning from observing someone else being rewarded, vicarious punishment involves learning by observing someone else being punished. Understanding the difference is key to grasping how we acquire and avoid behaviors. This article will delve into the nuances of vicarious punishment, providing clear examples and exploring its implications in various contexts.
What is Vicarious Punishment?
Vicarious punishment, also known as observational punishment, occurs when an individual observes another person being punished for a specific behavior, leading the observer to decrease the likelihood of performing that same behavior. It's a powerful learning mechanism because it doesn't require the observer to directly experience the negative consequences; the observed punishment serves as a deterrent. The key elements are:
- Observation: The individual must witness the punishment.
- Punishment: The observed consequence must be negative or unpleasant.
- Association: The observer must connect the behavior with the punishment.
- Inhibition: The observer reduces the likelihood of performing the same behavior.
Examples of Vicarious Punishment in Different Contexts
The principles of vicarious punishment are applicable across a wide range of scenarios, from childhood development to workplace dynamics. Let's examine several examples:
1. Childhood Development:
- Sibling Punishment: Imagine a young child witnessing their older sibling being grounded for breaking curfew. The younger child, observing the consequences (loss of privileges), is less likely to break curfew themselves. This is a clear example of vicarious punishment shaping their behavior.
- Classroom Setting: A teacher reprimanding a student for talking out of turn can serve as a vicarious punishment for the other students. Seeing a classmate face consequences (e.g., loss of recess time) can deter the others from repeating the same misbehavior.
- Peer Influence: A child observing a friend being teased for wearing a certain outfit might avoid wearing similar outfits themselves to prevent experiencing the same negative social consequences.
2. Workplace Scenarios:
- Employee Termination: Witnessing a coworker being fired for consistently arriving late to work can deter other employees from exhibiting similar tardiness. The fear of losing their job (the punishment) acts as a strong inhibitor.
- Public Reprimand: An employee receiving a public reprimand from their manager for making a significant error can serve as a vicarious punishment for other team members. This creates a culture of accountability and caution.
- Performance Reviews: Observing a colleague receive a negative performance review for lack of effort can motivate others to improve their work ethic to avoid similar negative feedback.
3. Social Contexts:
- Media Influence: News reports about individuals facing legal consequences for committing crimes (e.g., drunk driving accidents resulting in jail time) can serve as a form of vicarious punishment, deterring others from engaging in such behaviors.
- Social Media: Observing negative social media backlash directed at someone for making an offensive statement can discourage others from making similar remarks. The fear of public shaming and social isolation acts as a powerful deterrent.
- Celebrity Scandals: When celebrities face public criticism and career setbacks due to inappropriate behavior, it can act as a vicarious punishment, influencing others to consider the potential consequences of their actions.
Distinguishing Vicarious Punishment from Other Learning Processes
It's crucial to differentiate vicarious punishment from other related concepts:
- Direct Punishment: This involves personally experiencing a negative consequence for a behavior. In contrast, vicarious punishment involves observing someone else's negative experience.
- Vicarious Reinforcement: This is the opposite of vicarious punishment; it involves learning by observing someone else being rewarded for a behavior, increasing the likelihood of the observer repeating that behavior.
- Modeling: While vicarious punishment involves learning through consequences, modeling focuses on simply imitating observed behavior, regardless of its consequences.
Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Vicarious Punishment
Several factors influence the effectiveness of vicarious punishment:
- Similarity to the Observer: The more similar the observer is to the person being punished (in terms of age, gender, social status, etc.), the more impactful the vicarious punishment will be.
- Consistency: Consistent application of punishment is more effective than inconsistent application. If the punishment is sometimes applied and sometimes not, the observer may not learn to associate the behavior with the negative consequence.
- Severity of Punishment: The severity of the punishment observed can influence the effectiveness; however, excessively harsh punishments can have unintended negative consequences, such as fear and anxiety.
- Observer's Perspective: The observer's emotional response to the observed punishment (empathy, fear, etc.) also plays a role in shaping their behavior.
- Relationship to the Punished Individual: The closer the relationship between the observer and the punished individual, the stronger the impact of vicarious punishment tends to be.
Potential Drawbacks of Vicarious Punishment
While vicarious punishment can be an effective learning tool, it also has potential drawbacks:
- Emotional Distress: Observing someone being punished can cause emotional distress in the observer, particularly if they identify strongly with the punished individual.
- Fear and Anxiety: Excessive emphasis on punishment can lead to fear and anxiety, potentially hindering learning and creating a negative learning environment.
- Lack of Understanding: If the observer doesn't fully understand the reason for the punishment, the learning process may be less effective. Clear communication is essential.
- Unintended Consequences: Over-reliance on vicarious punishment without providing alternative positive reinforcement can stifle creativity, initiative, and positive risk-taking.
Applying Vicarious Punishment Effectively
To maximize the effectiveness and minimize the drawbacks of vicarious punishment, consider the following strategies:
- Clarity and Consistency: Ensure the behavior and its consequences are clearly communicated and consistently applied.
- Emphasis on Positive Reinforcement: Combine vicarious punishment with positive reinforcement to promote desirable behaviors.
- Focus on Understanding: Help observers understand the reasons behind the punishment to facilitate learning.
- Appropriate Severity: Use punishment judiciously; avoid excessively harsh or cruel methods.
- Emphasize Empathy and Compassion: Encourage observers to understand the perspective of the person being punished, fostering empathy and compassion rather than solely focusing on fear.
Conclusion: The Power and Limitations of Vicarious Punishment
Vicarious punishment is a significant element of observational learning, playing a crucial role in shaping behavior across diverse contexts. It offers a powerful mechanism for learning by avoiding negative consequences without direct personal experience. However, its effectiveness relies on several factors, and its application requires careful consideration to avoid potential drawbacks. By understanding the principles of vicarious punishment and employing it responsibly, we can leverage its potential for promoting desirable behaviors while minimizing its negative consequences. Remember that the most effective approaches combine both vicarious punishment and positive reinforcement to create a balanced and effective learning experience. This approach fosters a learning environment that is not only efficient but also emotionally healthy and conducive to positive growth and development.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Primary Concerns Of Shared Value And Sustainable Development
Mar 26, 2025
-
In Which Of The Following Situations Is Passing Always Forbidden
Mar 26, 2025
-
Economists Often Track Employment Trends By Measuring The Proportion
Mar 26, 2025
-
8 2 7 Sum Rows In A 2d Array
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Nims Component Includes The Ics
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Vicarious Punishment . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
