What Are Primary Concerns Of Shared Value And Sustainable Development
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 7 min read
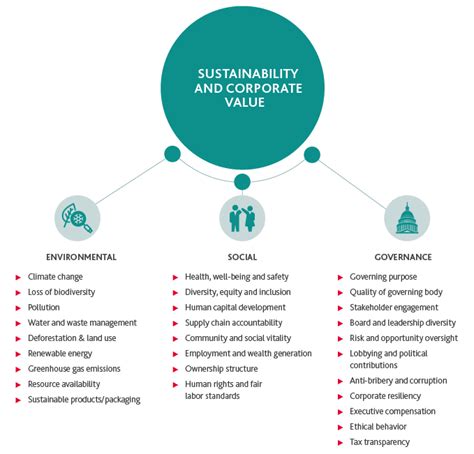
Table of Contents
- What Are Primary Concerns Of Shared Value And Sustainable Development
- Table of Contents
- What Are the Primary Concerns of Shared Value and Sustainable Development?
- Shared Value: Creating Economic Value While Addressing Social Needs
- 1. Reconceiving Products and Markets:
- 2. Redefining Productivity in the Value Chain:
- 3. Enabling Local Cluster Development:
- Sustainable Development: Balancing Economic Growth with Environmental Protection and Social Equity
- 1. Environmental Sustainability:
- 2. Social Equity and Inclusion:
- 3. Economic Growth and Development:
- The Overlapping Concerns of Shared Value and Sustainable Development
- Challenges and Opportunities
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What Are the Primary Concerns of Shared Value and Sustainable Development?
Shared value and sustainable development are intrinsically linked concepts, both striving for a future where economic prosperity and environmental and social well-being coexist harmoniously. While distinct in their origins and approaches, their primary concerns overlap significantly, focusing on creating a more equitable and resilient world. This article delves into the core concerns of both frameworks, exploring their interconnections and highlighting the challenges and opportunities they present.
Shared Value: Creating Economic Value While Addressing Social Needs
Shared value, a concept pioneered by Michael Porter and Mark Kramer, challenges the traditional notion of a trade-off between economic success and social responsibility. It posits that businesses can create economic value by addressing social and environmental issues that directly affect their operations and competitiveness. The core concerns driving shared value initiatives include:
1. Reconceiving Products and Markets:
This involves innovating to develop products and services that meet societal needs while simultaneously generating profits. The focus shifts from merely selling goods to providing solutions that improve the lives of consumers and communities. Examples include developing affordable healthcare solutions for underserved populations, creating sustainable agricultural practices that benefit farmers and the environment, or designing energy-efficient appliances that reduce carbon emissions and save consumers money.
2. Redefining Productivity in the Value Chain:
Shared value initiatives also examine the entire value chain, seeking opportunities to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This might involve improving resource management, reducing waste, minimizing pollution, and enhancing the working conditions of employees and suppliers. For example, a company might invest in renewable energy sources to power its operations, reducing its reliance on fossil fuels and lowering its energy costs. Similarly, investing in employee training and development can lead to increased productivity and lower turnover rates.
3. Enabling Local Cluster Development:
Shared value recognizes the importance of fostering thriving local ecosystems. Businesses can contribute to the development of strong, sustainable communities by investing in education, infrastructure, and local businesses. This can improve the living standards of the workforce, increase the availability of skilled labor, and enhance the overall business environment. An example would be a company investing in the education and training of local workers, creating a pool of skilled labor that benefits not only the company but also the entire region.
Sustainable Development: Balancing Economic Growth with Environmental Protection and Social Equity
Sustainable development, as defined by the Brundtland Report (Our Common Future), aims to "meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." This comprehensive framework integrates environmental, social, and economic considerations, addressing concerns such as:
1. Environmental Sustainability:
This is a cornerstone of sustainable development, focusing on minimizing the negative environmental impacts of human activities. Key concerns include:
- Climate Change: Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the effects of climate change are paramount. This includes transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable land management practices.
- Resource Depletion: Sustainable resource management is crucial to ensuring the long-term availability of essential resources like water, minerals, and forests. This requires reducing consumption, improving efficiency, and promoting the use of recycled and renewable materials.
- Biodiversity Loss: Protecting biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecosystem services and ensuring the resilience of the planet. This involves conserving habitats, preventing species extinction, and promoting sustainable agriculture.
- Pollution: Reducing pollution from various sources, including air, water, and soil pollution, is essential for protecting human health and the environment. This requires implementing stricter environmental regulations, promoting cleaner production technologies, and raising public awareness.
2. Social Equity and Inclusion:
Sustainable development emphasizes the importance of social justice and equity. Key concerns include:
- Poverty Eradication: Reducing poverty and inequality is crucial for ensuring that all people have access to basic needs such as food, water, shelter, healthcare, and education. This requires implementing social safety nets, promoting economic opportunities, and addressing systemic inequalities.
- Human Rights: Protecting human rights is essential for ensuring a just and equitable society. This includes respecting the rights of all individuals, regardless of their race, gender, religion, or other characteristics.
- Good Governance: Effective governance is essential for promoting sustainable development. This includes ensuring transparency, accountability, and participation in decision-making processes.
- Health and Wellbeing: Promoting physical and mental health is crucial for individual and societal well-being. This involves providing access to healthcare services, promoting healthy lifestyles, and addressing environmental health risks.
3. Economic Growth and Development:
Sustainable development recognizes the importance of economic growth as a means of improving living standards and reducing poverty. However, this growth must be inclusive and sustainable, avoiding environmental degradation and social inequalities. Key concerns include:
- Inclusive Growth: Ensuring that the benefits of economic growth are shared equitably across all segments of society. This involves creating opportunities for all people, regardless of their background or location.
- Green Jobs: Creating jobs in environmentally sustainable industries, such as renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and green building.
- Sustainable Consumption and Production: Encouraging patterns of consumption and production that are environmentally sustainable and socially responsible.
The Overlapping Concerns of Shared Value and Sustainable Development
The concerns of shared value and sustainable development are deeply intertwined. Both frameworks emphasize the importance of creating a more equitable and sustainable future, albeit through different approaches. Several key areas of overlap include:
-
Environmental Protection: Both frameworks recognize the critical importance of environmental sustainability. Shared value initiatives can contribute to environmental protection by reducing a company’s environmental footprint and developing environmentally friendly products and services. Sustainable development sets broader environmental goals and targets, providing a framework for these initiatives.
-
Social Equity: Both frameworks recognize the need for social equity and inclusion. Shared value initiatives can contribute to social equity by addressing social issues that affect a company's operations, such as improving working conditions or providing access to healthcare. Sustainable development sets broader goals for social equity, such as poverty eradication and human rights protection.
-
Economic Growth: Both frameworks recognize the importance of economic growth, but this growth must be sustainable and inclusive. Shared value initiatives can contribute to economic growth by creating new markets and improving efficiency. Sustainable development provides a framework for ensuring that economic growth is sustainable and does not compromise environmental or social goals.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the shared vision of shared value and sustainable development is compelling, numerous challenges exist in translating these concepts into tangible results:
-
Measurement and Reporting: Accurately measuring and reporting the social and environmental impacts of businesses remains a challenge. Standardized metrics and reporting frameworks are needed to ensure transparency and accountability.
-
Integration into Business Strategies: Integrating shared value and sustainable development principles into core business strategies requires a fundamental shift in mindset and organizational culture. Many companies struggle to move beyond superficial CSR initiatives to genuine integration.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for successful implementation. Companies need to engage with a wide range of stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and governments.
-
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Supportive policy and regulatory frameworks are essential for creating a level playing field and incentivizing sustainable business practices. Governments play a crucial role in setting the stage for widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, significant opportunities exist:
-
Innovation and New Business Models: Addressing social and environmental challenges can lead to innovation and the creation of new business models, driving economic growth and creating new job opportunities.
-
Enhanced Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty: Companies that demonstrate a commitment to shared value and sustainable development often enjoy enhanced brand reputation and increased customer loyalty.
-
Improved Risk Management: Addressing social and environmental risks can help companies mitigate potential financial and reputational risks.
-
Increased Investor Interest: Investors are increasingly interested in companies that demonstrate a strong commitment to ESG (environmental, social, and governance) factors.
Conclusion
Shared value and sustainable development are complementary frameworks that share a common goal: creating a more equitable and sustainable world. While distinct in their approaches, they converge on the critical importance of addressing social and environmental concerns to achieve long-term economic prosperity. By integrating these principles into core business strategies and collaborating across sectors, businesses, governments, and civil society can create a future where economic success and environmental and social well-being go hand in hand. The successful implementation of these frameworks will require ongoing innovation, collaboration, and a fundamental shift in how we view the relationship between business, society, and the environment. Addressing the challenges and seizing the opportunities presented by shared value and sustainable development is crucial for creating a truly resilient and prosperous future for all.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In Which Domains Are Algae Protozoa And Cyanobacteria Classified
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Instance Of Persuasive Speaking
Mar 30, 2025
-
Job Rotation Helps Lower Level Managers Prepare For Higher Level Positions By
Mar 30, 2025
-
In Person Centered Group Therapy The Leader
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is A Downfall To Just In Time Manufacturing And Inventory Management
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Primary Concerns Of Shared Value And Sustainable Development . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
