Which Of The Following Is An Advantage Of Primary Data
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
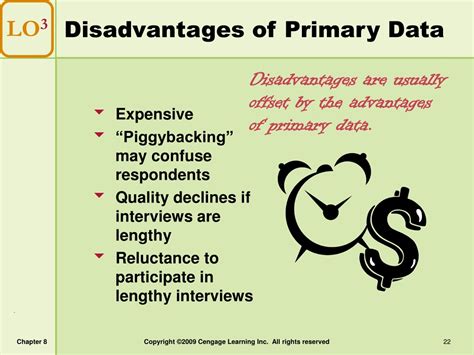
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is an Advantage of Primary Data? A Deep Dive into the Benefits
Collecting data is the bedrock of any successful research project, business strategy, or marketing campaign. But the type of data you collect is crucial. While secondary data offers convenience and readily available information, primary data holds a significant edge in many situations. This article will delve deep into the advantages of primary data, exploring why it's often the preferred choice for researchers and businesses striving for accurate, insightful, and actionable results.
The Undeniable Advantages of Primary Data
Primary data, defined as information collected directly from its original source, offers numerous advantages that secondary data simply can't match. Let's explore these key benefits:
1. Specificity and Relevance: Tailored to Your Needs
One of the most compelling advantages of primary data is its specificity. Unlike secondary data, which might be collected for general purposes, primary data is gathered specifically to answer your research questions or address your business objectives. This allows you to:
- Target your audience precisely: You can design your data collection methods (surveys, interviews, experiments) to focus on the exact demographics, behaviors, and characteristics relevant to your study.
- Ask the right questions: You have complete control over the questions asked, ensuring they align perfectly with your research goals and avoid ambiguity.
- Gather detailed information: You can probe deeper into specific aspects and gather richer, more nuanced data than might be available in pre-existing secondary sources.
This tailored approach leads to more accurate and relevant findings, directly contributing to more informed decision-making.
2. Accuracy and Reliability: Ensuring Data Integrity
The accuracy and reliability of primary data are significantly higher than that of secondary data. Because you are collecting the data yourself, you can:
- Control data collection methods: You choose the methodology best suited for your research, minimizing potential biases and errors inherent in pre-existing datasets.
- Verify data quality: You can implement quality control measures during the data collection process, ensuring the accuracy and consistency of your information.
- Understand data limitations: You have a clear understanding of the context in which the data was collected, allowing you to assess its limitations and potential biases more effectively.
This heightened level of accuracy and reliability translates to more trustworthy and dependable conclusions, crucial for critical decision-making processes.
3. First-hand Insights: Unveiling Unique Perspectives
Primary data offers unique insights that secondary data simply cannot provide. It allows you to:
- Gather firsthand perspectives: You can directly interact with your target audience, gaining firsthand insights into their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. This is particularly valuable for understanding complex phenomena or exploring nuanced perspectives.
- Explore unexplored areas: You are not limited to pre-existing data categories. You can explore new areas and uncover unanticipated insights that might not have been considered previously.
- Discover emerging trends: By engaging directly with your audience, you can identify emerging trends and patterns that might be too recent to be reflected in secondary data sources.
These unique insights contribute to a deeper understanding of your subject matter, enabling more innovative solutions and effective strategies.
4. Current and Up-to-Date Information: Staying Ahead of the Curve
The timeliness of data is crucial, particularly in rapidly changing environments. Primary data offers the significant advantage of being current and up-to-date. While secondary data can become outdated quickly, primary data collection ensures you have the latest information available, allowing you to:
- Make timely decisions: You can react quickly to changing market conditions, consumer preferences, or emerging trends.
- Stay ahead of the competition: Access to the latest information allows you to anticipate and respond to market changes more effectively than competitors relying on older secondary data.
- Develop more relevant strategies: Current information helps you to develop strategies that are better aligned with current market demands and customer expectations.
This timeliness is paramount for businesses operating in dynamic industries.
5. Confidentiality and Security: Protecting Sensitive Information
In some research areas, confidentiality and security are paramount. Primary data allows for greater control over:
- Data storage and access: You can implement strict security protocols to protect sensitive information during the entire data lifecycle.
- Data anonymity: You can design your data collection methods to ensure anonymity and confidentiality of participants, crucial in sensitive research areas.
- Data usage restrictions: You retain full control over how the data is used and shared, complying with ethical guidelines and legal regulations.
This enhanced control over data security is particularly crucial for sensitive topics or when dealing with personal information.
6. Ownership and Control: Maintaining Intellectual Property
Unlike secondary data, where you are typically limited by the terms of use and licensing agreements, primary data offers:
- Full ownership: You retain complete ownership of the data you collect, including the right to use, share, and analyze it as you see fit.
- Unrestricted access: You have unrestricted access to your data, allowing for flexible analysis and exploration of different research angles.
- Potential for commercialization: You can potentially commercialize your findings and insights derived from primary data.
This ownership and control are vital for intellectual property protection and commercial exploitation of research results.
Overcoming Challenges Associated with Primary Data Collection
While primary data offers significant advantages, it's essential to acknowledge the potential challenges:
- Cost: Collecting primary data can be expensive, particularly for large-scale studies involving diverse methodologies.
- Time: Gathering primary data takes time, from designing the research instrument to data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resources: Collecting primary data requires resources, including personnel, equipment, and software.
- Sampling bias: If not carefully planned, the sampling method can introduce bias, impacting the generalizability of the results.
- Ethical considerations: Researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines, ensuring informed consent, data confidentiality, and anonymity.
Careful planning, resource allocation, and adherence to ethical guidelines are crucial for mitigating these challenges and maximizing the benefits of primary data collection.
Choosing Between Primary and Secondary Data: A Strategic Approach
The decision of whether to use primary or secondary data, or a combination of both, is a strategic one. The choice depends on several factors, including:
- Research objectives: What specific questions are you trying to answer?
- Available resources: What is your budget and timeframe?
- Data availability: Is relevant secondary data readily available?
- Data quality requirements: How accurate and reliable does the data need to be?
- Time sensitivity: How current does the information need to be?
A well-defined research plan that considers these factors will guide you toward the most effective data collection strategy. Often, a mixed-methods approach, using both primary and secondary data, offers the most comprehensive and insightful results. Secondary data can provide a foundational understanding of the topic, while primary data can fill gaps, provide crucial details, and confirm or refute findings from secondary sources.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Primary Data for Superior Insights
In conclusion, the advantages of primary data are undeniable. Its specificity, accuracy, timeliness, and control over data ownership and security make it a crucial tool for researchers and businesses seeking high-quality, actionable insights. While acknowledging the challenges involved in its collection, the potential for unveiling unique perspectives and generating reliable, relevant findings often outweighs the costs and efforts involved. By carefully planning and executing primary data collection strategies, organizations can unlock a wealth of information that drives better decision-making, improves business outcomes, and positions them for success in today's competitive landscape. Understanding and harnessing the power of primary data is key to navigating the complexities of research and achieving impactful results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Rank Each Of The Following Firms Based On Market Power
Mar 18, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Anterior Muscles Of The Thigh
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Best Known Self Regulatory Group Is The Blank
Mar 18, 2025
-
Your Local Movie Theater Uses The Same Group Pricing Strategy
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Set Of Bivariate Data Was Used To Create
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is An Advantage Of Primary Data . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
