Which Of The Following Is A Ball And Socket Joint
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
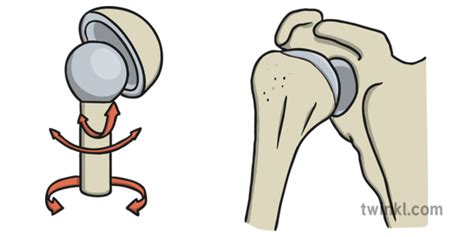
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Ball and Socket Joint? Understanding Synovial Joints
The human body is a marvel of engineering, a complex network of bones, muscles, and connective tissues working in perfect harmony. Crucial to this harmonious movement are our joints, which allow for a wide range of motion, from the delicate movements of our fingers to the powerful strides of our legs. Understanding the different types of joints is essential to appreciating the intricacies of human anatomy and the causes and treatments of various musculoskeletal conditions. This article delves into the fascinating world of synovial joints, focusing specifically on ball and socket joints and highlighting their unique characteristics and importance.
What is a Joint?
Before diving into the specifics of ball and socket joints, let's first establish a foundational understanding of joints themselves. Joints, also known as articulations, are the points where two or more bones meet. They provide stability and allow for movement, the specific type and degree of movement depending on the joint's structure. There are three main classifications of joints based on their structural characteristics and the degree of movement they allow: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial.
Fibrous Joints
Fibrous joints are characterized by the presence of fibrous connective tissue between the bones. This connective tissue holds the bones tightly together, resulting in limited or no movement. Examples include the sutures in the skull and the joints between the teeth and their sockets.
Cartilaginous Joints
Cartilaginous joints connect bones via cartilage. They offer more flexibility than fibrous joints but still provide significant stability. Cartilaginous joints are found in areas requiring a degree of flexibility combined with strength, like the intervertebral discs in the spine.
Synovial Joints
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body and are characterized by a fluid-filled cavity between the articulating bones. This synovial fluid lubricates the joint, reducing friction and allowing for a wide range of motion. Synovial joints are further categorized based on their shapes and the types of movement they permit. This is where ball and socket joints fit into the picture.
Understanding Synovial Joints: A Deeper Dive
Synovial joints are incredibly complex structures, featuring several key components that contribute to their functionality:
- Articular Cartilage: A smooth, protective layer covering the ends of the bones, reducing friction during movement.
- Synovial Fluid: A viscous fluid that lubricates the joint and nourishes the articular cartilage.
- Joint Capsule: A fibrous sac that encloses the joint, providing stability and containing the synovial fluid.
- Synovial Membrane: The inner lining of the joint capsule, responsible for producing synovial fluid.
- Ligaments: Strong, fibrous bands of connective tissue that connect bones and provide stability to the joint.
Ball and Socket Joints: The Freest Range of Motion
Among the various types of synovial joints, ball and socket joints stand out for their exceptional range of motion. These joints are characterized by a rounded head of one bone fitting into a cup-like cavity of another bone. This design allows for movement in three planes: flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, and rotation. This triaxial movement capability makes ball and socket joints the most mobile type of synovial joint.
Key Characteristics of Ball and Socket Joints
- Triaxial Movement: Movement in all three planes: sagittal, frontal, and transverse.
- High Degree of Mobility: The greatest range of motion compared to other types of synovial joints.
- Rounded Head: One bone possesses a spherical head.
- Cup-like Cavity (Socket): The other bone has a concave socket or cup that receives the rounded head.
- Stability vs. Mobility: While highly mobile, these joints are not inherently the most stable due to their design.
Examples of Ball and Socket Joints in the Human Body
Two prominent examples of ball and socket joints in the human body are:
-
Shoulder Joint (Glenohumeral Joint): This joint connects the humerus (upper arm bone) to the scapula (shoulder blade). Its remarkable mobility allows for a wide range of arm movements, including lifting, reaching, and throwing. However, this high mobility comes at the cost of reduced stability, making the shoulder joint prone to dislocations.
-
Hip Joint (Coxofemoral Joint): This joint connects the femur (thigh bone) to the acetabulum (socket) of the hip bone (pelvis). The hip joint is crucial for walking, running, and other lower body movements. While also highly mobile, it is more stable than the shoulder joint due to the deeper socket and surrounding muscles and ligaments.
Other Types of Synovial Joints: A Comparison
To fully appreciate the unique characteristics of ball and socket joints, it's beneficial to compare them to other types of synovial joints:
- Hinge Joints: Allow movement in one plane only (flexion and extension). Examples include the elbow and knee joints.
- Pivot Joints: Allow rotation around a single axis. An example is the joint between the first and second vertebrae in the neck (atlantoaxial joint).
- Condyloid Joints: Allow movement in two planes (flexion/extension and abduction/adduction). Examples include the metacarpophalangeal joints (knuckles).
- Saddle Joints: Allow movement in two planes with some rotation. An example is the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb.
- Plane Joints (Gliding Joints): Allow for sliding movements between flat articular surfaces. Examples include the intercarpal and intertarsal joints.
Ball and Socket Joints: Clinical Significance
Understanding the structure and function of ball and socket joints is crucial in various medical contexts:
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Injuries: Dislocations, fractures, and sprains are common injuries affecting ball and socket joints, particularly the shoulder. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for optimal recovery.
-
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can significantly affect ball and socket joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Management strategies may involve medication, physiotherapy, and in some cases, joint replacement surgery.
-
Joint Replacement Surgery: For severe cases of joint damage, surgical intervention, such as hip or shoulder replacement, may be necessary to restore functionality and improve quality of life.
Conclusion: The Importance of Ball and Socket Joints
Ball and socket joints are remarkable structures that provide the human body with an unparalleled range of motion. Their unique design, characterized by a spherical head fitting into a cup-like cavity, enables movement in three planes, contributing to the dexterity and mobility we take for granted. However, this high degree of mobility often comes at the cost of stability, making these joints prone to injury. Understanding the intricacies of ball and socket joints is essential for both healthcare professionals and individuals alike, promoting injury prevention, effective treatment, and a deeper appreciation of the marvels of human anatomy. By studying their characteristics and comparing them to other types of synovial joints, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the remarkable complexity and functionality of the human musculoskeletal system. This knowledge is vital in maintaining joint health and ensuring optimal physical function throughout our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Banks Typically Come Under Financial Stress Because Of
Mar 17, 2025
-
Choose All That Are Characteristics Of Neural Pools
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Two Topics Of Primary Concern In Macroeconomics Are
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Toy Rocket Is Launched Vertically From Ground Level
Mar 17, 2025
-
Experiment 34 An Equilibrium Constant Pre Lab Answers
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Ball And Socket Joint . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
