Choose All That Are Characteristics Of Neural Pools.
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 7 min read
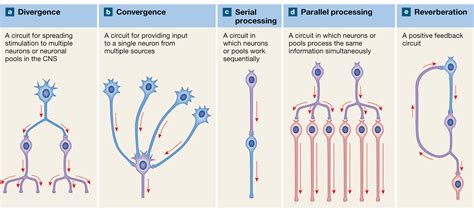
Table of Contents
Choose All That Are Characteristics of Neural Pools: A Deep Dive into Neural Network Organization
Neural pools are fundamental building blocks of the nervous system, representing interconnected groups of neurons that process and transmit information collectively. Understanding their characteristics is crucial to grasping the complexities of neural networks and brain function. This comprehensive guide delves into the defining features of neural pools, exploring their diverse roles in information processing and highlighting their significance in various neurological processes.
Key Characteristics of Neural Pools
Neural pools aren't simply random collections of neurons; they exhibit specific characteristics that dictate their function and interaction within larger neural networks. Let's explore these defining features:
1. Interconnectivity and Synaptic Weighting:
This is arguably the most defining characteristic. Neurons within a pool are extensively interconnected, forming a complex web of synaptic connections. Crucially, these connections aren't all equal. Synaptic weights, representing the strength of the connection between two neurons, vary considerably. A strong synapse indicates a significant influence of one neuron on another, while a weak synapse has a smaller impact. This weighted interconnectivity allows for sophisticated information processing, enabling the pool to perform complex computations.
The significance of synaptic weights: The dynamic adjustment of synaptic weights is central to learning and memory. Strengthening or weakening connections allows the neural pool to adapt its response to repeated stimuli, refining its processing capabilities over time. This plasticity is a hallmark of biological neural networks and a key element replicated in artificial neural networks.
2. Parallel Processing:
Unlike sequential processing, where information is handled step-by-step, neural pools excel at parallel processing. Multiple neurons within the pool can process information simultaneously, dramatically increasing processing speed and efficiency. This parallel architecture allows the pool to handle a large volume of input and produce multiple outputs concurrently.
Advantages of parallel processing: The inherent parallelism of neural pools allows for rapid response times, crucial for real-time processing of sensory information. Moreover, it allows for redundancy, meaning the failure of a single neuron doesn't necessarily compromise the function of the entire pool. This robustness is essential for the reliability of the nervous system.
3. Convergence and Divergence:
Neural pools demonstrate both convergence and divergence of neural signals. Convergence refers to multiple neurons converging onto a single neuron within the pool or even projecting to neurons outside the pool. This allows for the integration of information from various sources, summarizing or consolidating input before transmitting the result further. Conversely, divergence occurs when a single neuron in the pool projects to multiple neurons, broadcasting its signal to various targets. This allows for widespread dissemination of information, potentially influencing multiple downstream processes.
The interplay of convergence and divergence: The interplay of convergence and divergence is critical for signal amplification, distribution, and complex information routing within the nervous system. It facilitates both local processing within the pool and the communication of processed information to other brain regions.
4. Excitatory and Inhibitory Connections:
The connections within a neural pool are not all excitatory (promoting neuronal firing). Inhibitory connections, which suppress neuronal activity, play a crucial role in shaping the pool's overall response. The balance between excitation and inhibition fine-tunes the pool's output, preventing runaway excitation and allowing for sophisticated pattern recognition and discrimination.
The role of inhibition: Inhibition is essential for contrast enhancement, selective attention, and controlling the overall activity level of the neural pool. It prevents excessive neuronal firing, which could lead to instability or seizures. The precise interplay of excitation and inhibition is vital for the accurate and efficient functioning of neural pools.
5. Dynamic Activity Patterns:
Neural pools don't simply relay information passively. Their activity patterns are dynamic, constantly changing in response to incoming signals and internal states. This dynamic nature allows the pool to adapt its processing capabilities in response to changing demands. The collective firing patterns of neurons within the pool encode information, representing various aspects of the processed input.
Understanding dynamic patterns: Analyzing the dynamic activity patterns of neural pools is crucial for understanding how information is encoded and processed within the brain. Advanced techniques like EEG and fMRI are used to study these patterns, providing insights into cognitive processes and neurological disorders.
6. Thresholds and Activation Functions:
Each neuron within a neural pool has a threshold—a minimum level of excitation required to trigger an action potential (a neuronal "firing"). This threshold determines whether a neuron contributes to the pool's overall output. Moreover, the way a neuron responds to the sum of its input signals is governed by its activation function. This function determines the relationship between the total synaptic input and the neuron's output firing rate.
Nonlinearity of activation functions: Activation functions are typically nonlinear, meaning the output is not simply proportional to the input. This nonlinearity is crucial for the computational power of neural pools, allowing them to process complex patterns and perform sophisticated computations that linear systems cannot.
7. Plasticity and Learning:
As mentioned earlier, neural pools are not static structures; they exhibit plasticity, adapting their properties in response to experience. This plasticity is the basis of learning and memory. Changes in synaptic weights, neuronal thresholds, and even the structure of the pool itself can occur over time, altering the pool's response to future stimuli.
Long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD): Mechanisms like long-term potentiation (strengthening synapses) and long-term depression (weakening synapses) are key players in synaptic plasticity. These mechanisms allow neural pools to refine their processing capabilities, adapting to new information and strengthening relevant connections.
8. Spatial and Temporal Integration:
Neural pools integrate information both spatially and temporally. Spatial integration refers to the summation of signals from multiple neurons at the same time. Temporal integration refers to the summation of signals from a single neuron or multiple neurons over time. This integration enables the pool to respond to complex patterns of activity, both spatially distributed and occurring over time.
The importance of integration: The ability to integrate information spatially and temporally is critical for the extraction of meaningful information from noisy or ambiguous sensory inputs. It enables the pool to filter irrelevant information and focus on significant features.
9. Modular Organization:
In many cases, neural pools are not isolated entities; they are organized into modules, interacting with each other to perform complex tasks. This modular organization allows for the division of labor, with different pools specializing in different aspects of information processing. These modules may then work together in a coordinated manner to achieve a common goal.
Hierarchical processing: Often, neural pools are arranged hierarchically, with simpler pools processing basic features and higher-level pools integrating the processed information to extract more abstract meaning.
10. Feedback Loops:
Neural pools frequently incorporate feedback loops, where the output of the pool influences its own subsequent activity. This feedback can be excitatory, reinforcing the initial activity, or inhibitory, dampening it. Feedback loops play a crucial role in stabilizing activity patterns, generating oscillations, and contributing to rhythmic processes.
Implications and Applications
Understanding these characteristics is vital for various fields:
-
Neuroscience: Researching neural pool dynamics helps us unravel the mysteries of brain function, including learning, memory, perception, and cognitive processes.
-
Neurology: Understanding how neural pools malfunction can shed light on neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease. Targeted therapies may focus on restoring healthy neural pool dynamics.
-
Artificial Intelligence: Artificial neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of biological neural pools. Understanding the properties of biological neural pools informs the design and optimization of artificial networks, leading to more efficient and powerful AI systems.
-
Robotics and Control Systems: The principles of neural pool organization can be applied to design robust and adaptive control systems for robots and other autonomous agents.
Conclusion
Neural pools are remarkably sophisticated information processing units, characterized by their intricate interconnectivity, parallel processing capabilities, dynamic activity patterns, and adaptive plasticity. Understanding these characteristics is key to deciphering the complexities of the nervous system and developing advanced technologies inspired by its remarkable efficiency and adaptability. The diverse roles of neural pools highlight their fundamental importance in numerous biological and computational applications. Further research into the intricacies of neural pool dynamics promises to yield deeper insights into the functioning of the brain and pave the way for innovative technological advancements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Impact Of Technology On Internal Controls Includes
Mar 17, 2025
-
For The Substituted Cyclohexane Compound Shown
Mar 17, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About The Regulation Of Gastric Secretion
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Strategy Teaches Healthier Ways To Use Substances
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Dividend Growth Model Is Applicable To Companies That Pay
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Choose All That Are Characteristics Of Neural Pools. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
