The Impact Of Technology On Internal Controls Includes
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
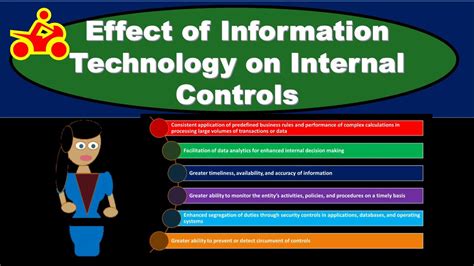
Table of Contents
The Impact of Technology on Internal Controls
The rapid advancement of technology has fundamentally reshaped the business landscape, significantly impacting how organizations manage their internal controls. While technology presents numerous opportunities to strengthen and streamline control processes, it also introduces new complexities and vulnerabilities that need careful consideration. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of technology on internal controls, exploring both the benefits and challenges, and offering strategies for effective implementation and management.
Technology's Enhancing Impact on Internal Controls
Technology offers a powerful arsenal of tools to enhance internal controls, leading to improved efficiency, accuracy, and security. Let's examine some key areas:
1. Automation and Streamlining Processes
Automation is a game-changer. Repetitive tasks prone to human error, such as data entry and reconciliation, can be automated, reducing the risk of mistakes and freeing up human resources for more strategic activities. Automated workflow systems ensure consistent application of policies and procedures, minimizing inconsistencies and improving overall control effectiveness.
- Example: Automated invoice processing systems can verify vendor information, match invoices to purchase orders, and automatically route approvals, minimizing the risk of fraudulent payments or duplicate invoices.
2. Enhanced Data Security and Access Controls
Technology plays a crucial role in securing sensitive data. Robust access control systems using technologies like role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) restrict access to data based on individual roles and responsibilities, minimizing unauthorized access and data breaches. Encryption technologies protect data both in transit and at rest, further enhancing security.
- Example: Cloud-based storage solutions with integrated security features, such as encryption and access logging, offer significantly enhanced data protection compared to traditional file servers.
3. Improved Monitoring and Real-time Visibility
Technology empowers organizations with real-time visibility into their operations. Advanced analytics and data visualization tools enable monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) and identifying potential control weaknesses in real-time. Automated exception reporting highlights deviations from established norms, allowing for prompt corrective action.
- Example: Real-time dashboards displaying financial transactions, inventory levels, and sales data provide immediate insights into operational efficiency and potential risks.
4. Enhanced Fraud Detection and Prevention
Technology plays a vital role in combating fraud. Advanced analytics techniques can identify unusual patterns and anomalies in data that might indicate fraudulent activities. Machine learning algorithms can continuously learn and adapt to new fraud patterns, improving detection accuracy over time.
- Example: Automated systems can flag suspicious transactions, such as unusually large payments or transactions outside normal business hours, alerting relevant personnel for immediate investigation.
5. Strengthened Audit Trails and Compliance
Technology creates detailed audit trails, providing irrefutable evidence of transactions and activities. This improves accountability and simplifies compliance audits. Automated logging and tracking ensure that all actions are documented, facilitating investigation and demonstrating adherence to regulations.
- Example: A system that automatically logs all user actions, including date, time, and changes made, provides a comprehensive audit trail for regulatory compliance and internal investigations.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Technology in Internal Controls
While technology offers substantial benefits, it also presents challenges and risks that organizations must address:
1. Dependence on Technology and System Failures
Over-reliance on technology can create vulnerabilities. System failures, cyberattacks, or power outages can disrupt operations and compromise internal controls. Organizations must have robust disaster recovery and business continuity plans to mitigate these risks.
- Example: A reliance on a single cloud provider without a backup plan could lead to significant disruptions in the event of a service outage.
2. Data Security Breaches and Cyberattacks
Technology increases the attack surface, making organizations more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Data breaches can expose sensitive information, leading to reputational damage, financial losses, and legal liabilities. Organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and employee security awareness training.
- Example: A phishing attack that compromises employee credentials can grant attackers access to sensitive data and systems.
3. Complexity and Cost of Implementation
Implementing and maintaining sophisticated technology solutions can be complex and costly. Organizations need to invest in skilled personnel to manage these systems, requiring substantial upfront and ongoing investments. Proper planning and a phased implementation approach are crucial to minimize disruption and maximize ROI.
- Example: Implementing a new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system requires significant investment in software, hardware, training, and ongoing maintenance.
4. Integration Challenges with Existing Systems
Integrating new technologies with existing systems can be challenging. Data inconsistencies, incompatible formats, and legacy systems can hinder effective implementation and integration. Organizations must carefully assess compatibility before selecting new technologies and develop a comprehensive integration plan.
- Example: Integrating a new CRM system with an existing accounting system may require extensive data mapping and custom development to ensure data consistency and seamless workflow.
5. Maintaining Data Integrity and Accuracy
While technology improves data accuracy, errors can still occur. Data entry errors, system glitches, or malicious manipulation can compromise data integrity. Organizations must implement robust data validation and error-checking mechanisms to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
- Example: Implementing data validation rules to prevent the entry of invalid data, such as negative inventory quantities or impossible transaction dates.
Strategies for Effective Implementation and Management
To effectively leverage technology for internal control, organizations must adopt a strategic approach:
1. Risk Assessment and Prioritization
Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify key vulnerabilities and prioritize technology investments based on their impact on mitigating those risks. Focus on areas with the highest potential for loss or damage.
2. Comprehensive Planning and Implementation
Develop a detailed implementation plan, including timelines, resource allocation, and training schedules. A phased approach, starting with pilot projects, can minimize disruption and allow for adjustments based on initial results.
3. Robust Security Measures
Implement comprehensive security measures to protect against cyberattacks and data breaches. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, access controls, encryption, regular security audits, and employee security awareness training.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of technology-based internal controls. Regular audits and performance reviews should be conducted to identify areas for improvement and ensure that controls remain effective. Regular updates and patches are crucial for maintaining system security.
5. Staff Training and Development
Invest in training and development programs for employees to ensure they possess the necessary skills to effectively use and manage technology-based internal controls. Regular training updates are essential to keep pace with evolving technologies and threats.
6. Choosing the Right Technology
Selecting the appropriate technology is crucial. Consider factors such as scalability, integration capabilities, security features, and user-friendliness. Consult with IT professionals and internal control experts to ensure the chosen technology aligns with organizational needs and objectives.
Conclusion
Technology has profoundly impacted internal controls, offering significant opportunities to enhance efficiency, security, and accuracy. However, organizations must carefully manage the risks associated with technology adoption. By implementing a strategic approach that prioritizes risk assessment, comprehensive planning, robust security measures, continuous monitoring, and staff training, organizations can leverage technology to strengthen internal controls and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. The ongoing evolution of technology demands a proactive and adaptable approach to ensure internal controls remain effective and aligned with the changing business landscape. This requires a commitment to continuous learning, investment in skilled personnel, and a culture that values strong internal control practices. Only then can organizations fully realize the benefits of technology while mitigating the inherent risks.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Fixed Position Production Layout Would Be Particularly Recommended If
Mar 17, 2025
-
When Direct Labor Costs Are Recorded
Mar 17, 2025
-
In Prompt Engineering Why It Is Important To Specify
Mar 17, 2025
-
Identify The Function Represented By The Following Power Series
Mar 17, 2025
-
Predict The Product For The Reaction Shown
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Impact Of Technology On Internal Controls Includes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
