For The Substituted Cyclohexane Compound Shown
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
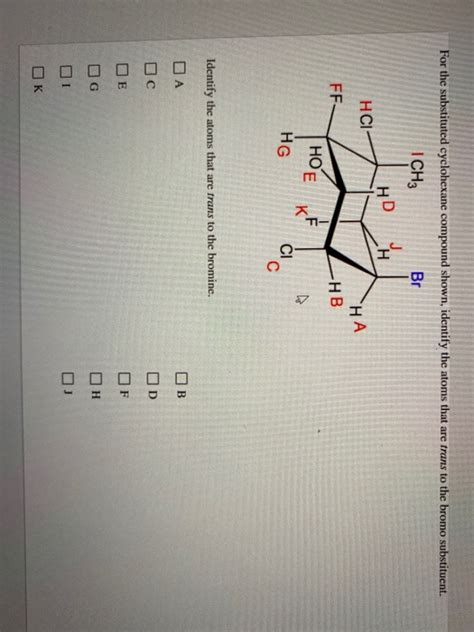
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into Substituted Cyclohexane Compounds: Conformational Analysis and Reactivity
Substituted cyclohexane compounds represent a cornerstone of organic chemistry, exhibiting fascinating conformational behavior and diverse reactivity. Understanding their properties is crucial for predicting their behavior in various chemical reactions and biological processes. This in-depth article will explore the nuances of substituted cyclohexane compounds, focusing on their conformational analysis, factors influencing stability, and reactivity patterns.
Understanding Cyclohexane's Chair Conformation
Before delving into substituted cyclohexanes, let's briefly revisit the fundamental characteristics of cyclohexane itself. Cyclohexane, a six-membered saturated ring, primarily exists in a chair conformation, which minimizes steric strain. This chair conformation features two distinct types of hydrogen atoms: axial and equatorial. Axial hydrogens are oriented perpendicular to the plane of the ring, while equatorial hydrogens lie roughly in the plane of the ring. These positions significantly influence the properties of substituted cyclohexanes.
The Impact of Substituents on Cyclohexane Conformation
The introduction of substituents to the cyclohexane ring dramatically alters its conformational preferences. The substituent's size and electronic properties play crucial roles in determining which chair conformation – with the substituent in the axial or equatorial position – is more stable.
Steric Effects: The Bulky Substituent Rule
Larger substituents prefer the equatorial position. This is primarily due to 1,3-diaxial interactions. When a bulky substituent occupies an axial position, it experiences steric clashes with the axial hydrogens on carbons three positions away. These unfavorable interactions destabilize the molecule. By adopting the equatorial position, the substituent minimizes these repulsive forces, leading to increased stability.
Example: Consider tert-butylcyclohexane. The bulky tert-butyl group overwhelmingly favors the equatorial position to avoid severe 1,3-diaxial interactions. The energy difference between the equatorial and axial conformations is substantial, making the equatorial conformer significantly more prevalent.
Electronic Effects: Ancillary Influence on Conformational Preference
While steric effects are dominant, electronic effects can also influence conformational preferences, particularly in cases with smaller substituents. For instance, certain polar substituents might exhibit a slight preference for an axial position due to favorable dipole-dipole interactions or hydrogen bonding with other parts of the molecule or solvent. However, these effects are often less pronounced than steric effects.
Analyzing Conformational Equilibria: The A-Value
The equilibrium between axial and equatorial conformers can be quantified using the A-value. The A-value is the difference in Gibbs free energy (ΔG°) between the axial and equatorial conformers. A larger A-value indicates a stronger preference for the equatorial conformation. The A-value is empirically determined and varies depending on the substituent.
Predicting Conformational Preferences: A Practical Guide
To predict the predominant conformation of a substituted cyclohexane, follow these steps:
- Identify the substituents: Determine the size and electronic nature of each substituent.
- Prioritize steric effects: Bulky substituents will overwhelmingly prefer the equatorial position.
- Consider electronic effects (if applicable): If the substituents are relatively small, subtle electronic effects might play a role.
- Draw both chair conformations: Depict both chair conformers with the substituents in axial and equatorial positions.
- Assess 1,3-diaxial interactions: Identify and evaluate the steric clashes in each conformer.
- Determine the more stable conformer: The conformer with minimized steric interactions is the more stable one.
Reactivity of Substituted Cyclohexanes: A Complex Landscape
The reactivity of substituted cyclohexanes is significantly influenced by the conformation of the molecule. The accessibility of the substituent plays a crucial role in determining the reaction pathway and the stereochemistry of the products.
Reactions Influenced by Conformational Factors
Many reactions, such as electrophilic substitutions, nucleophilic substitutions, and eliminations, exhibit a marked preference for the equatorial or axial approach, depending on the specific reaction mechanism and the steric hindrance around the reactive center.
Example: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2) on a substituted cyclohexane, the nucleophile preferentially attacks from the less hindered side, generally the side opposite to bulky equatorial substituents.
Stereochemistry and Conformational Analysis
Understanding the relationship between conformation and stereochemistry is critical in predicting the outcome of reactions. The stereochemistry of the product is often dictated by the conformation of the reactant. For example, the axial or equatorial orientation of a leaving group can determine the stereochemical outcome of an elimination reaction.
Analyzing Complex Systems: Multiple Substituents
When multiple substituents are present, predicting conformational preferences becomes more complex. The principle of minimizing overall steric interactions remains paramount. However, the interplay of multiple substituents requires careful consideration of all possible 1,3-diaxial interactions. In such cases, conformational analysis might require more sophisticated techniques like molecular modeling or NMR spectroscopy.
Advanced Techniques in Conformational Analysis
Several advanced techniques aid in the detailed study of substituted cyclohexane conformations:
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: NMR provides valuable information about the relative populations of different conformers. The chemical shifts and coupling constants of protons in axial and equatorial positions can reveal conformational preferences.
- X-ray crystallography: X-ray crystallography can determine the precise three-dimensional structure of a molecule in the solid state, providing direct evidence of its conformation.
- Computational methods: Molecular mechanics and density functional theory (DFT) calculations can predict conformational energies and equilibrium populations.
Applications of Substituted Cyclohexanes
Substituted cyclohexanes are ubiquitous in organic chemistry and beyond:
- Pharmaceuticals: Many drugs contain substituted cyclohexane rings as core structures, often influencing their biological activity and pharmacokinetic properties.
- Natural products: Many naturally occurring compounds incorporate cyclohexane rings with various substituents.
- Polymers: Substituted cyclohexanes are utilized as monomers in the synthesis of certain polymers.
- Industrial chemicals: Many industrial chemicals and intermediates contain substituted cyclohexane rings.
Conclusion: Bridging Theory and Application
The study of substituted cyclohexane compounds serves as a powerful example of the interplay between theory and application in organic chemistry. A thorough understanding of their conformational behavior and reactivity is essential for predicting their properties and designing reactions to produce specific products with controlled stereochemistry. The techniques described above provide powerful tools for investigating these fascinating molecules, opening doors to innovative applications in diverse fields. Continuous research in this area promises further breakthroughs in understanding and utilizing these fundamental organic building blocks. This knowledge is essential for researchers working across various disciplines, including medicinal chemistry, materials science, and polymer chemistry. The interplay between steric and electronic factors, often subtle, significantly impact the stability and behavior of substituted cyclohexane derivatives. Mastering the principles outlined in this article allows one to predict and manipulate the properties of these compounds effectively, opening new possibilities for designing innovative molecules with desired characteristics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Guest Is Not Showing Signs Of Intoxication
Mar 17, 2025
-
C A Mo Deben Almacenarse La Basura Y Los Art A Culos Reciclables
Mar 17, 2025
-
Predict The Major Product For The Reaction
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Type Of Research Source Provides The Best Firsthand Information
Mar 17, 2025
-
Vitamin D Is Unique Among The Vitamins Because
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about For The Substituted Cyclohexane Compound Shown . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
