Which Of The Following Events Would Increase Producer Surplus
Holbox
Mar 31, 2025 · 7 min read
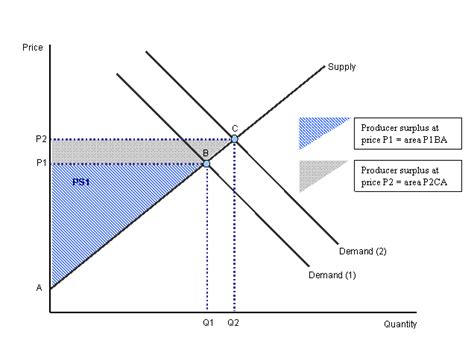
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Events Would Increase Producer Surplus
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following Events Would Increase Producer Surplus?
- Key Factors Affecting Producer Surplus
- Events That Increase Producer Surplus
- 1. Increase in Market Demand
- 2. Technological Advancements
- 3. Decrease in Input Prices
- 4. Favorable Government Policies
- 5. Reduction in Competition
- 6. Improved Infrastructure
- 7. Increased Productivity
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following Events Would Increase Producer Surplus?
Producer surplus, a fundamental concept in economics, represents the difference between the market price a producer receives for a good or service and the minimum price they are willing to accept. Understanding what factors influence producer surplus is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and economists alike. This article delves into the various events that can lead to an increase in producer surplus, providing detailed explanations and real-world examples.
Key Factors Affecting Producer Surplus
Before exploring specific events, let's establish the key factors that directly impact producer surplus. These factors are interconnected and often influence each other:
-
Market Price: A higher market price directly increases producer surplus. This is because producers receive more revenue for each unit sold, while their costs remain relatively constant (at least in the short run).
-
Production Costs: A decrease in production costs, such as lower input prices (raw materials, labor, energy), improved technology, or increased efficiency, leads to higher profits at any given market price, thereby increasing producer surplus.
-
Supply: Changes in supply, influenced by factors like technology advancements, government policies, or input price changes, affect the market price and consequently, producer surplus. A decrease in supply generally leads to higher prices, and an increase in supply typically leads to lower prices.
-
Demand: While not directly affecting production costs, changes in demand heavily influence the market price. Increased demand typically leads to higher prices and increased producer surplus, while decreased demand has the opposite effect.
Events That Increase Producer Surplus
Now, let's examine specific events that can demonstrably increase producer surplus:
1. Increase in Market Demand
An increase in market demand, driven by factors like changing consumer preferences, increased consumer income, or the introduction of complementary goods, leads to a higher equilibrium price and a higher quantity traded. This directly translates into a larger area representing producer surplus on a supply and demand graph.
Example: Imagine a sudden surge in demand for organic coffee beans due to a growing health-conscious population. This increased demand forces up the price of organic coffee beans. Coffee bean farmers, who were previously willing to sell at a lower price, now receive a significantly higher price for their product, resulting in a substantial increase in producer surplus.
Further Analysis: The increase in producer surplus is not just a matter of higher prices for existing beans. It also incentivizes farmers to increase production, leading to a larger overall quantity sold, further boosting surplus. This effect is particularly pronounced if the increased demand is persistent and signals a long-term shift in consumer preference.
2. Technological Advancements
Technological breakthroughs significantly reduce production costs and increase efficiency. This allows producers to supply more goods at a lower cost, even at the same market price. The lower costs directly increase profit margins, leading to a higher producer surplus.
Example: The advent of automation in manufacturing has drastically reduced production costs for many goods. Factories now use robots and sophisticated software to produce goods with fewer workers and lower energy consumption. This reduction in input costs, such as labor and energy, allows manufacturers to sell their goods at a lower price while still increasing their profit margin and producer surplus.
Further Analysis: Technological advancements not only reduce costs but can also improve product quality, leading to even higher market prices and a further increase in producer surplus. This virtuous cycle of technological advancement, cost reduction, and increased market value is a cornerstone of economic growth.
3. Decrease in Input Prices
Input prices – the costs of raw materials, labor, and energy – play a critical role in determining production costs. A decrease in any of these input prices will directly lower the cost of production and therefore increase profit margins, leading to a larger producer surplus.
Example: A significant drop in the price of crude oil would substantially reduce the production costs for various industries, including transportation, manufacturing, and plastics. Companies in these sectors would experience higher profit margins at the existing market prices, leading to an increase in producer surplus.
Further Analysis: The impact of decreased input prices is often felt across multiple industries. Lower energy prices, for example, don't just benefit energy-intensive industries directly; they also indirectly lower costs for businesses that rely on transportation and logistics. This ripple effect amplifies the positive impact on overall producer surplus across the economy.
4. Favorable Government Policies
Governments can influence producer surplus through various policies, including subsidies, tax breaks, and deregulation. Subsidies directly reduce production costs, while tax breaks decrease the tax burden on businesses. Deregulation reduces bureaucratic hurdles, leading to increased efficiency and lower administrative costs.
Example: A government subsidy to farmers producing organic produce would lower their production costs, allowing them to sell their products at a more competitive price while maintaining profitability. This would result in a larger producer surplus for organic farmers.
Further Analysis: The effectiveness of government policies in increasing producer surplus depends heavily on their design and implementation. Poorly designed policies can create unintended consequences, such as distorting markets or creating inefficiencies. Well-targeted policies, however, can significantly benefit specific industries and the overall economy.
5. Reduction in Competition
While competition is generally beneficial for consumers, a reduction in competition, such as through mergers or acquisitions, can potentially lead to higher prices and increased producer surplus for the remaining firms. This is because reduced competition allows firms to exercise more market power, leading to higher prices and larger profit margins.
Example: The merger of two major airline companies could result in less competition on specific routes, leading to higher airfares. The resulting higher prices would increase the producer surplus for the merged airline, even if it doesn't necessarily translate to better service or lower operational costs.
Further Analysis: It's crucial to note that while a reduction in competition may increase producer surplus for the surviving firms, it often comes at the expense of consumer surplus. This raises important questions about the trade-off between producer surplus and consumer welfare, which policymakers must carefully consider. Excessive concentration of market power is often subject to antitrust regulations.
6. Improved Infrastructure
Improved infrastructure, such as better roads, railways, ports, and communication networks, can significantly reduce transportation and communication costs for businesses. This reduction in operational costs directly contributes to higher profit margins and increased producer surplus.
Example: The construction of a new highway connecting a manufacturing hub to a major port would reduce transportation costs for manufacturers exporting their goods. This lower cost of logistics would increase their profit margin and producer surplus.
Further Analysis: Infrastructure improvements not only benefit businesses directly involved in transportation but also indirectly benefit other businesses that rely on efficient transportation networks. The ripple effect of improved infrastructure on productivity and overall economic efficiency is substantial.
7. Increased Productivity
Increased worker productivity leads to lower unit costs of production. This can stem from various factors, such as improved training, better management practices, and investment in human capital. Higher productivity translates directly to higher profit margins and a greater producer surplus.
Example: A company implementing a new training program for its employees that leads to improved efficiency and higher output per worker would see its unit production costs decrease, thus increasing its profit margin and producer surplus.
Further Analysis: Investments in human capital, such as employee training and education, are long-term strategies that pay off in the form of increased productivity and higher producer surplus. These investments are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Conclusion
Producer surplus is a dynamic measure that reflects the profitability of businesses within a given market. Several factors and events can contribute to its increase, including increased demand, technological advancements, lower input prices, favorable government policies, reduced competition, improved infrastructure, and increased productivity. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses to strategize for profit maximization and for policymakers to implement policies that promote economic growth and welfare. While increasing producer surplus is a desirable outcome, it's essential to consider the broader economic context, including consumer surplus and overall market efficiency, to ensure sustainable and equitable growth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Identify The Type Of Surface Represented By The Given Equation
Apr 04, 2025
-
Industrial Equipment Is An Example Of A
Apr 04, 2025
-
Unit 2 Algebraic Expressions Answer Key
Apr 04, 2025
-
6 10 6 Handling Multiple Exceptions Vending Machine Example
Apr 04, 2025
-
Select The Most Acidic Type Of Hydrogen In This Molecule
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Events Would Increase Producer Surplus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
