Which Food Item Is Being Stored Safely
Holbox
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
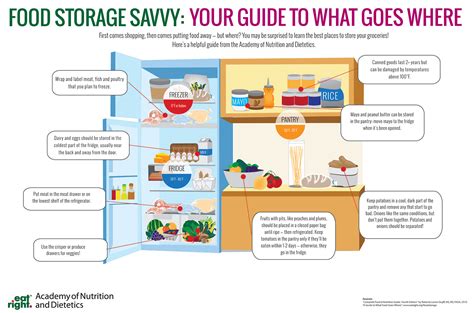
Table of Contents
- Which Food Item Is Being Stored Safely
- Table of Contents
- Which Food Item Is Being Stored Safely? A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Food Storage
- Understanding Food Spoilage and Contamination
- Bacterial Growth: The Major Culprit
- Mold and Yeast: Spoilage Agents
- Cross-Contamination: A Silent Threat
- Safe Food Storage Techniques: A Room-by-Room Guide
- The Refrigerator: The Heart of Safe Food Storage
- Freezer: Long-Term Preservation
- Pantry: The Dry Goods Haven
- Food-Specific Storage Guidelines: Which Food Item Is Being Stored Safely?
- Meats: Handling with Care
- Poultry: Similar to Meats, But with Added Precautions
- Fish and Seafood: Perishable Delights
- Dairy Products: Temperature Sensitive
- Fruits and Vegetables: A Balancing Act
- Eggs: A Delicate Matter
- Bread: Keeping it Fresh
- Identifying Signs of Spoilage
- Conclusion: Prioritize Food Safety
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Food Item Is Being Stored Safely? A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Food Storage
Food safety is paramount. Improper food storage can lead to foodborne illnesses, spoilage, and significant waste. Understanding the best practices for storing different food items is crucial for maintaining a healthy and efficient kitchen. This comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of safe food storage, helping you identify which food items are being stored correctly and what adjustments you might need to make.
Understanding Food Spoilage and Contamination
Before diving into specific food items, let's understand the primary causes of food spoilage and contamination.
Bacterial Growth: The Major Culprit
Bacteria are microscopic organisms that thrive in specific conditions: temperature, moisture, and time. The "danger zone" for bacterial growth is generally considered to be between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C). Keeping food outside this range significantly inhibits bacterial multiplication.
Mold and Yeast: Spoilage Agents
Molds and yeasts are also microorganisms that contribute to food spoilage. They often appear as fuzzy growths on surfaces or cause changes in texture and smell. While some molds are harmless, others can produce toxins harmful to humans.
Cross-Contamination: A Silent Threat
Cross-contamination occurs when harmful bacteria or microorganisms transfer from one food item to another. This commonly happens through improper handwashing, using contaminated utensils, or storing raw and cooked foods together.
Safe Food Storage Techniques: A Room-by-Room Guide
Safe food storage isn't just about placing food in the refrigerator; it's about a holistic approach encompassing various aspects of your kitchen and storage areas.
The Refrigerator: The Heart of Safe Food Storage
The refrigerator is your primary weapon against bacterial growth. However, even within the refrigerator, certain techniques are critical:
- Temperature Control: Ensure your refrigerator maintains a consistent temperature of 40°F (4°C) or below. Use a thermometer to verify.
- Proper Placement: Avoid overcrowding. Allow for proper air circulation to maintain consistent temperature throughout.
- First In, First Out (FIFO): Rotate your food items, placing older items in front and newer ones behind. This minimizes the risk of spoilage.
- Food Packaging: Store food in airtight containers or wrap them securely with plastic wrap or aluminum foil to prevent moisture loss and cross-contamination.
Freezer: Long-Term Preservation
The freezer offers long-term food preservation. However, proper freezing and storage techniques are key:
- Freezing Temperature: Maintain a freezer temperature of 0°F (-18°C) or below.
- Freezing Methods: Freeze food quickly to maintain quality. Portion food into smaller containers for easier thawing.
- Labeling and Dating: Clearly label and date all frozen items to prevent accidental long-term storage.
- Thawing Safely: Thaw food safely in the refrigerator, under cold running water, or in the microwave using the defrost setting. Never thaw at room temperature.
Pantry: The Dry Goods Haven
Your pantry should be cool, dry, and dark. Proper storage in the pantry prevents insect infestations and spoilage.
- Airtight Containers: Store dry goods like flour, sugar, and grains in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and insect infestation.
- Rotation: Follow the FIFO method in your pantry as well.
- Pest Control: Regularly inspect your pantry for signs of insects.
Food-Specific Storage Guidelines: Which Food Item Is Being Stored Safely?
Let's examine specific food items and their ideal storage methods:
Meats: Handling with Care
- Raw Meats: Store raw meats on the bottom shelf of your refrigerator to prevent dripping onto other foods. Use airtight containers or wrap them securely. Consume raw meats within a few days.
- Cooked Meats: Store cooked meats in airtight containers in the refrigerator for up to 3-4 days.
- Frozen Meats: Freeze meats promptly after purchasing. Frozen meats can be stored for several months, depending on the type of meat.
Poultry: Similar to Meats, But with Added Precautions
Poultry requires even more careful handling than red meat.
- Raw Poultry: Store raw poultry on the bottom shelf of your refrigerator, well-separated from other foods.
- Cooked Poultry: Store cooked poultry in airtight containers in the refrigerator for up to 3-4 days. Leftover poultry should be refrigerated as quickly as possible.
- Frozen Poultry: Freeze poultry promptly after purchasing. Frozen poultry can be stored for several months, depending on the type of poultry.
Fish and Seafood: Perishable Delights
Fish and seafood are highly perishable and require immediate refrigeration or freezing.
- Fresh Fish: Store fresh fish in the refrigerator in an airtight container or sealed bag. Consume within 1-2 days.
- Cooked Fish: Store cooked fish in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 3-4 days.
- Frozen Fish: Freeze fish promptly after purchasing. Frozen fish can be stored for several months, depending on the type of fish.
Dairy Products: Temperature Sensitive
Dairy products are highly susceptible to bacterial growth and require proper refrigeration.
- Milk: Store milk in the refrigerator in its original container. Use by the expiration date.
- Cheese: Store different types of cheese according to their specific requirements. Hard cheeses can be stored at room temperature for short periods; soft cheeses require refrigeration.
- Yogurt: Store yogurt in the refrigerator in its original container.
Fruits and Vegetables: A Balancing Act
Fruits and vegetables vary widely in their storage requirements.
- Fruits: Some fruits like bananas and berries are best kept at room temperature; others, like apples and pears, should be refrigerated.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens should be stored in airtight containers or plastic bags in the refrigerator crisper drawer. Root vegetables can be stored in a cool, dark place.
Eggs: A Delicate Matter
Eggs are best stored in their original carton in the refrigerator. Avoid washing eggs before storing, as this can remove the natural protective coating.
Bread: Keeping it Fresh
Bread can be stored at room temperature in an airtight container or breadbox for several days. Freezing bread is also an excellent option for long-term storage.
Identifying Signs of Spoilage
Knowing when food has spoiled is essential. Look out for these common signs:
- Unpleasant Odor: A sour, foul, or unusual smell is a clear indication of spoilage.
- Changes in Texture: Slimy, mushy, or unusually hard textures often signal spoilage.
- Molds or Fungi: Visible molds or fungi indicate that the food is no longer safe to eat.
- Off-Colors: Discoloration or unusual color changes can indicate spoilage.
Conclusion: Prioritize Food Safety
Safe food storage is not just a matter of convenience; it’s a critical aspect of maintaining good health and minimizing food waste. By understanding the principles of food safety and implementing these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses, preserving the quality and safety of your food for longer. Remember to always prioritize safety and err on the side of caution when dealing with potentially spoiled food. Regularly check your refrigerator, freezer, and pantry to ensure that all your food items are being stored correctly and safely.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Where Would You Click To Begin To Fix It
Mar 24, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Eye
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Food Worker Needs To Thaw A Frozen Pizza
Mar 24, 2025
-
Conversion Of 2 Methyl 2 Butene Into A Secondary Alkyl Halide
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Food Item Is Being Stored Safely . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
