Which Description Most Accurately Summarizes The Yield Curves Shown
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
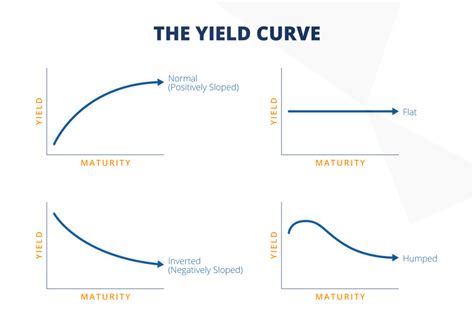
Table of Contents
Decoding Yield Curves: Which Description Best Summarizes the Shown Trends?
Understanding yield curves is crucial for investors, economists, and anyone interested in the financial markets. A yield curve graphically represents the relationship between the yield (or interest rate) and the time to maturity of a debt instrument, usually government bonds, of the same credit quality. Its shape reveals valuable insights into market sentiment, economic expectations, and potential future economic activity. This article delves deep into interpreting various yield curve shapes, examining which description best summarizes different scenarios. We'll explore several examples, analyzing their implications and highlighting the nuances involved in accurate interpretation.
Understanding the Basics of Yield Curves
Before we dive into specific examples, let's establish a firm grasp on the fundamental concepts. A yield curve typically plots the yields of bonds with identical credit quality but differing maturities. The most common type is the Treasury yield curve, which uses U.S. Treasury securities.
There are three primary shapes:
-
Normal Yield Curve (Upward Sloping): This is the most common shape, where longer-term bonds offer higher yields than shorter-term bonds. This typically reflects investor expectations of higher future interest rates and a healthy, expanding economy.
-
Inverted Yield Curve (Downward Sloping): This occurs when short-term yields exceed long-term yields. This is often considered a recessionary predictor, suggesting investors anticipate future interest rate cuts.
-
Flat Yield Curve: This shape shows little difference between short-term and long-term yields. It's often seen as a transition phase, potentially leading to either a normal or inverted curve.
Analyzing Different Yield Curve Scenarios and Their Descriptions
Let's now examine various yield curve scenarios and determine the most accurate summarizing descriptions. We'll use hypothetical examples for illustrative purposes.
Scenario 1: A Steeply Upward Sloping Yield Curve
Yield Curve Data (Hypothetical):
- 3-Month Treasury Bill: 2%
- 2-Year Treasury Note: 4%
- 5-Year Treasury Note: 6%
- 10-Year Treasury Note: 7%
- 30-Year Treasury Bond: 8%
Possible Descriptions:
A. "Mildly expansionary economic outlook." This is inaccurate; the steep slope suggests a more robust expansion.
B. "Strong economic growth expectations and anticipated inflation." This is a more accurate description. The steep slope reflects market expectations of significant future interest rate hikes by the central bank, likely in response to robust economic growth and rising inflation.
C. "Uncertainty in the financial markets." This is less likely given the clear upward trend. Uncertainty usually leads to flatter or more volatile curves.
Most Accurate Description: B. The significant yield spread between short-term and long-term bonds strongly points towards an expectation of substantial economic growth and inflation.
Scenario 2: A Flat Yield Curve
Yield Curve Data (Hypothetical):
- 3-Month Treasury Bill: 3%
- 2-Year Treasury Note: 3.1%
- 5-Year Treasury Note: 3.2%
- 10-Year Treasury Note: 3.3%
- 30-Year Treasury Bond: 3.4%
Possible Descriptions:
A. "Impending economic recession." While a flat curve can precede a recession, it's not definitive.
B. "Economic stagnation and uncertainty about future interest rates." This is a better description. The minimal difference in yields indicates limited confidence in future economic growth and uncertainty about the direction of interest rates.
C. "Transitional period before a potential shift to either a normal or inverted curve." This is a highly probable interpretation. A flat curve often represents a temporary state before the market signals a clearer direction.
Most Accurate Description: C. While B provides some insights, C is more comprehensive. The flat curve signifies a pause or uncertainty, potentially paving the way for an upward or downward trend.
Scenario 3: A Slightly Inverted Yield Curve
Yield Curve Data (Hypothetical):
- 3-Month Treasury Bill: 4%
- 2-Year Treasury Note: 3.9%
- 5-Year Treasury Note: 3.7%
- 10-Year Treasury Note: 3.5%
- 30-Year Treasury Bond: 3.3%
Possible Descriptions:
A. "Robust economic growth with stable inflation." This is entirely inaccurate; an inverted curve signals the opposite.
B. "Weak economic outlook and expectations of future interest rate cuts." This is largely correct. An inverted yield curve is often viewed as a warning sign of an impending economic slowdown. Investors expect future interest rate cuts by the central bank to stimulate the economy.
C. "Market anomaly with limited predictive power." While short-term inversions can be temporary, a sustained inversion is a significant indicator.
Most Accurate Description: B. The slight inversion strongly indicates a pessimistic outlook on the economy, with investors anticipating lower interest rates in the future.
Scenario 4: A Humped Yield Curve
A humped yield curve is less common than normal, inverted, or flat curves. It features a peak in intermediate-term yields, with yields declining at both the short and long ends of the maturity spectrum. This can occur due to various factors, including specific market events or regulatory changes.
Yield Curve Data (Hypothetical):
- 3-Month Treasury Bill: 2.5%
- 2-Year Treasury Note: 4%
- 5-Year Treasury Note: 4.5%
- 10-Year Treasury Note: 4%
- 30-Year Treasury Bond: 3.5%
Possible Descriptions:
A. "Imminent economic recession." While a humped curve can sometimes be associated with future economic weakness, it's not a direct indicator of an imminent recession.
B. "Complex interplay of market forces and potentially temporary phenomenon." This is a more accurate description. Humped curves are often caused by a confluence of factors, and their implications aren't always straightforward.
C. "Significant uncertainty and liquidity issues in the market." This could contribute, but a more encompassing explanation is needed.
Most Accurate Description: B. The humped shape signals that the interpretation requires a more nuanced understanding, considering the specific economic conditions and market dynamics.
Factors Influencing Yield Curve Shapes
Numerous factors impact the shape of the yield curve, including:
-
Inflation Expectations: Higher inflation expectations generally lead to higher yields across the curve.
-
Economic Growth: Strong economic growth usually results in an upward-sloping curve.
-
Monetary Policy: Central bank actions, particularly interest rate changes, significantly influence yield curve movements.
-
Risk Premiums: Investors demand higher yields for longer-term bonds to compensate for increased risk.
-
Market Sentiment: Investor confidence and risk aversion levels play a role in shaping yield curves.
Limitations of Yield Curve Analysis
It's crucial to acknowledge limitations:
-
Not a perfect predictor: Yield curves are valuable indicators, but they aren't foolproof predictors of economic events.
-
Influence of other factors: Numerous economic and market factors beyond the yield curve impact economic performance.
-
Timing and duration of inversions: The length and depth of an inversion are important considerations.
Conclusion
Accurately summarizing yield curve shapes requires careful consideration of various factors. While a steeply upward sloping curve often signals strong economic growth, a flat or inverted curve often suggests a weaker outlook. However, understanding the nuances and limitations of yield curve analysis is critical for accurate interpretation and informed decision-making. The most appropriate description will always depend on the specific data and broader economic context. Remember, analyzing yield curves should be part of a broader economic analysis rather than a standalone predictor. Using diverse economic indicators, analyzing market news, and evaluating political and geopolitical factors all enhance the interpretation of yield curves and improve the accuracy of forecasts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
An Increase In Nominal Gdp Will
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Distinguishes Snap From Programs Like Medicare Or Social Security
Mar 18, 2025
-
State Whether The Following Statements Are True Or False
Mar 18, 2025
-
Experiment 10 Report Sheet Vinegar Analysis
Mar 18, 2025
-
At Kairas Caribbean Cuisine Kaira Improves Focuses On Efficiency By
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Description Most Accurately Summarizes The Yield Curves Shown . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
