When The Fed Buys Bonds The Supply Of Money
Holbox
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
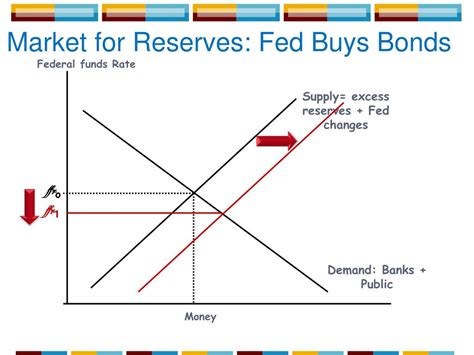
Table of Contents
When the Fed Buys Bonds: The Impact on the Money Supply
The Federal Reserve (Fed), the central bank of the United States, plays a crucial role in managing the nation's money supply and influencing economic activity. One of its primary tools is open market operations, which involve the buying and selling of government bonds. When the Fed buys bonds, it significantly impacts the money supply, leading to a range of economic consequences. This article will delve into the mechanics of this process, exploring the intricacies of how bond purchases increase the money supply, examining the effects on interest rates, inflation, and overall economic growth, and finally addressing potential limitations and unintended consequences.
Understanding Open Market Operations: The Fed's Key Tool
Open market operations are the Fed's primary means of implementing monetary policy. They involve the buying and selling of U.S. Treasury securities (bonds) and agency mortgage-backed securities in the open market. These transactions are conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York's trading desk. The goal is to influence the federal funds rate – the target rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans.
When the Fed buys bonds: It injects money into the banking system. Think of it this way: the Fed buys a bond from a commercial bank, paying for it with newly created money. This newly created money increases the bank's reserves, enabling them to lend more money, thus increasing the overall money supply.
When the Fed sells bonds: It withdraws money from the banking system. Banks must use their reserves to purchase the bonds, reducing their lending capacity and consequently contracting the money supply.
The Mechanics of Bond Purchases and Money Supply Expansion
The process of money supply expansion through bond purchases is more complex than simply injecting cash. Let's break it down step-by-step:
-
The Transaction: The Fed buys a government bond from a commercial bank or other financial institution.
-
Increased Bank Reserves: The Fed pays for the bond by crediting the seller's reserve account at the Fed. This increases the bank's reserves – the amount of money it holds in its account at the central bank.
-
Increased Lending Capacity: With higher reserves, the bank now has more money available to lend. This increased lending capacity is the key to expanding the money supply.
-
The Money Multiplier Effect: The impact of the initial bond purchase isn't limited to the initial increase in reserves. Banks lend out a portion of their increased reserves, creating new deposits in the process. These new deposits become reserves for other banks, leading to further lending and deposit creation. This is known as the money multiplier effect. The size of the multiplier depends on the reserve requirement – the percentage of deposits that banks are legally required to hold in reserve. A lower reserve requirement leads to a larger multiplier effect.
-
Expansion of the Money Supply: The combined effect of increased lending and the money multiplier is a significant expansion of the overall money supply (M1 and M2). M1 includes currency in circulation and demand deposits, while M2 also incorporates savings deposits, money market accounts, and small-time deposits.
The Impact on Interest Rates
When the Fed buys bonds, it increases the demand for bonds, pushing their prices up. Since bond prices and yields (interest rates) have an inverse relationship, an increase in bond prices leads to a decrease in interest rates. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers, potentially stimulating investment and spending. This is a crucial part of expansionary monetary policy, aiming to boost economic growth. The lower interest rates also make it less expensive for the government to borrow money.
The Impact on Inflation
Increased money supply, a consequence of the Fed buying bonds, can lead to inflation. When there's more money chasing the same amount of goods and services, the prices of those goods and services tend to rise. This is a fundamental principle of economics. However, the relationship isn't always direct or immediate. The impact of bond purchases on inflation depends on several factors, including the overall state of the economy, the velocity of money (how quickly money changes hands), and expectations of future inflation. If the economy is already operating at full capacity, increased money supply is more likely to lead to significant inflation.
The Impact on Economic Growth
The effect of bond purchases on economic growth is multifaceted. Lower interest rates stimulated by bond purchases encourage investment and consumption, potentially leading to higher economic growth. Businesses might invest more in new equipment and expansion, while consumers might borrow more to buy houses or cars. However, this growth can come at a cost. Excessive money supply growth can lead to inflation, which can erode purchasing power and create economic instability. Furthermore, artificially stimulating growth through monetary policy can create asset bubbles, leading to financial instability.
Potential Limitations and Unintended Consequences
While bond purchases can be effective in stimulating the economy, there are limitations and potential unintended consequences:
-
Liquidity Trap: In periods of severe economic downturn, businesses and consumers may be reluctant to borrow even at very low interest rates. This situation, known as a liquidity trap, renders monetary policy less effective.
-
Inflationary Pressures: As mentioned earlier, excessive bond purchases can lead to significant inflation, potentially eroding the purchasing power of consumers and harming long-term economic stability.
-
Asset Bubbles: Low interest rates can inflate asset prices (stocks, real estate), creating asset bubbles that can burst, causing significant economic damage.
-
Global Impact: The Fed's actions affect global financial markets. Bond purchases can influence exchange rates and capital flows, potentially causing unintended consequences in other countries.
-
Ineffectiveness in Addressing Supply-Side Shocks: Monetary policy is primarily focused on demand-side management. It's less effective in addressing supply-side issues, such as disruptions in supply chains or resource scarcity, which can also lead to inflation.
The Importance of Timing and Communication
The effectiveness of open market operations, including bond purchases, depends significantly on the timing and communication of the Fed. The Fed must carefully assess the state of the economy and the potential risks involved before implementing any monetary policy actions. Clear communication with the public about the Fed's intentions and rationale is crucial to manage expectations and prevent market instability. Overly aggressive or poorly timed bond purchases can lead to unpredictable outcomes.
Conclusion: A Delicate Balancing Act
When the Fed buys bonds, it injects money into the economy, leading to an expansion of the money supply. This has significant consequences for interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. While it can be a powerful tool for stimulating economic activity and navigating economic downturns, it's a delicate balancing act. The Fed must carefully consider the potential risks and unintended consequences, including inflation, asset bubbles, and global market impacts. The effectiveness of this policy tool hinges on precise timing, clear communication, and a deep understanding of the complexities of the economy. It's a continuous process of monitoring, adjusting, and adapting to changing economic conditions. The goal is to achieve sustainable economic growth without creating excessive inflation or destabilizing the financial system. It's a constant challenge requiring expertise, judgment, and a long-term perspective.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Responsibility Accounting Performance Report Displays
Mar 21, 2025
-
Both Learned Helplessness And Depression Are Marked By
Mar 21, 2025
-
Histamine Causes All The Following Except
Mar 21, 2025
-
Cash Flow To Stockholders Is Defined As
Mar 21, 2025
-
Final Step To Installing A Floating Vinyl Floor
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When The Fed Buys Bonds The Supply Of Money . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
