When Conducting An Open Market Sale The Fed
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
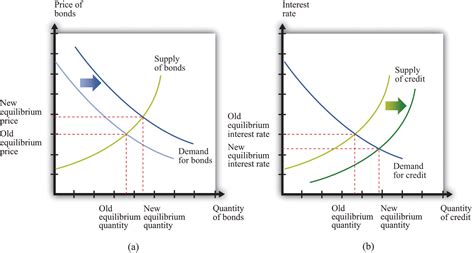
Table of Contents
When the Fed Conducts an Open Market Sale
The Federal Reserve (Fed), the central bank of the United States, plays a crucial role in managing the nation's monetary policy. One of its key tools is open market operations, specifically open market sales. Understanding how and why the Fed conducts these sales is critical to grasping the complexities of monetary policy and its impact on the broader economy. This article delves deep into the mechanics, implications, and overall significance of open market sales undertaken by the Federal Reserve.
What is an Open Market Sale?
An open market sale is a monetary policy tool employed by the Federal Reserve to reduce the money supply within the economy. In essence, the Fed sells U.S. Treasury securities (like bonds) it holds to commercial banks and other financial institutions. These institutions then pay the Fed for these securities, thus transferring funds from the commercial banks’ reserves to the Fed's account. This reduces the amount of reserves commercial banks have available to lend, thereby decreasing the money supply and influencing various economic factors.
The Mechanics of an Open Market Sale
The process is relatively straightforward:
-
The Fed's decision: The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), the Fed's policy-making body, decides to conduct an open market sale based on its assessment of economic conditions. This decision is typically made to combat inflationary pressures or to slow down an overheating economy.
-
The sale itself: The Federal Reserve Bank of New York, acting on behalf of the FOMC, executes the sale by selling Treasury securities through primary dealers—large financial institutions that maintain ongoing relationships with the Fed. These securities can be short-term Treasury bills, intermediate-term notes, or long-term bonds.
-
Payment and reserve reduction: The primary dealers purchase these securities, transferring funds from their reserve accounts at the Federal Reserve to the Fed’s account. This directly reduces the level of reserves held by the commercial banking system.
-
Ripple effect: The reduction in reserves forces banks to curtail lending activities. This decrease in lending ultimately leads to a contraction in the money supply, impacting interest rates, investment, and overall economic activity.
Why Does the Fed Conduct Open Market Sales?
The primary reason for the Fed's implementation of open market sales is to control inflation. When the economy is growing too rapidly, leading to increased demand and potentially rising prices, the Fed might intervene to cool things down. By decreasing the money supply, the Fed aims to:
-
Reduce inflation: Less money circulating in the economy means less demand-pull inflation. Increased interest rates make borrowing more expensive, dampening spending and investment, further contributing to reduced inflationary pressure.
-
Slow economic growth: A decrease in the money supply and higher interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to invest and for consumers to borrow, slowing economic growth. This can help prevent an economic overheating, which could lead to unsustainable levels of inflation.
-
Strengthen the currency: Reduced money supply and increased interest rates can attract foreign investment, leading to an increase in demand for the US dollar and strengthening its value relative to other currencies. However, this also has potential negative impacts on exports as they become more expensive.
The Impact of Open Market Sales on the Economy
The consequences of open market sales extend far beyond just reducing the money supply. The impacts are felt across various economic sectors and indicators:
-
Interest rates: A decrease in the money supply leads to higher interest rates. This is because banks, with fewer reserves, charge more for loans to compensate for the reduced availability of funds. Higher interest rates affect borrowing costs for individuals, businesses, and governments, influencing their spending and investment decisions.
-
Investment and spending: Higher interest rates discourage investment and spending. Businesses postpone capital expenditures, and consumers delay large purchases like houses and cars.
-
Economic growth: The combined effect of reduced investment and spending leads to a slowdown in economic growth. While this might seem negative, it’s often a necessary measure to prevent runaway inflation.
-
Employment: A slower economy can lead to a reduction in job creation or even job losses in some sectors. However, controlled economic slowing can help prevent a more severe economic downturn later.
-
Stock market: Open market sales can impact the stock market. Higher interest rates, reduced investment, and a slowing economy may lead to lower stock prices.
Open Market Sales vs. Other Monetary Policy Tools
The Fed employs several monetary policy tools, and open market sales are just one of them. Other key tools include:
-
Reserve requirements: This refers to the percentage of deposits that banks are required to keep in reserve. Changing this requirement directly impacts the amount of money banks can lend.
-
Discount rate: This is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money directly from the Federal Reserve. Adjusting this rate influences the cost of borrowing for banks.
-
Quantitative easing (QE): This involves the Fed buying long-term government bonds or other securities to increase the money supply and lower long-term interest rates. This is the opposite of an open market sale.
Open market sales are preferred because they are highly flexible and precise. The Fed can adjust the amount and frequency of sales to fine-tune the money supply, making it a more effective tool for managing the economy compared to other less precise interventions.
Open Market Sales and the Current Economic Climate
The impact of open market sales depends heavily on the prevailing economic climate. In times of high inflation, such sales are frequently used to curb price increases. However, if the economy is already weak or facing a recession, aggressive open market sales could exacerbate the downturn. The Fed must carefully balance its actions to avoid triggering a recession while still managing inflation effectively. This requires a complex evaluation of economic data and forecasts, and the constant monitoring of various economic indicators.
Challenges and Criticisms of Open Market Sales
While open market sales are a powerful tool, they are not without challenges and criticisms:
-
Unpredictability: The precise impact of open market sales on the economy is difficult to predict. Various factors can influence the effectiveness of these actions, including consumer confidence, business investment decisions, and global economic conditions. A change in one area can impact the effectiveness of monetary policy significantly.
-
Time lags: The effects of open market sales are not immediate. It often takes time for changes in the money supply and interest rates to impact the broader economy. This lag can make it challenging for the Fed to fine-tune its response to changing economic conditions.
-
Global interconnectedness: The global nature of financial markets means that the impact of the Fed’s actions extends beyond the US borders. Changes in US interest rates can influence capital flows and exchange rates worldwide, potentially impacting other countries' economies.
-
Political pressures: The Fed is an independent institution, but it is not immune to political pressure. Decisions regarding monetary policy can be influenced by political considerations, which may not always align with the best interests of the economy in the long-term.
Conclusion: Open Market Sales – A Vital Tool in the Fed's Arsenal
Open market sales represent a crucial tool in the Federal Reserve's monetary policy arsenal. Their use in managing the money supply, influencing interest rates, and moderating economic growth is a cornerstone of sound monetary policy. While not without their challenges and limitations, open market sales, when employed strategically and with a clear understanding of the economic landscape, can contribute significantly to maintaining economic stability and promoting sustainable economic growth. The ongoing debate surrounding their effectiveness highlights the complex interplay between monetary policy and the broader economic environment, reinforcing the need for careful consideration and a nuanced approach to their implementation. Understanding the intricacies of open market sales is essential for anyone seeking a comprehensive grasp of the complexities of the US economy and the role of its central bank.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Product Of This Reaction
Mar 18, 2025
-
Record The Entry To Close The Dividends Account
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes The Operational Period Briefing
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Second Largest Number Of Pacs Are Those Associated With
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Accompanying Graph Represents Haydens Fro Yo
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When Conducting An Open Market Sale The Fed . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
