What Is Involved In Safety Monitoring
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
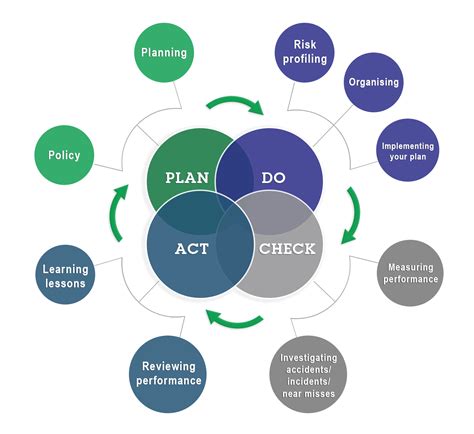
Table of Contents
What is Involved in Safety Monitoring? A Comprehensive Guide
Safety monitoring is a critical process encompassing various activities designed to identify, assess, and mitigate hazards, ensuring the well-being of individuals and the protection of assets. It's a proactive approach that goes beyond simply reacting to accidents; it aims to prevent them in the first place. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted nature of safety monitoring, exploring its key components, methodologies, and the benefits it offers across diverse sectors.
Understanding the Scope of Safety Monitoring
Safety monitoring isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. Its scope varies significantly depending on the industry, the specific environment, and the potential hazards involved. Consider these aspects:
1. Identifying Potential Hazards: The Foundation of Safety Monitoring
The process begins with a thorough hazard identification. This involves systematically reviewing work processes, equipment, and the environment to pinpoint potential risks. Techniques include:
- Job Hazard Analysis (JHA): A systematic process of examining each step of a job to identify potential hazards and recommend control measures.
- Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP): A structured and systematic technique used to identify deviations from the intended operation of a process and the consequences of those deviations.
- What-If Analysis: A brainstorming technique that explores various scenarios and their potential consequences.
- Checklists and Inspections: Regularly scheduled inspections using checklists to ensure compliance with safety standards and identify potential hazards.
2. Risk Assessment: Evaluating the Likelihood and Severity
Once hazards are identified, a risk assessment is crucial. This involves evaluating the likelihood of each hazard occurring and the potential severity of its consequences. This evaluation informs the prioritization of safety measures. Common risk assessment methodologies include:
- Qualitative Risk Assessment: Uses descriptive terms (e.g., low, medium, high) to assess likelihood and severity. Simple and easy to understand but less precise.
- Quantitative Risk Assessment: Uses numerical data to express likelihood and severity, providing a more precise risk level. More complex but offers greater accuracy.
- Bow Tie Analysis: A visual tool that helps to understand the chain of events leading to an incident and the barriers that prevent it.
3. Implementing Control Measures: Reducing Risk to Acceptable Levels
Based on the risk assessment, appropriate control measures are implemented to reduce risks to acceptable levels. These measures are often categorized into:
- Engineering Controls: Physical modifications to the workplace or equipment to eliminate or reduce hazards (e.g., machine guarding, ventilation systems). These are often the most effective controls.
- Administrative Controls: Changes in work practices, procedures, or policies to reduce hazards (e.g., safety training, permits-to-work systems).
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Equipment worn by individuals to protect themselves from hazards (e.g., hard hats, safety glasses, gloves). PPE is usually considered the last line of defense.
Methods and Technologies in Safety Monitoring
Safety monitoring employs various methods and technologies to gather data, analyze risks, and ensure compliance. These include:
1. Traditional Methods: Observation and Reporting
- Workplace Inspections: Regular inspections conducted by safety personnel to identify hazards and compliance issues.
- Incident Reporting and Investigation: A systematic process of reporting, investigating, and analyzing incidents to identify root causes and prevent recurrence.
- Near Miss Reporting: Encouraging employees to report near misses (incidents that could have resulted in an injury or damage) to identify potential hazards before they cause an accident.
2. Advanced Technologies: Enhancing Safety Monitoring
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of safety monitoring:
- CCTV and Video Surveillance: Provides real-time monitoring of the work environment, enabling prompt detection and response to hazards.
- Wearable Sensors and IoT Devices: These devices collect data on worker location, activity, and environmental conditions, providing real-time insights into potential risks.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data and advanced algorithms to predict potential incidents and proactively implement preventive measures.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Collecting and analyzing data from various sources to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in safety performance.
Key Sectors Utilizing Safety Monitoring
Safety monitoring is essential across diverse sectors, each with specific challenges and requirements:
1. Construction: Managing High-Risk Environments
The construction industry faces numerous hazards, including falls, electrocution, and struck-by incidents. Safety monitoring in construction involves rigorous inspections, risk assessments, and the use of advanced technologies like wearable sensors to track worker location and activity.
2. Manufacturing: Ensuring Safe Operations in Industrial Settings
Manufacturing facilities involve complex machinery and processes, requiring meticulous safety monitoring to prevent accidents. Regular inspections, machine guarding, and emergency response plans are crucial.
3. Healthcare: Protecting Patients and Staff
Hospitals and healthcare facilities must prioritize patient and staff safety. Safety monitoring involves infection control protocols, incident reporting systems, and the use of technology to monitor patient vital signs and prevent falls.
4. Transportation: Enhancing Road and Rail Safety
The transportation industry relies heavily on safety monitoring to prevent accidents. This includes vehicle inspections, driver training, and the use of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to enhance safety.
5. Mining and Energy: Addressing High-Hazard Industries
Mining and energy sectors operate in high-risk environments. Rigorous safety monitoring is essential, incorporating hazard identification, risk assessment, emergency response plans, and the use of specialized equipment and technology.
Benefits of Effective Safety Monitoring
Implementing a robust safety monitoring program offers numerous benefits:
- Reduced Accidents and Injuries: The primary benefit is a significant reduction in workplace accidents and injuries, protecting employees and minimizing disruption.
- Improved Employee Morale and Productivity: A safe work environment fosters a positive work culture, boosting employee morale and productivity.
- Lower Insurance Premiums: A strong safety record often translates into reduced insurance premiums.
- Enhanced Compliance: Effective safety monitoring ensures compliance with regulations and legal requirements, avoiding penalties.
- Increased Efficiency and Reduced Downtime: Preventing accidents minimizes downtime, increasing operational efficiency.
- Improved Reputation and Brand Image: A commitment to safety enhances the company's reputation and brand image, attracting customers and talent.
- Sustainable Operations: Integrating safety monitoring into daily operations promotes sustainability by minimizing environmental impact and resource waste.
Conclusion: Proactive Safety for a Secure Future
Safety monitoring is not just a compliance requirement; it's an investment in a safer, more productive, and sustainable future. By combining traditional methods with advanced technologies, organizations can create a comprehensive safety program that proactively identifies and mitigates risks, protecting people and assets while fostering a positive and productive work environment. The key to success lies in continuous improvement, regular review, and a commitment to a culture of safety at all levels of the organization. By embracing proactive safety monitoring, organizations can minimize the risk of incidents, protect their workforce, and build a strong reputation for safety and responsibility.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Favorable Labor Rate Variance Indicates That
Mar 17, 2025
-
Split The Worksheet Into Panes At Cell D16
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Winning Strategy Is One That
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Objective Of Inventory Management Is To
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Bond Is Issued At Par Value When
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Involved In Safety Monitoring . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
