Use The Given Graph To Evaluate The Following Expressions
Holbox
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
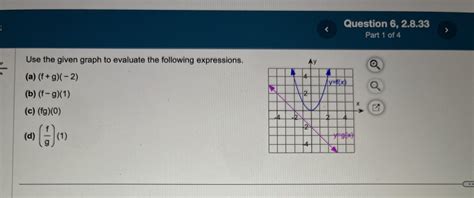
Table of Contents
- Use The Given Graph To Evaluate The Following Expressions
- Table of Contents
- Evaluating Expressions Using a Graph: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Foundation: Types of Graphs and Their Representations
- Evaluating Simple Expressions: A Step-by-Step Approach
- Handling More Complex Expressions
- Dealing with Non-Linear Relationships
- Scatter Plots and Expression Evaluation
- Bar Graphs and Pie Charts: A Different Approach
- Pitfalls to Avoid
- Advanced Techniques and Considerations
- Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Graph Interpretation
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Evaluating Expressions Using a Graph: A Comprehensive Guide
Graphs are powerful visual tools used to represent relationships between variables. They provide a convenient way to understand trends, make predictions, and, importantly, evaluate expressions involving those variables. This article will delve into the process of evaluating expressions using a given graph, covering various scenarios and techniques to ensure you master this crucial skill. We'll explore different types of graphs, handle various expression complexities, and discuss potential pitfalls to avoid.
Understanding the Foundation: Types of Graphs and Their Representations
Before we dive into expression evaluation, it's vital to understand the different types of graphs commonly used. The method of evaluating expressions differs slightly depending on the graph type:
-
Line Graphs: These graphs represent a continuous relationship between two variables. They're ideal for showing trends and changes over time or across a range of values. Evaluating expressions using a line graph often involves finding the y-value corresponding to a given x-value (or vice-versa).
-
Scatter Plots: Scatter plots show the relationship between two variables without implying a continuous function. They're useful for identifying correlations and patterns. Evaluating expressions with scatter plots requires careful consideration of the data points and potential trends. Interpolation and extrapolation might be necessary, but must be done cautiously.
-
Bar Graphs: Bar graphs represent categorical data, showing comparisons between different groups. Evaluating expressions with bar graphs often involves adding, subtracting, or comparing values represented by the bars' heights.
-
Pie Charts: Pie charts represent proportions of a whole. Evaluating expressions with pie charts often involves calculating percentages or ratios based on the segments' sizes.
Evaluating Simple Expressions: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's start with simple expressions using a hypothetical line graph. Imagine a line graph representing the relationship between hours studied (x-axis) and exam scores (y-axis).
Example: Suppose the line graph shows a linear relationship, and we want to evaluate the expression "Exam Score when Hours Studied = 4".
Steps:
-
Locate the x-value: Find the point on the x-axis corresponding to "Hours Studied = 4".
-
Trace vertically: Draw a vertical line upwards from this point until it intersects the line representing the relationship.
-
Trace horizontally: From the intersection point, draw a horizontal line to the y-axis.
-
Read the y-value: The point where the horizontal line intersects the y-axis represents the "Exam Score" corresponding to "Hours Studied = 4". This is the value of the expression.
Important Note: The accuracy of the evaluation depends on the precision of the graph and the reader's ability to accurately interpret the graph.
Handling More Complex Expressions
The process becomes slightly more complex with more intricate expressions. Let's consider expressions involving multiple variables or operations:
Example: Assume the same line graph as before, and we need to evaluate "Exam Score when Hours Studied = 6, minus Exam Score when Hours Studied = 2".
Steps:
-
Evaluate individual components: Follow the steps outlined above to find the "Exam Score" when "Hours Studied = 6" and the "Exam Score" when "Hours Studied = 2" separately.
-
Perform the operation: Subtract the "Exam Score" at "Hours Studied = 2" from the "Exam Score" at "Hours Studied = 6". The result is the value of the expression.
Dealing with Non-Linear Relationships
Line graphs don't always depict linear relationships. Dealing with curves requires more care. For instance, if the relationship between hours studied and exam scores exhibits diminishing returns (a curve that flattens out), evaluating expressions requires careful observation of the curve's shape to accurately interpolate the corresponding y-value for a given x-value.
Scatter Plots and Expression Evaluation
Scatter plots present a different challenge. Because they don't represent a continuous function, evaluating expressions involves a degree of approximation and interpretation. The goal is to estimate the likely y-value based on the observed pattern in the data points. Interpolation (estimating values within the range of the data) is generally preferred over extrapolation (estimating values outside the range of the data), as extrapolation is far less reliable. Regression analysis techniques (like linear regression or polynomial regression) can help establish a model to aid in the evaluation of expressions.
Bar Graphs and Pie Charts: A Different Approach
Evaluating expressions using bar graphs and pie charts differs from line graphs and scatter plots. These graphs primarily represent categorical data or proportions.
Bar Graphs: Expressions typically involve comparing the heights (or lengths) of the bars, often involving addition, subtraction, or ratio calculations.
Pie Charts: Expressions generally revolve around calculating percentages, ratios, or proportions of the whole based on the size of the individual segments. This frequently entails using the percentage values directly or performing calculations based on the angles represented by the segments.
Pitfalls to Avoid
Several common pitfalls can lead to inaccurate evaluations:
-
Incorrect Interpretation of the Axes: Ensure you correctly identify the variables represented on the x-axis and y-axis.
-
Poor Precision in Reading Values: Carefully estimate values from the graph, avoiding unnecessary rounding errors. A ruler or straight edge can improve accuracy.
-
Over-reliance on Extrapolation: Avoid relying too heavily on extrapolation, as the relationship between variables may change beyond the range of the data shown on the graph.
-
Ignoring the Context: Always consider the context of the graph and the units of measurement when interpreting and evaluating expressions.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
For more complex scenarios, advanced techniques may be necessary:
-
Interpolation Methods: Linear interpolation is a simple method for estimating values between data points. More sophisticated methods, such as spline interpolation, can provide better accuracy for non-linear relationships.
-
Regression Analysis: As mentioned earlier, regression analysis can help fit a mathematical model to the data, facilitating more accurate evaluation of expressions.
-
Numerical Differentiation and Integration: If the graph represents a function, numerical methods can estimate the derivative or integral of the function at specific points, enabling the evaluation of more complex expressions involving rates of change or accumulated quantities.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Graph Interpretation
Evaluating expressions using graphs is a fundamental skill in various fields. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for tackling different graph types and expression complexities. Remember to carefully analyze the graph, understand the underlying relationship, use appropriate techniques, and avoid common pitfalls to ensure accurate and reliable evaluations. By practicing diligently and carefully considering the context, you'll become proficient in extracting valuable information from graphs and efficiently solving a wide range of mathematical problems involving graphical data.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sexual Harassment Is Unwelcome Or Unwanted Behavior Based On
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Ge Business Screen Portfolio Model Evaluates Business On Dimetion
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Company Started The Year With 10 000 Of Inventory
Mar 26, 2025
-
Costs Developed Which Identify What Products Should Cost Are Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
3 Examples Of Things With Low Kinetic Energy
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Use The Given Graph To Evaluate The Following Expressions . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
