Top Management Usually Performs All Of The Following Tasks Except
Holbox
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
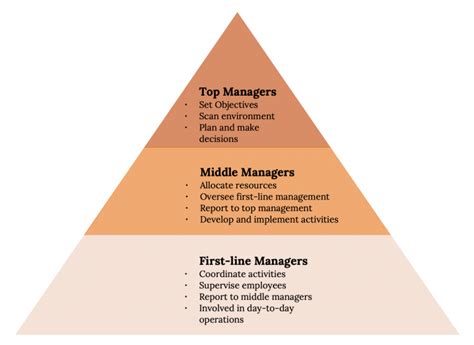
Table of Contents
- Top Management Usually Performs All Of The Following Tasks Except
- Table of Contents
- Top Management: A Deep Dive into Roles and Responsibilities (Excluding One Key Task)
- The Core Functions of Top Management
- What Top Management DOESN'T Do: Hands-on Operational Tasks
- The Importance of Effective Delegation
- Conclusion: Strategic Vision vs. Operational Execution
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Top Management: A Deep Dive into Roles and Responsibilities (Excluding One Key Task)
Top management, the apex of an organization's hierarchy, plays a pivotal role in shaping its strategic direction, fostering growth, and ensuring long-term sustainability. Their responsibilities are multifaceted and demanding, requiring a blend of strategic vision, operational acumen, and leadership prowess. While they oversee a vast array of tasks crucial to the organization's success, there's one key area they typically don't directly perform: hands-on operational tasks. This article will delve into the core responsibilities of top management, highlighting the areas of focus that drive organizational performance and success, while emphasizing the exception – the direct execution of day-to-day operational functions.
The Core Functions of Top Management
Top management's role transcends the minutiae of daily operations. Instead, their focus rests on establishing the overarching vision, strategy, and culture that guide the entire organization. This involves a multitude of crucial tasks, including:
1. Strategic Planning & Vision Setting: The Foundation of Success
The cornerstone of top management's role is crafting a compelling vision and translating it into a robust strategic plan. This involves:
- Analyzing the external environment: Identifying market trends, competitive landscapes, technological advancements, and economic fluctuations are critical for informed decision-making. SWOT analysis, PESTLE analysis, and other strategic tools are frequently employed.
- Defining organizational goals: These goals should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) and aligned with the overall vision.
- Developing strategic initiatives: This involves outlining the specific actions and resource allocations required to achieve the defined goals. This might include market expansion, product development, or operational improvements.
- Monitoring and adapting the strategic plan: The business landscape is dynamic. Top management must constantly monitor progress, assess market shifts, and adjust the strategic plan accordingly. This requires flexibility and a willingness to adapt to changing circumstances.
2. Resource Allocation & Management: Fueling Organizational Growth
Effective resource allocation is paramount for organizational success. Top management is responsible for:
- Budgeting and financial planning: Allocating financial resources strategically across different departments and initiatives to maximize return on investment (ROI).
- Human resource management (strategic level): While not directly involved in daily HR operations, top management sets the overall HR strategy, including recruitment of high-level executives, talent development programs, compensation structures, and overall company culture.
- Technology and infrastructure investment: Making crucial decisions regarding technology adoption, infrastructure development, and the overall technological direction of the organization.
3. Leadership and Team Building: Cultivating a High-Performing Organization
Top management's leadership style significantly impacts the organization's performance and culture. This involves:
- Setting the organizational culture: Defining the values, norms, and behaviors expected from employees. This sets the tone for the entire organization.
- Building a strong leadership team: Selecting, developing, and mentoring mid-level and senior managers who can effectively execute the strategic plan.
- Motivating and inspiring employees: Creating a positive and motivating work environment to foster employee engagement and productivity. This often involves effective communication and recognition of achievements.
- Managing organizational change: Implementing and managing change initiatives effectively, minimizing disruption and maximizing employee buy-in. This often involves clear communication and a well-defined change management process.
4. Risk Management and Crisis Response: Navigating Uncertainties
Top management plays a crucial role in mitigating risks and responding to crises. This involves:
- Identifying and assessing potential risks: Proactively identifying potential threats to the organization, such as market changes, competitive pressures, or regulatory changes.
- Developing risk mitigation strategies: Implementing strategies to reduce the likelihood and impact of potential risks.
- Responding to crises effectively: Developing and executing plans to address crises promptly and effectively, minimizing damage and preserving the organization's reputation.
5. Stakeholder Management: Building and Maintaining Relationships
Top management is responsible for managing relationships with various stakeholders, including:
- Shareholders: Communicating the organization's performance, strategic direction, and financial health to shareholders.
- Customers: Ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty through effective product development and customer service strategies.
- Employees: Fostering a positive and productive work environment to attract and retain top talent.
- Government and regulatory bodies: Ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
- Suppliers and partners: Building strong relationships with key suppliers and partners to ensure smooth operations.
What Top Management DOESN'T Do: Hands-on Operational Tasks
While top management oversees all these critical areas, they do not typically perform hands-on operational tasks. This is a crucial distinction. Their expertise lies in strategic thinking, leadership, and overall direction, not in the day-to-day execution of specific operational activities. Examples of tasks generally delegated to lower management levels include:
- Processing customer orders: This is handled by customer service and order fulfillment teams.
- Managing inventory: This falls under the purview of supply chain and logistics departments.
- Producing goods or services: This is the responsibility of production and operations teams.
- Troubleshooting technical issues: IT support and maintenance teams handle these day-to-day technical problems.
- Responding to individual customer complaints: Customer service representatives address individual customer concerns.
Delegation is Key: Top management's effectiveness relies heavily on their ability to delegate effectively. They empower lower-level managers and employees to handle operational tasks, freeing up their time to focus on high-level strategic initiatives. This ensures efficiency and allows for the development of expertise within the organization.
The Importance of Effective Delegation
Effective delegation is not simply about offloading tasks; it's about empowering individuals, fostering growth, and improving organizational efficiency. Top management needs to:
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities: Ensure each team member understands their tasks and authority.
- Provide adequate training and resources: Equip employees with the skills and tools they need to succeed.
- Monitor progress and provide feedback: Regularly check on progress and offer support and guidance as needed.
- Trust and empower employees: Allow employees autonomy to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
- Recognize and reward success: Acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of team members.
By focusing on strategic initiatives and delegating operational tasks, top management can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the organization. This allows them to maintain a long-term perspective, anticipating future challenges and opportunities, while fostering a culture of growth and innovation.
Conclusion: Strategic Vision vs. Operational Execution
In conclusion, the role of top management is fundamentally about strategic direction, vision, and leadership. While they are responsible for overseeing all aspects of the organization, their primary focus is not on the execution of day-to-day operational tasks. Effective delegation, coupled with strong leadership and strategic planning, allows top management to guide the organization towards its long-term goals and navigate the complexities of the modern business environment. Understanding this distinction between strategic vision and operational execution is crucial for both top management and the organization as a whole to achieve sustained success. The ability to delegate effectively and trust lower management with operational tasks is a hallmark of successful top management teams. It frees them to focus on the critical strategic decisions that shape the organization's future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Engage Medical Surgical Alterations In Health
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Would Be Transcribed Into Mrna
Mar 23, 2025
-
Organizations Who Accomplish Continuity Also Have To Focus On Their
Mar 23, 2025
-
Record The Adjusting Entry Related To Outstanding Checks If Necessary
Mar 23, 2025
-
When Must A Signal Person Be Used
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Top Management Usually Performs All Of The Following Tasks Except . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
