The Probability Distribution Of The Sample Mean Is Called The
Holbox
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
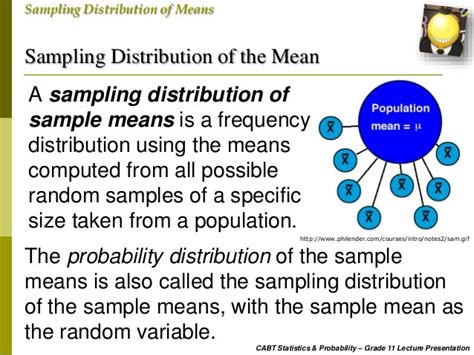
Table of Contents
- The Probability Distribution Of The Sample Mean Is Called The
- Table of Contents
- The Probability Distribution of the Sample Mean is Called the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
- Understanding the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
- Key Characteristics of the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
- The Central Limit Theorem: A Cornerstone of Statistical Inference
- Implications of the Central Limit Theorem
- Applications of the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
- Beyond the Mean: Sampling Distributions of Other Statistics
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Probability Distribution of the Sample Mean is Called the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
The probability distribution of the sample mean is a crucial concept in statistics, forming the bedrock of inferential statistics. Understanding this distribution allows us to make inferences about a population based on a sample drawn from it. This article delves deep into the intricacies of this distribution, exploring its characteristics, applications, and the underlying theoretical foundations. We'll also explore the conditions under which the Central Limit Theorem applies, a cornerstone theorem in statistics that simplifies the analysis of the sampling distribution.
Understanding the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
Before diving into the specifics, let's clarify the terminology. The sampling distribution of the mean refers to the probability distribution of the means of all possible samples of a given size (n) drawn from a population. It's not the distribution of the data within a single sample; instead, it's the distribution of the means calculated from numerous samples. Imagine repeatedly taking samples, calculating the mean of each, and then plotting those means – this plot represents the sampling distribution of the mean.
This distribution is particularly important because it allows us to understand the variability of sample means. Even if we draw samples from the same population, the sample means will vary due to random sampling fluctuation. The sampling distribution helps us quantify this variability.
Key Characteristics of the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
Several key characteristics define the sampling distribution of the mean:
-
Mean of the Sampling Distribution: The mean of the sampling distribution of the mean (often denoted as μ<sub>x̄</sub>) is equal to the population mean (μ). This implies that the sampling distribution is centered around the true population mean.
-
Standard Deviation of the Sampling Distribution (Standard Error): The standard deviation of the sampling distribution is called the standard error (often denoted as σ<sub>x̄</sub>). It measures the variability of the sample means. The standard error is calculated as:
σ<sub>x̄</sub> = σ / √n
Where:
- σ is the population standard deviation.
- n is the sample size.
Notice that the standard error is inversely proportional to the square root of the sample size. This means that as the sample size increases, the standard error decreases. Larger sample sizes lead to more precise estimates of the population mean, resulting in a narrower sampling distribution.
-
Shape of the Sampling Distribution: The shape of the sampling distribution depends on the shape of the population distribution and the sample size. This is where the Central Limit Theorem comes into play.
The Central Limit Theorem: A Cornerstone of Statistical Inference
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) is one of the most significant theorems in statistics. It states that the sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal distribution as the sample size increases, regardless of the shape of the population distribution. This holds true as long as the population has a finite mean and variance.
Conditions for the Central Limit Theorem to Apply:
-
Independence: The samples must be independent of each other. This means that the selection of one sample doesn't influence the selection of another.
-
Random Sampling: The samples should be randomly selected from the population. This ensures that the sample is representative of the population.
-
Sample Size: While the CLT technically holds for any sample size, the approximation to a normal distribution is better with larger sample sizes. A common rule of thumb is that a sample size of at least 30 is sufficient for the approximation to be reasonably accurate, especially if the population distribution isn't too skewed. However, for highly skewed distributions, larger sample sizes might be necessary.
Implications of the Central Limit Theorem
The CLT has profound implications for statistical inference:
-
Simplified Analysis: Even if we don't know the shape of the population distribution, the CLT allows us to assume that the sampling distribution of the mean is approximately normal for sufficiently large sample sizes. This simplifies statistical analysis considerably, as we can use the properties of the normal distribution to make inferences.
-
Confidence Intervals: The CLT is essential for constructing confidence intervals for the population mean. Confidence intervals provide a range of values within which we are confident the true population mean lies.
-
Hypothesis Testing: The CLT underpins many hypothesis tests concerning the population mean. These tests allow us to determine whether there is sufficient evidence to reject a null hypothesis about the population mean.
Applications of the Sampling Distribution of the Mean
The sampling distribution of the mean finds wide applications across diverse fields:
-
Quality Control: In manufacturing, the sampling distribution is used to monitor the quality of products. By taking samples and calculating their means, manufacturers can assess whether the production process is meeting specifications.
-
Opinion Polls: Opinion polls rely heavily on the sampling distribution to estimate the proportion of the population that holds a particular opinion. The sample mean (proportion) is used to estimate the population mean (proportion), with the standard error quantifying the uncertainty in the estimate.
-
Medical Research: In clinical trials, the sampling distribution plays a critical role in analyzing the effectiveness of a new treatment. By comparing the means of treatment and control groups, researchers can determine whether the treatment is significantly effective.
-
Financial Modeling: The sampling distribution is used extensively in financial modeling to assess the risk and return of investments. By simulating numerous scenarios and calculating the mean returns, investors can get a better understanding of the potential outcomes.
Beyond the Mean: Sampling Distributions of Other Statistics
While this article focuses on the sampling distribution of the mean, it's important to note that similar concepts apply to other sample statistics. For example, there's a sampling distribution for the sample variance, the sample proportion, and other statistics. Each has its own characteristics and applications, with the underlying principle of understanding the variability of sample statistics remaining central.
Conclusion
The sampling distribution of the mean is a fundamental concept in statistics with far-reaching implications for data analysis and inference. Understanding its properties, especially in light of the Central Limit Theorem, empowers us to draw meaningful conclusions about populations based on samples. Whether you're in quality control, medical research, finance, or any field dealing with data, grasping the concept of the sampling distribution is crucial for making sound statistical decisions. Its practical applications are vast, enabling us to confidently estimate population parameters and test hypotheses with a quantified level of uncertainty. The importance of the sampling distribution cannot be overstated, highlighting its position as a cornerstone in the field of statistical inference. Further exploration of related concepts, such as confidence intervals and hypothesis testing, will only deepen one's understanding of this crucial statistical tool.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Are Reasons Firms Expand Internationally
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Specificity Of Hormone Action Derives From
Mar 23, 2025
-
Based On Your Well Done Risk Assessment
Mar 23, 2025
-
Draw The Product Of The Reaction Shown Between Propanoyl Chloride
Mar 23, 2025
-
Dento Donto And Odonto All Mean
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Probability Distribution Of The Sample Mean Is Called The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
