The Global Product Strategy A Firm Chooses Depends On
Holbox
Mar 25, 2025 · 7 min read
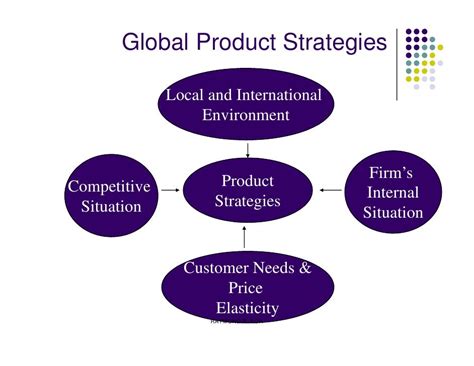
Table of Contents
- The Global Product Strategy A Firm Chooses Depends On
- Table of Contents
- The Global Product Strategy a Firm Chooses Depends On: A Comprehensive Guide
- Key Factors Determining Global Product Strategy
- 1. Market Characteristics: Understanding Your Target Audience
- 2. Product Characteristics: Adaptability and Standardization
- 3. Company Characteristics: Resources and Capabilities
- 4. Competitive Landscape: Analyzing the Market Dynamics
- 5. Global Marketing Strategies: The Integrated Approach
- Global Product Strategy Models: A Comparative Analysis
- 1. Standardization Strategy: Economies of Scale and Efficiency
- 2. Adaptation Strategy: Customization and Market Relevance
- 3. Glocalization Strategy: Balancing Standardization and Adaptation
- 4. Combination Strategy: A Multi-pronged Approach
- Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Global Product Strategy
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Global Product Strategy a Firm Chooses Depends On: A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right global product strategy is paramount for any firm aiming to expand internationally. The success or failure of a global venture hinges significantly on this crucial decision. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted factors influencing a firm's selection of its global product strategy, providing a detailed analysis for businesses navigating the complexities of international markets.
Key Factors Determining Global Product Strategy
A firm's global product strategy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It's a carefully considered approach tailored to specific circumstances. Several key factors play a crucial role in shaping this strategy:
1. Market Characteristics: Understanding Your Target Audience
The characteristics of the target market are fundamental. These include:
-
Cultural Differences: Culture significantly impacts consumer preferences. What's popular in one country might be completely unacceptable in another. Consider factors like language, religion, values, and social norms when adapting your product or marketing message. A product requiring significant cultural adaptation might necessitate a different strategy compared to one requiring minimal adjustments. For example, food products often need significant modification to cater to local tastes and dietary restrictions.
-
Consumer Behavior: Understanding consumer buying patterns is essential. Are consumers price-sensitive? Do they prefer established brands or are they open to new products? The level of brand loyalty and the presence of substitute products within the market influence strategic choices. A high brand loyalty market might require a different approach than one where consumers readily switch brands.
-
Economic Conditions: Economic factors like purchasing power, disposable income, and infrastructure significantly influence product adaptation. High-income markets might afford premium products, whereas lower-income markets demand cost-effective solutions. Infrastructure limitations, such as unreliable electricity or poor transportation networks, must be considered when introducing certain products.
-
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: Each country has specific laws and regulations affecting product development, labeling, and distribution. Compliance with these regulations is non-negotiable, often influencing design modifications or marketing claims. For instance, certain ingredients might be banned in one market, necessitating a reformulation of the product. Safety standards and intellectual property protection also play a crucial role.
2. Product Characteristics: Adaptability and Standardization
The nature of the product itself plays a significant role in shaping the global product strategy:
-
Standardization vs. Adaptation: This core decision determines whether to offer a uniform product globally (standardization) or tailor the product to suit individual markets (adaptation). Standardization offers cost economies of scale, but it might not resonate with diverse consumer preferences. Adaptation provides greater market relevance, but it raises costs due to modifications and localized marketing efforts.
-
Product Complexity: Complex products requiring extensive technical support might necessitate a more tailored approach, providing localized service and training. Simple products with straightforward usage might be more easily standardized.
-
Product Life Cycle: The stage of the product's life cycle – introduction, growth, maturity, or decline – influences strategy. New products in international markets often require greater adaptation to gain traction, while mature products might be more easily standardized.
-
Perishability and Shelf Life: Perishable products require efficient supply chains and distribution networks, often limiting the scope for standardization. Non-perishable products allow for more flexibility in global distribution strategies.
3. Company Characteristics: Resources and Capabilities
The firm's internal capabilities and resources greatly influence its global product strategy:
-
Financial Resources: Adaptation requires significant investment in research, development, and marketing. Firms with ample financial resources can afford a more tailored approach, whereas those with limited resources might favor standardization.
-
Technological Capabilities: Firms with advanced technological capabilities might be better positioned to develop and adapt products for diverse markets. This is especially crucial for products involving complex technology or requiring customized solutions.
-
Marketing Expertise: Successful global marketing requires understanding diverse consumer behaviors and adapting messaging accordingly. Firms with experienced global marketing teams can manage complex adaptation strategies more effectively.
-
Production Capacity and Supply Chain: A robust global supply chain is critical for managing both standardization and adaptation strategies. The ability to efficiently manufacture and distribute products globally influences the feasibility of different approaches.
4. Competitive Landscape: Analyzing the Market Dynamics
The competitive environment significantly shapes global product strategy:
-
Competitive Intensity: Highly competitive markets might require a greater emphasis on product differentiation and adaptation to stand out from the competition. Less competitive markets might allow for a more standardized approach.
-
Competitive Strategies of Rivals: Analyzing competitor strategies is crucial. Are competitors adapting products for local markets? Are they pursuing a standardization strategy? Understanding the actions of rivals informs the best response.
-
Presence of Global Brands: The existence of strong global brands might influence the need for significant product adaptation or differentiation to compete effectively.
5. Global Marketing Strategies: The Integrated Approach
Global marketing strategies are inextricably linked with product strategy. Factors influencing the marketing strategy choice include:
-
Global Branding: A consistent global brand image can provide significant benefits, but it needs to be adapted to resonate with local cultures. Brand localization can enhance consumer engagement while maintaining a sense of global unity.
-
Pricing Strategies: Pricing decisions must consider factors like local costs, consumer purchasing power, and competitive pricing. Different pricing strategies might be employed across various markets.
-
Distribution Channels: Effective distribution channels are crucial for reaching target consumers. The selection of distribution channels depends on market infrastructure, consumer preferences, and logistics.
Global Product Strategy Models: A Comparative Analysis
Several established models guide global product strategy decisions:
1. Standardization Strategy: Economies of Scale and Efficiency
A standardization strategy focuses on offering a consistent product globally, minimizing adaptation costs and leveraging economies of scale. This approach is suitable for products with universal appeal and minimal cultural sensitivity. Examples include electronics, software, and certain types of apparel. Advantages include cost savings and simplified management, while disadvantages include potential lack of market relevance and reduced competitiveness in culturally diverse markets.
2. Adaptation Strategy: Customization and Market Relevance
An adaptation strategy emphasizes tailoring the product to specific market needs and preferences. This involves modifying product features, packaging, or messaging to resonate with local consumers. This strategy is suited for products with significant cultural sensitivity, such as food, personal care items, and certain types of clothing. Advantages include increased market penetration and strong brand loyalty, whereas disadvantages include higher costs, increased complexity, and longer lead times.
3. Glocalization Strategy: Balancing Standardization and Adaptation
Glocalization represents a hybrid approach, balancing standardization and adaptation. It involves offering a standardized core product while making minor modifications to suit local preferences. This strategy enables firms to benefit from economies of scale while maintaining market relevance. This approach works well for products with a globally recognizable brand but needing minor adjustments for local tastes. Advantages include cost efficiency and market relevance, but disadvantages include the difficulty in finding the right balance between standardization and adaptation.
4. Combination Strategy: A Multi-pronged Approach
In some instances, a firm might adopt a combination strategy, offering different product variations across different markets. This might involve standardized products for some markets and adapted products for others. This strategy is particularly suitable for large multinational corporations with diverse product portfolios and extensive global reach. Advantages include flexibility and adaptability to diverse market conditions, however, disadvantages include increased complexity and management challenges.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Global Product Strategy
Choosing the optimal global product strategy requires a thorough understanding of market characteristics, product attributes, company capabilities, and the competitive landscape. No single strategy guarantees success; the ideal approach depends on a careful assessment of these intertwined factors. Careful market research, rigorous analysis, and a well-defined strategic plan are crucial for navigating the complexities of international markets and achieving sustainable global growth. By thoughtfully considering the factors outlined above, businesses can make informed decisions that maximize their chances of success in the global arena. Continuous monitoring and adaptation of the chosen strategy are also essential in the ever-evolving global marketplace.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write The Equation For The Solubility Product For Lead Iodide
Mar 28, 2025
-
Confined Space Tasks May Use General Industry Regulations When They
Mar 28, 2025
-
One Implication Of Todays Flatter Corporate Structures Is That
Mar 28, 2025
-
Sierra Company Manufactures Soccer Balls In Two Sequential Processes
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Economically Beneficial Specialization
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Global Product Strategy A Firm Chooses Depends On . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
