The Account Allowance For Uncollectible Accounts Is Classified As
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
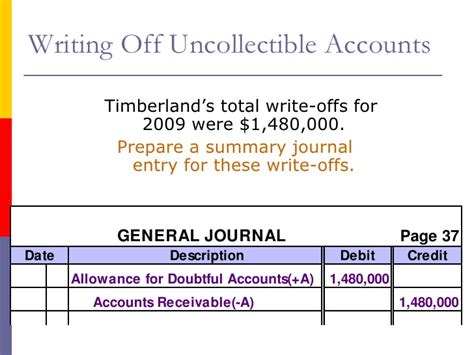
Table of Contents
The Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts: A Comprehensive Guide
The allowance for uncollectible accounts, also known as the allowance for doubtful accounts or bad debt expense, is a crucial element of financial accounting. It represents a company's best estimate of the receivables it won't be able to collect. Understanding this account is vital for accurate financial reporting and effective credit management. This in-depth guide will explore the classification, calculation, and implications of the allowance for uncollectible accounts.
Classification of the Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts
The allowance for uncollectible accounts is classified as a contra-asset account. This means it's paired with another account—accounts receivable—on the balance sheet. While accounts receivable represents the total amount owed to a company by its customers, the allowance for uncollectible accounts reduces this amount to reflect the portion that's likely uncollectible. This results in a more realistic portrayal of a company's true financial position. It's important to understand that the allowance account itself is not an expense account. The expense related to uncollectible accounts is recorded separately.
Why is it a contra-asset account and not an expense? The key difference lies in the timing of recognition. The expense (bad debt expense) is recognized in the period the receivables become uncollectible, whereas the allowance account is established before the receivables are deemed uncollectible. It's a proactive measure to estimate potential future losses.
Methods for Estimating Uncollectible Accounts
Several methods exist for estimating the allowance for uncollectible accounts. The choice depends on factors such as the company's industry, historical data, and management's judgment. The two most common methods are:
1. Percentage of Sales Method
This method focuses on the relationship between credit sales and the expected percentage of those sales that will become uncollectible. It's a relatively simple approach, particularly useful for companies with a large number of small transactions or inconsistent historical data on receivables.
How it Works: The company estimates the percentage of credit sales that are likely to become uncollectible based on past experience or industry benchmarks. This percentage is then multiplied by the current period's credit sales to arrive at the estimated bad debt expense. The resulting amount is then debited to bad debt expense and credited to the allowance for uncollectible accounts.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
- Timely: Estimates are made based on current sales, providing a timely reflection of potential losses.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Historical Data Reliance: It doesn't directly consider the existing balance in the allowance account. If the existing allowance is already significant, this method may overestimate the required allowance.
- Ignores Age of Receivables: It fails to account for the varying likelihood of collection based on how long a receivable has been outstanding.
2. Percentage of Receivables Method (Aging Method)
This method focuses on the existing balance of accounts receivable and estimates the percentage of each aging category that is likely to be uncollectible. Accounts receivable are categorized by their age (e.g., 0-30 days, 31-60 days, 61-90 days, over 90 days). Each aging category is assigned a percentage representing its expected uncollectibility.
How it Works: The company analyzes its outstanding accounts receivable and categorizes them by age. For each category, a percentage representing the estimated uncollectibility is applied. The sum of these amounts represents the desired balance in the allowance for uncollectible accounts. The difference between the current balance in the allowance account and the desired balance is adjusted through a debit or credit to bad debt expense.
Advantages:
- Considers Age of Receivables: Accounts that have been outstanding longer are assigned higher percentages, reflecting their increased risk of uncollectibility. This makes it more accurate than the percentage of sales method.
- More Accurate Estimate: A more comprehensive and often more accurate estimate of the needed allowance.
Disadvantages:
- More Complex: Requires more detailed analysis of receivables and may involve more subjective judgment in assigning percentages.
- Potential for Inaccuracy: The assigned percentages are based on estimates and past experience, which might not always accurately predict future outcomes.
Journal Entries for Uncollectible Accounts
The accounting entries related to uncollectible accounts vary depending on the method used and whether a specific account is written off.
Estimating Bad Debt Expense (Both Methods):
- Debit: Bad Debt Expense (increases the expense)
- Credit: Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts (increases the contra-asset account)
Writing Off a Specific Uncollectible Account:
- Debit: Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts (reduces the contra-asset account)
- Credit: Accounts Receivable (reduces the asset account)
Recovering a Previously Written-Off Account:
-
Debit: Accounts Receivable (increases the asset account)
-
Credit: Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts (increases the contra-asset account)
-
Debit: Cash (increases the asset account)
-
Credit: Accounts Receivable (reduces the asset account)
Impact on Financial Statements
The allowance for uncollectible accounts significantly impacts the balance sheet and the income statement.
Balance Sheet: It directly reduces the value of accounts receivable, providing a more accurate representation of the company's net realizable value of receivables (the amount expected to be collected). This, in turn, affects the company's current assets and overall net worth.
Income Statement: The bad debt expense, the amount added or adjusted to the allowance account, is reported as an expense on the income statement, reducing net income. This reflects the cost of extending credit to customers.
Importance of Effective Credit Management
Accurate estimation of uncollectible accounts is intrinsically linked to effective credit management. A robust credit policy, including thorough credit checks and timely collection efforts, can significantly reduce the likelihood of bad debts. This minimizes the need for a large allowance and, ultimately, improves profitability. Conversely, lax credit policies can lead to higher bad debt expenses and a need for a larger allowance, negatively impacting financial performance.
Factors Affecting the Allowance
Several factors influence the amount of the allowance for uncollectible accounts a company should maintain:
- Economic Conditions: During economic downturns, businesses may experience higher rates of uncollectible accounts due to decreased customer purchasing power.
- Industry Norms: Certain industries are inherently riskier than others regarding credit extension, leading to potentially higher bad debt percentages.
- Company-Specific Factors: A company's internal credit policies, customer base, and collection efforts all influence the level of uncollectible accounts.
- Aging of Receivables: As receivables age, the likelihood of collection decreases, necessitating a higher allowance for older receivables.
Analyzing the Allowance Account
Regular monitoring and analysis of the allowance account are critical to ensuring its accuracy. This includes:
- Reviewing the Allowance Method: Periodically assess whether the chosen method accurately reflects the company's circumstances and if adjustments are needed.
- Analyzing Write-Offs: Investigate patterns in write-offs to identify areas for improvement in credit policies or collection practices.
- Comparing to Industry Benchmarks: Benchmarking against industry peers can help determine if the allowance is appropriately sized.
Conclusion
The allowance for uncollectible accounts is a crucial component of financial reporting, reflecting a company's estimate of potential losses from extending credit. Choosing the appropriate method, maintaining effective credit policies, and regularly reviewing the allowance's accuracy are essential for accurate financial reporting and effective business management. Understanding its classification as a contra-asset account, its impact on both the balance sheet and income statement, and the factors affecting its size are all critical for financial professionals and business owners alike. The accuracy of this allowance directly impacts a company's financial health and provides crucial insights into the effectiveness of its credit and collection strategies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Your Company Offers A Single Premium Mobile Phone Handset
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Select All That Apply
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Can A User Navigate To Alteryx Community From Designer
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Merchandise Inventory Is False
Mar 17, 2025
-
With Double Entry Accounting Each Transaction Requires
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Account Allowance For Uncollectible Accounts Is Classified As . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
