Research On Sex Hormones And Human Sexual Behavior Indicates That
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
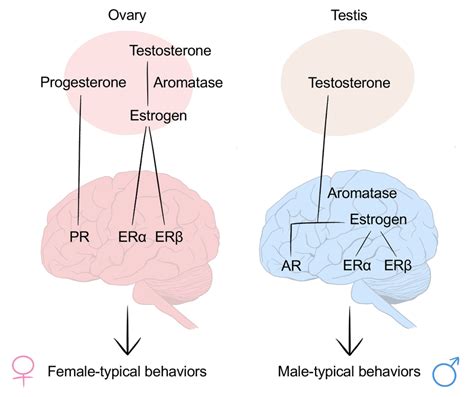
Table of Contents
Research on Sex Hormones and Human Sexual Behavior Indicates That… a Complex Interplay
Research on sex hormones and human sexual behavior reveals a far more nuanced picture than simple cause-and-effect relationships. While hormones undeniably play a significant role, their influence is interwoven with a complex tapestry of factors including genetics, environment, social learning, and individual experiences. This article delves into the current understanding of this intricate interplay, exploring the roles of testosterone, estrogen, and other hormones, while highlighting the limitations of simplistic interpretations.
The Roles of Key Sex Hormones
Testosterone: More Than Just Male Libido
Testosterone, often associated solely with male sexuality, is a crucial hormone in both sexes, albeit with differing concentrations. In males, it's primarily produced in the testes and is fundamentally linked to the development of secondary sexual characteristics and the drive for sexual activity. Higher testosterone levels are often correlated with increased libido and sexual behavior. However, it's crucial to avoid a deterministic view. Many men with high testosterone levels don't experience hypersexuality, and conversely, some with lower levels maintain a healthy sex life. This underscores the influence of other contributing factors.
Testosterone's impact on sexual behavior isn't solely about desire: It also influences sexual function, impacting aspects like erectile function in men and potentially contributing to clitoral sensitivity in women. Further research is ongoing to fully understand the complex relationship between testosterone and different facets of sexual experience.
Studies on testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) in men with hypogonadism (low testosterone) show mixed results regarding its impact on sexual function and desire. While some men report improvements, others experience little to no change. This variability highlights the complexities involved and the limitations of attributing sexual behavior solely to testosterone levels.
Estrogen: Beyond Female Reproduction
Estrogen, primarily associated with female reproductive health, also plays a crucial role in female sexual behavior. During different phases of the menstrual cycle, estrogen levels fluctuate, potentially impacting libido and arousal. Higher estrogen levels during the follicular phase are often linked to increased sexual desire, while lower levels during the luteal phase may be associated with decreased interest. However, the relationship isn't always linear, and individual responses vary widely.
Furthermore, estrogen's influence extends beyond libido. It impacts vaginal lubrication and elasticity, crucial components of sexual function. Post-menopausal women, experiencing a significant drop in estrogen levels, often report difficulties with vaginal dryness and discomfort, impacting their sexual experiences. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can sometimes alleviate these issues, but its use is often associated with potential health risks, necessitating careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional.
Other Hormones: A Supporting Cast
While testosterone and estrogen are the most prominently discussed sex hormones in relation to sexual behavior, other hormones also play significant supporting roles. These include:
- Progesterone: This hormone, crucial during pregnancy, can influence libido, with some women reporting decreased sexual desire during the luteal phase of their cycle when progesterone levels are high.
- Oxytocin: Often referred to as the "love hormone," oxytocin plays a critical role in bonding, attachment, and intimacy, influencing the emotional and social aspects of sexual experiences. It's released during sexual activity, contributing to feelings of connection and pleasure.
- Vasopressin: Similar to oxytocin, vasopressin contributes to social bonding and pair-bonding, influencing long-term relationships and potentially influencing sexual behavior within committed partnerships.
Beyond Hormones: The Wider Context
Attributing human sexual behavior solely to hormonal influences is an oversimplification. A multitude of factors interact to shape an individual's sexual experience:
Genetics: Predispositions and Variations
Genetic factors influence hormonal production and the sensitivity of receptors to hormones. Individual variations in genetic makeup can impact the way individuals respond to hormonal fluctuations and contribute to diverse sexual experiences. Research is ongoing to identify specific genes involved in sexual behavior, but the complexity of the human genome presents a significant challenge.
Environmental Factors: Early Experiences and Social Influences
Early childhood experiences, including parental relationships and social interactions, can significantly shape an individual's sexual development and behavior. Social learning, cultural norms, and religious beliefs also play a profound role in influencing attitudes towards sexuality and sexual expression. These environmental factors often interact with hormonal influences, creating complex and diverse patterns of sexual behavior.
Psychological Factors: Mental Health and Personal Beliefs
Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, and body image issues can significantly impact sexual desire and function. Mental health conditions can often interfere with the experience of pleasure and lead to decreased sexual activity. Personal beliefs, attitudes, and values also play a crucial role in shaping sexual behavior and preferences.
Lifestyle Choices: Diet, Exercise, and Sleep
Lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, and sleep patterns, can influence hormonal balance and overall well-being, potentially impacting sexual function and desire. A healthy lifestyle, encompassing regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, can contribute to optimal hormonal function and overall sexual health.
The Limitations of Simplifying the Relationship
The relationship between sex hormones and human sexual behavior is far more intricate than simple cause-and-effect relationships suggest. While hormones undeniably play a vital role, their influence is moderated and mediated by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, psychological, and lifestyle factors. Oversimplifying this relationship can lead to inaccurate and potentially harmful conclusions.
For example, attributing low libido solely to low testosterone levels without considering other potential contributing factors can lead to inappropriate and ineffective interventions. Similarly, focusing exclusively on hormonal treatments for sexual dysfunction without addressing underlying psychological or relational issues can be counterproductive.
Future Directions in Research
Further research is needed to fully elucidate the complex interplay between sex hormones and human sexual behavior. This includes:
- Advanced genetic studies: Investigating specific genes and gene interactions influencing hormone production and sensitivity.
- Longitudinal studies: Tracking hormonal changes and sexual behavior over time to better understand the dynamic nature of their relationship.
- Interdisciplinary approaches: Integrating insights from endocrinology, psychology, sociology, and neuroscience to provide a more holistic understanding.
- Personalized medicine: Developing tailored interventions based on individual genetic profiles, hormonal levels, and other relevant factors.
Conclusion: A Holistic Perspective
In conclusion, research on sex hormones and human sexual behavior indicates a far more intricate relationship than previously understood. While hormones play a crucial role in influencing sexual desire, arousal, and function, their influence is inseparable from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, psychological, and lifestyle factors. A holistic perspective that acknowledges this complexity is essential for developing effective interventions and fostering a more nuanced understanding of human sexuality. Future research, employing advanced methodologies and interdisciplinary collaborations, is crucial for unlocking the full spectrum of this multifaceted relationship. This will not only enhance our scientific understanding but also empower individuals to navigate their own sexual experiences with greater self-awareness and informed decision-making. The simplistic view of hormones as the sole drivers of sexual behavior needs to be replaced with a comprehensive model that accounts for the rich tapestry of factors contributing to the human sexual experience.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Outdoor Exit Discharge Requirements Include All Of These Factors Except
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Would Yield The Highest Performance
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Knee Jerk Reflex Is An Example Of A
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Can Tangled Lead Wires Lead To
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Third Party Network Analysis Tool
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Research On Sex Hormones And Human Sexual Behavior Indicates That . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
