Outdoor Exit Discharge Requirements Include All Of These Factors Except
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
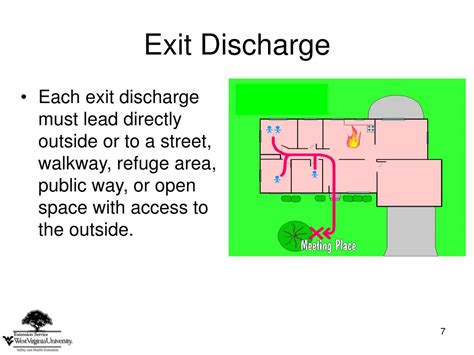
Table of Contents
Outdoor Exit Discharge Requirements: Everything You Need to Know (Except One Thing!)
Designing safe and accessible buildings requires careful consideration of numerous factors, especially concerning emergency exits. Outdoor exit discharge requirements are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient evacuation of occupants in case of fire or other emergencies. These regulations cover various aspects, from the width and number of exits to the accessibility and surrounding environment. But what's often overlooked is the exception – the one factor that isn't explicitly covered by these requirements. Let's delve into the comprehensive details of outdoor exit discharge regulations and uncover that missing piece.
Understanding Outdoor Exit Discharge Requirements
Outdoor exit discharge requirements aim to prevent bottlenecks and ensure a swift and orderly evacuation. They are typically governed by building codes and fire safety regulations, which vary slightly depending on the location and the type of building. However, some common elements consistently appear across most jurisdictions.
1. Adequate Exit Width and Number
The minimum width and number of exits are determined by factors like the building's occupancy load and the intended use. High-occupancy buildings, such as schools, hospitals, and commercial complexes, necessitate wider and more numerous exits to accommodate a larger potential outflow of people. These dimensions are carefully calculated to ensure sufficient space for safe and rapid evacuation without congestion. The calculations often incorporate factors like the expected rate of egress and the potential for panic during an emergency.
2. Unobstructed Access and Travel Distance
Exit routes must be free from obstructions that could hinder evacuation. This includes ensuring that corridors, stairwells, and pathways leading to the exterior are clear and accessible at all times. Obstructions such as furniture, storage items, or even poorly placed signage can significantly impact the speed and efficiency of evacuation. The maximum travel distance from any point within the building to the nearest exit is also strictly regulated, preventing occupants from being too far from safety.
3. Accessibility for People with Disabilities
Outdoor exit discharge requirements place strong emphasis on accessibility for people with disabilities. This includes providing ramps, appropriately sized doorways, and tactile paving to guide visually impaired individuals. Accessible exits must adhere to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) standards or equivalent regulations in other jurisdictions. The goal is to ensure that everyone, regardless of physical ability, can safely escape the building during an emergency.
4. Adequate Lighting and Signage
Clearly visible signage and adequate lighting along the exit routes are critical for guiding occupants to safety. Emergency lighting systems are designed to activate automatically during power outages, ensuring that exits remain visible even in darkness. Signage must be prominent, unambiguous, and comply with relevant regulations concerning size, color, and placement.
5. Safe Discharge Area
The area where occupants exit the building must be safe and free from hazards. This means ensuring sufficient space for people to gather once they are outside the building, without obstructing traffic or posing a risk of being injured. The discharge area should be well-lit, free from obstructions, and located away from potential hazards such as traffic or hazardous materials.
6. Environmental Considerations
Outdoor exit discharge requirements sometimes incorporate environmental considerations, especially in areas prone to extreme weather conditions. For instance, exits might need to be sheltered from inclement weather or protected from potential hazards like falling debris. The design must take into account local climate and environmental risks.
The Missing Factor: Predicting Human Behavior
All the elements mentioned above are crucial components of outdoor exit discharge requirements. However, one crucial aspect frequently overlooked is the unpredictable nature of human behavior during emergencies. While building codes can specify dimensions and accessibility, they cannot fully account for the panic, confusion, or irrational decisions that individuals might make in a life-threatening situation.
While regulations aim to minimize chaos through proper planning, they cannot fully eliminate the unpredictable element of human response. People might deviate from designated routes, become overwhelmed by panic, or fail to follow instructions, leading to unforeseen bottlenecks or delays in evacuation.
This unpredictable factor highlights the limitations of solely relying on building codes and regulations. Effective emergency planning requires more than just meeting minimum requirements. It necessitates comprehensive training programs for occupants, regular drills to familiarize people with exit routes, and clear communication strategies during emergencies.
Furthermore, simulating emergency scenarios using advanced modeling techniques can help identify potential bottlenecks and weaknesses in the evacuation plan, allowing for timely adjustments and improvements. These supplementary measures address the inherent unpredictability of human behavior and enhance the overall effectiveness of emergency preparedness.
Beyond the Code: Proactive Measures for Safety
To truly ensure a safe and efficient evacuation, building owners and managers must go beyond simply complying with minimum requirements. Here are some key proactive measures:
-
Regular Fire Drills: Conducting regular and well-organized fire drills is essential for familiarizing occupants with evacuation procedures. Drills should be realistic and cover various scenarios, allowing people to practice escaping safely and efficiently.
-
Clear Signage and Communication: Ensure that all signage is clear, consistent, and visible, even in low-light conditions. Establish a clear communication system for emergencies, allowing for rapid and effective instructions to be relayed to occupants.
-
Staff Training: Train staff members on emergency procedures, including evacuation plans, assisting occupants with disabilities, and managing potential emergencies. Well-trained staff are vital for guiding people to safety and ensuring a smooth evacuation.
-
Accessibility Audits: Regularly conduct accessibility audits to identify and address any potential barriers to evacuation for people with disabilities. This includes checking for obstructions, ensuring adequate signage, and verifying the functionality of accessible features.
-
Emergency Lighting and Power Systems: Invest in robust emergency lighting and power systems to ensure that exits remain visible even during power outages. These systems should be regularly inspected and maintained to guarantee their effectiveness.
-
Security and Monitoring Systems: Install security and monitoring systems to enhance building security and to detect potential emergencies early. This allows for timely intervention and potentially prevents the emergency from escalating.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Safety
Outdoor exit discharge requirements are essential for ensuring safe and efficient evacuation during emergencies. However, simply complying with minimum regulations is not sufficient. A truly comprehensive approach requires proactive measures to mitigate the unpredictable element of human behavior during emergencies. By implementing regular drills, effective communication strategies, comprehensive staff training, and regular safety audits, building owners and managers can significantly improve the safety of their occupants and ensure that everyone can escape safely and efficiently in case of an emergency. The focus should shift from mere code compliance to a holistic approach that prioritizes the well-being of all building occupants.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Serviceability Is The Dimension Of Quality That Refers To
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Company Sells 10000 Shares Indeed
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Velocity Field Of A Flow Is Given By
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Hawthorne Studies Found That Employees In The Experimental Group
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Does Cmg Have A Higher Wacc Than Sbux
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Outdoor Exit Discharge Requirements Include All Of These Factors Except . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
