On May 1 Foxtrot Company Agreed To Sell
Holbox
Mar 20, 2025 · 7 min read
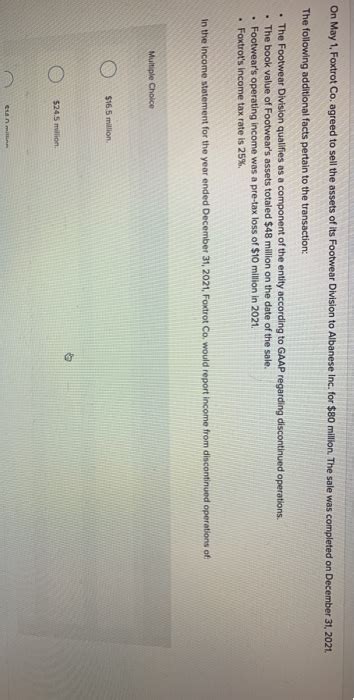
Table of Contents
On May 1, Foxtrot Company Agreed to Sell: A Deep Dive into Contract Law and Business Implications
On May 1st, when Foxtrot Company agreed to sell its assets, a pivotal moment occurred, triggering a cascade of legal and financial implications. This seemingly simple act initiates a complex process governed by contract law, demanding meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of the involved parties' rights and obligations. This article delves into the intricacies of such an agreement, exploring the key legal aspects, potential challenges, and the broader business context surrounding the transaction.
Understanding the Contractual Agreement: The Foundation of the Sale
The agreement reached on May 1st forms the bedrock of the entire transaction. Its validity hinges on several critical elements: offer, acceptance, consideration, intention to create legal relations, and capacity.
-
Offer: Foxtrot Company made an offer to sell its assets, specifying the terms and conditions of the sale. This offer must be clear, unambiguous, and demonstrably communicated to the buyer. Vague or incomplete offers can be challenged in court, potentially leading to lengthy disputes.
-
Acceptance: The buyer accepted Foxtrot Company's offer, signifying their agreement to the terms. Acceptance must be unequivocal and mirror the offer. Any changes or counter-offers constitute a rejection of the initial offer and the creation of a new one.
-
Consideration: Both parties must exchange something of value. For Foxtrot Company, this is the assets being sold; for the buyer, it's the agreed-upon purchase price. Consideration must be sufficient, although it doesn't need to be adequate (meaning its value doesn't have to perfectly match the market value of the assets).
-
Intention to Create Legal Relations: Both parties must have intended the agreement to be legally binding. Social or domestic agreements generally lack this intention, while commercial agreements usually do. However, the specific circumstances of each case will determine whether this element is satisfied.
-
Capacity: Both parties must have the legal capacity to enter into a contract. This means they must be of legal age, of sound mind, and not subject to any legal restrictions that would prevent them from making such an agreement. Minors, individuals declared mentally incapacitated, or corporations acting outside their permitted powers lack the capacity to enter into binding contracts.
Due Diligence: Unveiling Potential Pitfalls
Before the contract is finalized, the buyer will conduct thorough due diligence. This process involves a detailed examination of Foxtrot Company's financial records, legal standing, assets, liabilities, and any potential risks associated with the acquisition. Due diligence is crucial in identifying:
-
Financial Health: Analyzing Foxtrot Company's financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, is critical in assessing its profitability, liquidity, and overall financial stability. Hidden debts, contingent liabilities, or unsustainable business practices could significantly impact the deal.
-
Legal Compliance: The buyer will verify Foxtrot Company's compliance with all relevant laws and regulations. This includes checking for any pending lawsuits, outstanding tax obligations, or environmental violations. Failure to comply could expose the buyer to significant legal and financial risks.
-
Asset Valuation: An independent valuation of Foxtrot Company's assets is often conducted to ensure the purchase price is fair and reasonable. This involves assessing the market value of tangible assets (e.g., property, equipment) and intangible assets (e.g., intellectual property, brand reputation).
-
Intellectual Property Rights: A thorough examination of Foxtrot Company's intellectual property portfolio is crucial, particularly if these assets are a significant part of the sale. The buyer needs to ensure that all necessary licenses, patents, and trademarks are included in the transaction and that there are no encumbrances on these rights.
-
Environmental Liabilities: Potential environmental contamination or non-compliance with environmental regulations could lead to substantial cleanup costs and penalties for the buyer. Environmental due diligence is therefore a critical aspect of the process.
Contractual Clauses: Navigating the Fine Print
The contract itself will contain numerous clauses addressing specific aspects of the sale. Key clauses to consider include:
-
Purchase Price and Payment Terms: This specifies the total price and the payment schedule. This could involve a lump-sum payment, installments, or a combination of both. Escrow accounts are often used to ensure secure payment and protect both parties' interests.
-
Representations and Warranties: These statements made by Foxtrot Company assure the buyer of certain facts about the business and its assets. These could include statements about the accuracy of financial statements, compliance with laws, and the absence of material liabilities. Breaches of these representations and warranties can give the buyer grounds to sue for damages or rescind the contract.
-
Covenants: These are promises made by the parties to perform certain actions or refrain from specific actions during the period leading up to the closing of the sale and potentially beyond. For example, Foxtrot Company might agree not to enter into new contracts that could negatively impact the business's value.
-
Conditions Precedent: These are conditions that must be met before the contract becomes legally binding. For example, the buyer might require financing approval or a satisfactory environmental audit before proceeding with the sale.
-
Indemnification Clauses: These protect the buyer against losses or liabilities arising from unforeseen circumstances related to the acquisition. Foxtrot Company might be required to indemnify the buyer against certain claims or liabilities related to past actions or omissions.
-
Termination Clause: This outlines the conditions under which either party can terminate the agreement. This might include breaches of contract, failure to satisfy conditions precedent, or material adverse changes in the business.
Post-Sale Obligations and Transition Planning
Even after the sale is completed, there are ongoing obligations for both parties. Foxtrot Company might be required to cooperate with the buyer during the transition period, providing assistance with transferring employees, intellectual property, and other assets. The contract will typically specify the duration and scope of this post-sale cooperation. Furthermore, the buyer needs to integrate the acquired assets effectively into their existing operations, which often involves significant strategic planning and operational changes.
Tax Implications: A Crucial Consideration
The sale of Foxtrot Company's assets will have significant tax implications for both the seller and the buyer. Capital gains taxes will likely be applicable to Foxtrot Company, while the buyer might be able to deduct certain expenses related to the acquisition. Tax planning is crucial in minimizing tax liabilities and ensuring compliance with all relevant tax laws. Seeking professional tax advice is essential to navigate the complexities of this aspect of the transaction.
Potential Disputes and Legal Recourse
Despite the careful planning and execution, disputes can still arise during or after the sale. These might involve disagreements over the purchase price, breaches of contract, or disputes over liabilities. Mediation or arbitration can be used to resolve these disputes outside of court, offering a more efficient and cost-effective approach. However, if these methods fail, litigation might be necessary to enforce the contract or resolve outstanding issues.
Conclusion: A Holistic Perspective
The agreement reached on May 1st to sell Foxtrot Company's assets is a significant event with far-reaching consequences. Navigating the legal, financial, and operational complexities requires a thorough understanding of contract law, due diligence procedures, and the specific circumstances of the transaction. Careful planning, experienced legal counsel, and a meticulous approach are vital to ensure a successful and mutually beneficial outcome for all parties involved. This multifaceted transaction underscores the importance of comprehensive legal documentation and a proactive approach to risk management throughout the entire process. From the initial offer and acceptance to post-sale integration and potential dispute resolution, each step demands a high level of attention to detail to safeguard the interests of all stakeholders. The complexities of this scenario highlight the need for professional guidance at every stage, ensuring a smooth and legally sound transaction. The success of this agreement rests not only on the initial terms but also on the diligent execution and ongoing collaboration between the involved parties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Standard Overhead Rate Is Computed Separately For
Mar 21, 2025
-
Knowledge Drill 9 7 Serum Appearance
Mar 21, 2025
-
Draw The Expected Major Elimination Product And Identify The Mechanism
Mar 21, 2025
-
In Which Case Can Alphaland Consume At Point Z
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Inside Force For Change
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about On May 1 Foxtrot Company Agreed To Sell . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
