How Do Financial Capital Markets Transform Financial Capital Flows
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
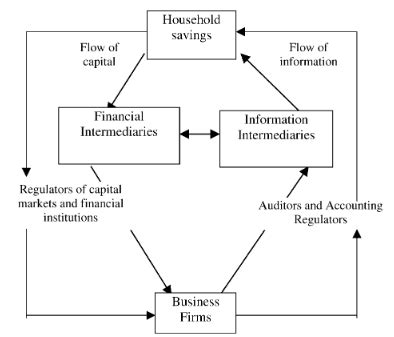
Table of Contents
How Financial Capital Markets Transform Financial Capital Flows
Financial capital markets play a pivotal role in the global economy, acting as the crucial conduits through which financial capital flows are channeled, transformed, and ultimately allocated. Understanding how these markets achieve this transformation is key to grasping the dynamics of international finance and economic development. This article delves into the intricate mechanisms by which financial capital markets impact capital flows, exploring their influence on both the volume and direction of these flows.
The Fundamental Role of Financial Capital Markets
Financial capital markets, encompassing stock markets, bond markets, foreign exchange markets, and derivatives markets, provide a platform for the efficient allocation of capital. They connect savers (individuals, corporations, and governments with surplus funds) with borrowers (individuals, corporations, and governments needing funds for investment). This fundamental function is crucial because without efficient markets, capital would be misallocated, hindering economic growth and development.
Facilitation of Capital Mobility
One of the primary ways financial capital markets transform capital flows is by dramatically increasing their mobility. Before the development of sophisticated financial markets, capital movement was largely restricted by geographical boundaries and information asymmetry. Transactions were costly and time-consuming, limiting the ability of funds to flow to their most productive uses. Financial capital markets break down these barriers:
- Reduced Transaction Costs: Modern markets use technology to facilitate transactions, lowering costs significantly. Electronic trading platforms, for instance, allow for instantaneous trades at competitive prices, drastically reducing the expense and time involved.
- Improved Information Availability: The transparency of publicly traded securities provides investors with readily accessible information about companies and their performance. This reduces information asymmetry, allowing for more informed investment decisions and promoting efficient capital allocation.
- Increased Liquidity: Financial markets offer high liquidity, meaning that assets can be easily bought and sold without significantly impacting their price. This liquidity encourages investment as investors know they can readily convert their assets into cash when needed.
Transforming the Nature of Capital Flows
Beyond simply facilitating capital movement, financial capital markets fundamentally alter the nature of capital flows. They do this through several key mechanisms:
Diversification and Risk Management
Financial markets allow investors to diversify their portfolios, spreading their risk across different assets and geographies. This reduces the overall risk of investment, encouraging investment in higher-risk but potentially higher-return ventures. This diversification is particularly crucial for international capital flows, allowing investors to hedge against country-specific risks. Derivatives markets offer further risk management tools, enabling investors to manage exposure to currency fluctuations, interest rate changes, and other market risks.
Enhancing Capital Allocation Efficiency
Markets act as powerful mechanisms for directing capital towards its most productive uses. Through price signals generated by supply and demand, capital is automatically channeled towards projects with the highest expected returns. This efficient allocation fuels economic growth and innovation. Inefficient markets, conversely, lead to misallocation, stifling growth and hindering development.
Fostering Innovation and Entrepreneurship
The availability of capital through financial markets encourages innovation and entrepreneurship. Startups and small businesses, often lacking access to traditional funding sources, can leverage equity markets or venture capital to obtain funding for growth and expansion. This access to capital fuels innovation and drives economic dynamism.
Impact on Volume and Direction of Capital Flows
Financial capital markets significantly influence both the volume and direction of global capital flows.
Increased Volume of Capital Flows
The efficiency and accessibility provided by these markets have exponentially increased the volume of cross-border capital flows. Investors can now easily invest in assets across borders, leading to larger and more frequent capital movements. This increased volume has profound implications for global economic integration and interdependence.
Shifting Direction of Capital Flows
Financial capital markets also affect the direction of capital flows. Changes in market sentiment, interest rates, economic growth prospects, and political stability can all influence where capital flows. For example, periods of high economic growth in a particular region often attract large capital inflows, while political instability may lead to capital outflows.
- Interest Rate Differentials: Capital tends to flow from countries with lower interest rates to countries with higher interest rates, seeking higher returns. This dynamic is a key driver of international capital flows.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates influence the attractiveness of investments in different countries. A strengthening currency can attract foreign investment, while a weakening currency may lead to capital outflows.
- Economic Growth Prospects: Countries with strong economic growth prospects typically attract larger capital inflows as investors seek to benefit from high returns.
- Political and Economic Stability: Investors generally prefer to invest in politically and economically stable countries, avoiding regions with high levels of risk and uncertainty.
The Role of Market Regulation and Supervision
The efficient functioning of financial capital markets relies heavily on robust regulation and supervision. These mechanisms aim to:
- Maintain Market Integrity: Regulations are essential to prevent fraud, manipulation, and other forms of market abuse.
- Protect Investors: Regulations help to protect investors from unscrupulous practices and ensure fair and transparent markets.
- Promote Systemic Stability: Strong regulatory frameworks are crucial to prevent financial crises and maintain the stability of the financial system.
- Manage Systemic Risk: Supervisory bodies play a vital role in monitoring and managing systemic risk, the risk of a widespread collapse of the financial system.
The absence or inadequacy of regulation can lead to market instability, financial crises, and ultimately, harm to the global economy.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite their many benefits, financial capital markets also face challenges:
- Increased Volatility: Global financial markets are increasingly interconnected, making them more susceptible to volatility and contagion effects. A crisis in one market can quickly spread to others.
- Regulatory Arbitrage: Differences in regulations across countries can create opportunities for regulatory arbitrage, where firms exploit loopholes to avoid regulations.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The increasing reliance on technology in financial markets exposes them to significant cybersecurity risks, including hacking and data breaches.
- Climate Change Risks: The integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions is becoming increasingly important, posing both opportunities and challenges for financial markets.
Future trends in financial capital markets include:
- Increased use of Fintech: Fintech innovations are transforming financial markets, offering new products, services, and trading platforms.
- Growing Importance of ESG Investing: Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing is gaining traction, with investors increasingly considering sustainability and ethical factors in their investment decisions.
- Rise of Digital Currencies: The emergence of cryptocurrencies and other digital currencies is reshaping the landscape of financial markets.
- Cross-border Regulatory Cooperation: Enhanced cooperation among regulators is crucial to address the challenges of globalized financial markets.
Conclusion
Financial capital markets are the engines of global capital flows, fundamentally transforming their volume, direction, and nature. By providing a platform for efficient capital allocation, risk management, and innovation, these markets play a critical role in driving economic growth and development. However, the effective functioning of these markets depends on robust regulation, supervision, and adaptation to emerging challenges. Understanding the dynamics of financial capital markets is essential for policymakers, investors, and anyone interested in the workings of the global economy. As technology and globalization continue to evolve, the role of financial capital markets in shaping the global financial landscape will only become more pronounced. The future of these markets promises exciting innovations, but also necessitates a cautious approach to managing risks and ensuring stability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Time Series Model
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Maturity Date Of A Note Receivable
Mar 16, 2025
-
Safety And Health Directors Should Be
Mar 16, 2025
-
Solve For V Where V Is A Real Number
Mar 16, 2025
-
Match The Following Terms With Their Definitions
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do Financial Capital Markets Transform Financial Capital Flows . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
