The Maturity Date Of A Note Receivable
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
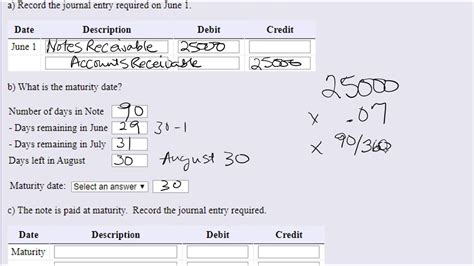
Table of Contents
The Maturity Date of a Note Receivable: A Comprehensive Guide
The maturity date of a note receivable is a crucial element in accounting and finance. Understanding this date is vital for accurate financial reporting, effective cash flow management, and avoiding potential legal complications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of note receivable maturity dates, covering their calculation, implications, and best practices for management.
What is a Note Receivable?
Before we dive into maturity dates, let's define a note receivable. A note receivable is a formal written promise by a debtor (borrower) to pay a specified sum of money to a creditor (lender) on a predetermined date. Unlike informal agreements, a note receivable provides a legally binding document outlining the terms of the loan, including:
- Principal amount: The total amount of money borrowed.
- Interest rate: The percentage charged on the principal amount.
- Maturity date: The date on which the principal and interest are due.
- Payment terms: The frequency and method of payment (e.g., lump sum, installments).
Determining the Maturity Date: Key Methods
The maturity date is typically specified in the note receivable itself. However, understanding how this date is determined is essential. Here are the common methods:
1. Specific Date
The simplest method is specifying a concrete calendar date. For example, "The borrower promises to pay the creditor $10,000 on January 15, 2025." This clearly defines the maturity date.
2. Term of Months or Years
Often, the maturity date is expressed as a period of time. For instance, "The borrower promises to pay the creditor $5,000 plus interest in six months from the date of the note." In such cases, the maturity date is calculated by adding the specified number of months or years to the note's issuance date.
Important Consideration: When calculating a maturity date based on months, the calculation usually results in the same day of the month as the issuance date, or the last day of the month if that day doesn't exist in the maturity month. For example, if a note is issued on January 31st and the term is one month, the maturity date would be February 28th (or 29th in a leap year).
3. On Demand Notes
These notes are payable upon the demand of the creditor. This means there isn't a predetermined maturity date. The creditor can request payment at any time. While seemingly flexible, demand notes present challenges in forecasting cash flows.
Accounting Implications of the Maturity Date
The maturity date significantly impacts accounting entries. At the maturity date:
- Cash is debited: This reflects the increase in cash received from the debtor.
- Notes receivable is credited: This reduces the balance of the notes receivable account, as the obligation has been fulfilled.
- Interest revenue is debited: This represents the interest earned during the note's term. (If interest was not explicitly included in the note, the interest account will not be included)
Implications of a Missed Maturity Date
Failure to pay on the maturity date has several consequences:
- Legal action: The creditor can pursue legal action to recover the outstanding amount. This might involve court proceedings, potentially leading to significant legal costs.
- Interest penalties: Many notes include stipulations for late payment penalties, adding to the amount owed.
- Damaged credit rating: Defaulting on a note can negatively impact the debtor's credit score, making it difficult to secure future loans.
- Account Receivable Write-off: The creditor might have to write off the note as uncollectible, resulting in a loss on the income statement.
Best Practices for Managing Note Receivable Maturity Dates
Effective management of note receivable maturity dates is vital for maintaining sound financial health. Consider these best practices:
- Clear Documentation: Ensure the note receivable includes clear and unambiguous details about the principal amount, interest rate, and maturity date. Any disagreements about these key elements can lead to legal disputes.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of all notes receivable and their upcoming maturity dates using a tracking system or spreadsheet. This allows for proactive planning and ensures timely follow-up.
- Early Communication: If a debtor anticipates difficulty making a payment on the maturity date, encourage early communication. This opens up possibilities for negotiation, such as extensions or payment plans.
- Professional Legal Advice: For complex transactions or situations involving potential defaults, seek professional legal advice to understand your rights and options.
- Credit Risk Assessment: Thoroughly assess the creditworthiness of the borrower before issuing a note receivable. This helps mitigate the risk of non-payment.
Accrual Accounting and Note Receivables
Accrual accounting requires recognizing interest revenue over the life of the note receivable, not just on the maturity date. This means periodically recording the accrued interest as it is earned. The amount of accrued interest is calculated based on the outstanding principal balance and the applicable interest rate.
Example: A $10,000 note with a 6% annual interest rate over one year would have an annual interest income of $600. Using the straight-line method of amortization, $50 of interest is recorded each month. Although the entire $600 is not collected until maturity, it is recognized in the financial statements throughout the year.
Impact of Prepayment on Maturity Date
If the debtor pays the note before the maturity date, the creditor should calculate the amount due based on the actual time the money was outstanding. This typically involves using a formula that adjusts the interest calculation to reflect the early payment. The interest paid will likely be less than the full amount calculated for the original maturity date.
Analyzing Note Receivable Maturity Dates for Cash Flow Forecasting
The maturity dates of notes receivable are key to effective cash flow forecasting. By accurately predicting when payments will be received, businesses can better plan for expenses, investments, and other financial obligations. Incorporating these maturity dates into a detailed cash flow projection allows for improved financial management and reduces the risk of unexpected shortfalls.
Using Technology to Manage Note Receivable Maturity Dates
Many accounting software packages offer features to track and manage notes receivable, including automated reminders approaching maturity dates. Leveraging technology can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of managing these financial instruments.
Conclusion: The Significance of the Maturity Date
The maturity date of a note receivable is not simply a date on a document; it's a critical element with significant financial and legal ramifications. A clear understanding of how the maturity date is determined, its accounting implications, and the potential consequences of missed payments is crucial for both creditors and debtors. By proactively managing note receivables and applying sound financial practices, businesses can minimize risks and maximize opportunities. Remember, detailed documentation, regular monitoring, and proactive communication are essential for a successful management of note receivables and their maturity dates. This comprehensive understanding ensures sound financial practices and helps avoid potential problems in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Transfer Prices Check All That Apply
Mar 16, 2025
-
Job A3b Was Ordered By A Customer On September 25
Mar 16, 2025
-
Silver Ions React With Thiocyanate Ions As Follows
Mar 16, 2025
-
Supervisory Managers Spend Most Of Their Time On
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Would You Describe The Social Networking Site Youtube
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Maturity Date Of A Note Receivable . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
