Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Male Reproductive System
Holbox
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
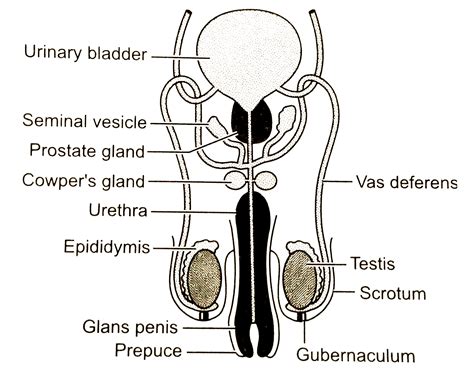
Table of Contents
- Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Male Reproductive System
- Table of Contents
- Correctly Label the Following Parts of the Male Reproductive System: A Comprehensive Guide
- The External Male Reproductive Organs: A Closer Look
- 1. Penis: The Organ of Sexual Intercourse and Urine Elimination
- 2. Scrotum: Protecting the Testes
- The Internal Male Reproductive Organs: The Engine Room of Reproduction
- 3. Testes (Testicles): Sperm Production Factories
- 4. Epididymis: Sperm Maturation and Storage
- 5. Vas Deferens (Ductus Deferens): Transporting Sperm
- 6. Ejaculatory Ducts: The Final Stage Before Ejaculation
- 7. Seminal Vesicles: Providing Nutrients for Sperm
- 8. Prostate Gland: Adding Volume and Nutrients to Semen
- 9. Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper's Glands): Pre-Ejaculate Production
- 10. Urethra: The Passageway for Semen and Urine
- Maintaining Reproductive Health: A Holistic Approach
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Correctly Label the Following Parts of the Male Reproductive System: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the male reproductive system is crucial for overall health and well-being. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricate anatomy of the male reproductive system, providing detailed descriptions and accurate labeling of each component. We'll explore the functions of each part, their interrelationships, and the importance of maintaining their health. This in-depth look will help you correctly label diagrams and deepen your understanding of this vital system.
The External Male Reproductive Organs: A Closer Look
The external male reproductive organs are readily visible and play a critical role in sexual function and reproduction. Let's examine them in detail:
1. Penis: The Organ of Sexual Intercourse and Urine Elimination
The penis is the most prominent external male reproductive organ. Its primary functions are sexual intercourse and urination. It's composed of three cylindrical masses of erectile tissue:
- Corpora Cavernosa: Two dorsal columns of erectile tissue that fill with blood during arousal, causing an erection.
- Corpus Spongiosum: A single ventral column of erectile tissue that surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries both urine and semen. The glans penis, the sensitive tip of the penis, is formed by the expanded end of the corpus spongiosum.
The prepuce, or foreskin, is a fold of skin covering the glans penis. Circumcision involves the surgical removal of the prepuce. The frenulum is a small fold of tissue on the underside of the penis connecting the prepuce to the glans. Understanding the distinct anatomical features of the penis is crucial for accurate labeling and comprehending its functionality.
2. Scrotum: Protecting the Testes
The scrotum is a sac-like structure that hangs below the penis. It contains the testes and plays a vital role in regulating their temperature. The scrotum's temperature must be slightly lower than body temperature for optimal sperm production. This temperature regulation is achieved through a complex interplay of muscles and blood vessels within the scrotum. The scrotum's wrinkled appearance allows for expansion and contraction, further contributing to temperature regulation. Accurate labeling should include identifying the distinct left and right scrotal halves.
The Internal Male Reproductive Organs: The Engine Room of Reproduction
The internal male reproductive organs are located within the pelvis and are responsible for sperm production, maturation, and delivery. Let's explore these crucial components:
3. Testes (Testicles): Sperm Production Factories
The testes (singular: testis) are the primary male reproductive organs. They are responsible for producing sperm (spermatozoa) and the male sex hormone, testosterone. Each testis is composed of numerous seminiferous tubules, where sperm production takes place. These tubules are tightly coiled and highly organized, maximizing the surface area for sperm generation. The testes are also responsible for producing inhibin, a hormone that regulates sperm production. Proper labeling should clearly differentiate between the left and right testis.
4. Epididymis: Sperm Maturation and Storage
The epididymis is a long, coiled tube located on the surface of each testis. It receives immature sperm from the testes and provides an environment for sperm maturation. The epididymis is crucial for sperm acquiring the ability to swim and fertilize an egg. It also serves as a storage site for mature sperm before ejaculation. The epididymis plays a vital role in the reproductive process, and accurate labeling requires an understanding of its intricate structure and location.
5. Vas Deferens (Ductus Deferens): Transporting Sperm
The vas deferens (plural: vasa deferentia) is a muscular tube that carries mature sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct. It's part of the spermatic cord, a bundle of tissues that also includes blood vessels, nerves, and the cremaster muscle, which helps regulate testicular temperature. The vas deferens undergoes peristaltic contractions to propel sperm towards the ejaculatory duct during ejaculation. Accurate labeling should clearly distinguish the vas deferens from other structures within the spermatic cord.
6. Ejaculatory Ducts: The Final Stage Before Ejaculation
The ejaculatory ducts are short tubes formed by the union of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle duct. They carry sperm and seminal fluid towards the urethra, preparing for ejaculation. These ducts are crucial for the final stages of sperm transport, and their accurate labeling requires a good understanding of their location and function within the reproductive system.
7. Seminal Vesicles: Providing Nutrients for Sperm
The seminal vesicles are a pair of sac-like glands that produce a significant portion of the seminal fluid. Seminal fluid provides nutrients and a protective environment for sperm. It's an alkaline fluid that helps neutralize the acidic environment of the vagina, increasing sperm survival rates. The components of seminal fluid, such as fructose, provide energy for sperm motility. Accurate labeling should highlight their location and relationship to the ejaculatory ducts and vas deferens.
8. Prostate Gland: Adding Volume and Nutrients to Semen
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland that surrounds the urethra just below the bladder. It secretes a milky, alkaline fluid that makes up a significant portion of semen. This fluid contributes to the volume of semen and provides additional nutrients and protection for sperm. The prostate also contains enzymes that help liquefy semen after ejaculation, allowing for easier sperm movement. Accurate labeling of the prostate gland requires careful consideration of its relationship to the urethra and bladder.
9. Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper's Glands): Pre-Ejaculate Production
The bulbourethral glands (also known as Cowper's glands) are two small glands located below the prostate gland. They secrete a clear, viscous fluid called pre-ejaculate before ejaculation. This fluid lubricates the urethra and neutralizes any remaining acidic urine, creating a more favorable environment for sperm. While contributing only a small volume to the ejaculate, pre-ejaculate plays a significant role in preparing the urethra for sperm passage. Accurate labeling requires understanding their position relative to the urethra and prostate.
10. Urethra: The Passageway for Semen and Urine
The urethra is a tube extending from the bladder through the penis. It serves as a passageway for both urine and semen. During ejaculation, the urinary sphincter closes, preventing urine from mixing with semen. The urethra's dual function highlights its importance in both urinary and reproductive systems. Accurate labeling of the urethra should emphasize its role in both systems and its passage through the penis.
Maintaining Reproductive Health: A Holistic Approach
Maintaining the health of the male reproductive system is crucial for overall well-being and fertility. This requires a holistic approach that includes:
-
Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to a healthcare professional for check-ups and screenings are essential for early detection of any potential problems.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, contributes significantly to reproductive health.
-
Sexual Health Awareness: Understanding sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and practicing safe sex are vital for preventing complications.
-
Early Detection of Issues: Being aware of potential issues such as testicular cancer, prostate cancer, and infertility, and seeking prompt medical attention if any symptoms arise, is crucial.
By understanding the anatomy and physiology of the male reproductive system, you can better appreciate its complexity and the importance of maintaining its health. This detailed guide, along with accurate labeling of each component, will contribute to a deeper understanding of this vital system and its role in reproduction and overall well-being. Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking regular medical check-ups are key to preserving reproductive health throughout life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Record The Adjusting Entry Related To Outstanding Checks If Necessary
Mar 23, 2025
-
When Must A Signal Person Be Used
Mar 23, 2025
-
For This Graph Mark The Statements That Are True
Mar 23, 2025
-
Prepare The Current Year End Balance Sheet For Armani Company
Mar 23, 2025
-
Based On The Sign Of The Standard Cell Potential
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Male Reproductive System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
