Choose The Best Lewis Structure For Ocl2.
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 4 min read
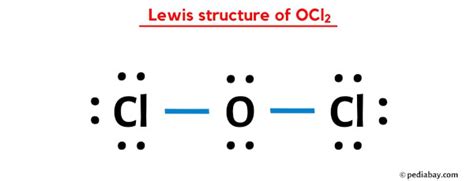
Table of Contents
Choosing the Best Lewis Structure for OCl₂: A Deep Dive
Determining the optimal Lewis structure for a molecule is crucial for understanding its bonding, geometry, and properties. OCl₂, or dichlorine monoxide, presents a particularly interesting case study because several possible Lewis structures can be drawn. This article will explore the various possible structures, analyze their validity using formal charge calculations and octet rule considerations, and ultimately identify the best representation of OCl₂'s bonding.
Understanding Lewis Structures and Formal Charges
A Lewis structure, also known as a Lewis dot diagram, is a visual representation of the valence electrons in a molecule. It shows how atoms are bonded together and the distribution of lone pairs of electrons. The goal is to create a structure that minimizes formal charges and satisfies the octet rule (or duet rule for hydrogen) for all atoms where possible.
Formal charge is a theoretical charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming equal sharing of electrons in a bond. It's calculated using the formula:
Formal Charge = (Valence electrons) - (Non-bonding electrons) - (1/2 * Bonding electrons)
A lower formal charge on each atom generally indicates a more stable Lewis structure.
Possible Lewis Structures for OCl₂
Several Lewis structures can be initially drawn for OCl₂. Let's explore a few:
Structure 1: Oxygen as the Central Atom with Double Bonds
..
:O::
/ \
:Cl: :Cl:
..
In this structure, oxygen forms double bonds with each chlorine atom. Oxygen has eight valence electrons, satisfying the octet rule. Each chlorine atom also has eight valence electrons.
Structure 2: Oxygen as the Central Atom with Single Bonds and Lone Pairs
..
:O:
/ | \
:Cl: :Cl:
.. ..
Here, oxygen forms single bonds with each chlorine atom, and it also has two lone pairs of electrons. Oxygen still has eight valence electrons, satisfying the octet rule. Each chlorine atom has eight valence electrons.
Structure 3: Chlorine as the Central Atom (Less Likely)
While less probable given oxygen's higher electronegativity, we can also consider a structure with chlorine as the central atom:
..
:Cl:
/ \
:O: :Cl:
..
This structure is less likely due to the significantly higher electronegativity of oxygen compared to chlorine. Electronegativity dictates that the more electronegative atom is more likely to be the central atom.
Evaluating the Structures Using Formal Charges
Let's calculate the formal charges for each atom in each structure:
Structure 1:
- Oxygen: 6 - 0 - (1/2 * 4) = +2
- Chlorine (each): 7 - 6 - (1/2 * 2) = 0
Structure 2:
- Oxygen: 6 - 4 - (1/2 * 4) = 0
- Chlorine (each): 7 - 6 - (1/2 * 2) = 0
Structure 3:
- Chlorine (central): 7 - 4 - (1/2 * 4) = +1
- Oxygen: 6 - 6 - (1/2 * 2) = -1
- Chlorine (terminal): 7 - 6 - (1/2 * 2) = 0
Choosing the Best Lewis Structure
Based on the formal charge calculations, Structure 2 is the best Lewis structure for OCl₂. This is because:
- Minimized Formal Charges: Structure 2 has a formal charge of zero on all atoms. Structure 1 has a +2 formal charge on oxygen, which is highly unfavorable. Structure 3 has a positive formal charge on the central Chlorine and a negative formal charge on the Oxygen. A structure with zero formal charges on all atoms is generally preferred.
- Octet Rule Satisfaction: All atoms in Structure 2 satisfy the octet rule.
- Electronegativity Considerations: Structure 2 places the more electronegative oxygen atom in the central position, which is consistent with electronegativity trends.
Further Considerations: Resonance Structures and Molecular Geometry
While Structure 2 is the best single Lewis structure, it's important to note that resonance structures can also be considered. Although the formal charges suggest a single optimal structure, a slight resonance contribution from structures where a double bond exists between oxygen and one of the chlorines could be considered. However, the contribution of such resonance structures is minor compared to the dominant structure with single bonds to both chlorines.
The molecular geometry of OCl₂, predicted using VSEPR theory based on the preferred Lewis structure (Structure 2), is bent or V-shaped. This is because the central oxygen atom has two bonding pairs and two lone pairs of electrons, resulting in a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry and a bent molecular geometry.
Conclusion: OCl₂'s Best Representation
In conclusion, the best Lewis structure for OCl₂ is the one where oxygen is the central atom, forming single bonds with each chlorine atom and possessing two lone pairs of electrons. This structure minimizes formal charges, satisfies the octet rule for all atoms, and aligns with electronegativity principles. While resonance structures might exist, their contribution to the overall structure is negligible. Understanding this optimal structure is critical for predicting the molecule's geometry, reactivity, and other properties. The bent molecular geometry arising from this structure significantly influences OCl₂'s behavior and interactions. This detailed analysis of Lewis structures highlights the importance of formal charge calculations and the octet rule in determining the most accurate and stable representation of molecular bonding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Important Characteristics Of Antimicrobic Drugs Include
Mar 19, 2025
-
All Amino Acids Have Two Ionizable Functional Groups
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Suggested Active Reading Strategy Is To
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Goal Of Any Marketing Communication Is To
Mar 19, 2025
-
Prepare An Income Statement For The Year Ended December 31
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Choose The Best Lewis Structure For Ocl2. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
