Based On This Model Households Earn Income When
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
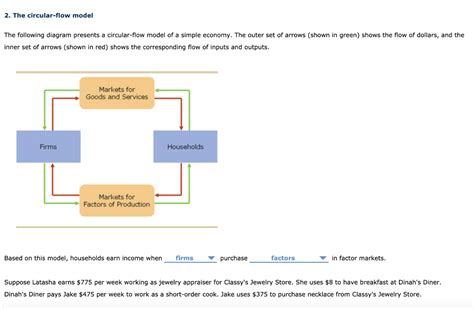
Table of Contents
Based on This Model, Households Earn Income When… A Deep Dive into Household Income Generation
Understanding how households earn income is fundamental to comprehending economic activity and societal well-being. This article will delve deep into the various income streams available to households, analyzing the contributing factors and exploring the complexities of modern economic models. We will examine the theoretical underpinnings and real-world applications, providing a comprehensive overview of this crucial aspect of economics.
The Foundation: Factors Influencing Household Income
Before exploring the when of income generation, let's establish the how. Several key factors directly influence a household's income potential:
1. Human Capital: Skills, Education, and Experience
Human capital represents the economic value of an individual's skills, knowledge, and experience. This is arguably the most significant factor determining earning potential. Higher levels of education, specialized training, and practical experience typically translate into higher-paying jobs and increased earning capacity. The when a household earns income related to human capital is directly linked to employment – whether it's securing a job after graduation, switching careers for higher pay, or receiving promotions based on demonstrated skills.
2. Labor Market Conditions: Supply and Demand
The overall state of the labor market significantly impacts income generation. A strong economy with high demand for labor often results in higher wages and more job opportunities. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to unemployment, wage stagnation, or even wage reductions. The when income is earned in this context is influenced by the cyclical nature of the economy, with periods of robust income generation followed by potentially leaner times. Understanding these cycles is crucial for financial planning.
3. Occupational Choice: Specialized vs. General Skills
The specific occupation chosen also plays a crucial role. Highly specialized professions often command higher salaries due to the specialized skills and training required. However, the demand for these professions can fluctuate. General skills, while potentially offering more employment stability, may not yield as high a return in terms of income. The when the household earns a higher income here relates to career progression within a chosen field, often requiring significant time and investment.
4. Capital Assets: Investments and Ownership
Capital assets, such as investments, real estate, and business ownership, represent a significant source of income for many households. These assets generate income through dividends, rental income, capital gains, and business profits. The when income is earned from capital assets is less predictable than employment income, relying on market fluctuations and investment returns. This income stream often represents a more long-term strategy for financial growth.
5. Government Transfers: Social Security and Welfare
Government transfer payments, such as social security benefits, unemployment insurance, and welfare programs, provide a crucial safety net for households facing financial hardship or retirement. These payments are not earned in the traditional sense but are crucial for maintaining a minimum standard of living. The when a household receives these payments is determined by eligibility criteria and specific government programs.
6. Entrepreneurial Activity: Business Ownership and Innovation
Starting and running a business provides the potential for significant income generation, but it also involves a higher level of risk. Successful businesses can generate substantial profits, while unsuccessful ventures can result in financial losses. The when income is earned in this context is tied to the success and growth of the business, often requiring significant upfront investment and time commitment.
Dissecting the "When": Timing of Household Income Generation
Understanding the when of income generation is critical for effective financial planning and economic analysis. Several key aspects influence the timing:
1. Regular Employment Income: Salaried vs. Hourly
For households relying on employment income, the timing is usually regular and predictable. Salaried employees receive income at fixed intervals (e.g., monthly, bi-weekly), while hourly workers' income varies depending on the number of hours worked. However, even regular employment income can be disrupted by factors like layoffs, seasonal work, or unexpected illness.
2. Irregular Income Streams: Gig Economy and Freelancing
The rise of the gig economy has introduced more irregular income streams. Freelancers, independent contractors, and gig workers often experience fluctuating income, depending on project availability and client demand. Financial planning for households relying on these income streams requires careful budgeting and savings strategies to manage periods of low income.
3. Investment Income: Dividend Payments and Capital Gains
Investment income is less predictable and often depends on market conditions. Dividend payments are usually scheduled but can vary depending on the performance of the company. Capital gains are realized only when assets are sold, making their timing dependent on investment strategy and market fluctuations.
4. Seasonal Income: Agriculture and Tourism
Certain industries, like agriculture and tourism, exhibit significant seasonal variations in income. Households in these sectors experience periods of high income followed by periods of lower income. Effective financial management requires saving during peak seasons to offset income lows during the off-season.
5. Unexpected Income: Inheritance and Windfalls
Unexpected income, such as inheritance or lottery winnings, can significantly impact household finances. The timing is completely unpredictable, highlighting the importance of having a solid financial plan in place to manage such sudden influxes of funds.
Modeling Household Income: A Multifaceted Approach
Modeling household income requires considering the interplay of various factors. Simple models might focus on a single income source, such as wages, while more sophisticated models incorporate multiple income streams, risk factors, and the impact of government policies.
1. Simple Models: Focusing on Wage Income
Basic models might assume a stable wage income, ignoring other sources of income or potential disruptions. These models are useful for illustrating fundamental economic concepts but lack the complexity to reflect the reality of most households.
2. Dynamic Models: Incorporating Multiple Income Streams and Risk
More sophisticated models incorporate multiple income streams, fluctuating wages, and the likelihood of unemployment or other income disruptions. These dynamic models provide a more realistic picture of household income generation, especially when considering long-term financial planning.
3. Microsimulation Models: Simulating Individual Household Behavior
Microsimulation models simulate the behavior of individual households, taking into account factors such as education, occupation, family structure, and access to social safety nets. These models can be used to analyze the impact of various policies on income distribution and household well-being.
Policy Implications: Addressing Income Inequality and Poverty
Understanding household income generation is crucial for developing effective policies to address income inequality and poverty. Policy interventions can target various aspects of income generation:
1. Investing in Human Capital: Education and Training
Investing in education and training programs enhances human capital, increasing earning potential and reducing income inequality. These investments can take the form of scholarships, apprenticeships, and job training initiatives.
2. Strengthening the Labor Market: Job Creation and Wage Regulation
Policies aimed at job creation and wage regulation can improve labor market conditions, leading to higher wages and reduced unemployment. These policies can include infrastructure investments, tax incentives for businesses, and minimum wage legislation.
3. Expanding Social Safety Nets: Unemployment Benefits and Welfare Programs
Strengthening social safety nets provides crucial support for households facing economic hardship. This includes improving access to unemployment benefits, affordable healthcare, and other welfare programs.
4. Promoting Entrepreneurship: Access to Capital and Business Support
Supporting entrepreneurship through access to capital, business training, and mentorship programs can create new income opportunities and reduce reliance on traditional employment.
Conclusion: A Holistic View of Household Income
Understanding how and when households earn income is vital for both individual financial planning and broader economic policy. This article has explored the multiple factors contributing to household income generation, from human capital and labor market conditions to capital assets and government transfers. We’ve also examined the complexities of timing, considering regular versus irregular income streams, and the limitations and applications of different income modeling approaches. By incorporating this holistic perspective, we can better understand the dynamics of income distribution, inequality, and the overall economic well-being of households. Further research and analysis in this area are crucial for crafting effective policies that promote economic prosperity and social equity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Important Characteristics Of Antimicrobic Drugs Include
Mar 19, 2025
-
All Amino Acids Have Two Ionizable Functional Groups
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Suggested Active Reading Strategy Is To
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Goal Of Any Marketing Communication Is To
Mar 19, 2025
-
Prepare An Income Statement For The Year Ended December 31
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Based On This Model Households Earn Income When . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
