At What Point Are The Atria Repolarizing
Holbox
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
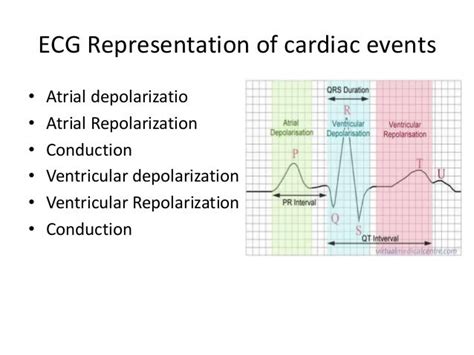
Table of Contents
- At What Point Are The Atria Repolarizing
- Table of Contents
- At What Point Are the Atria Repolarizing? Understanding Atrial Repolarization in the ECG
- The Cardiac Cycle and Atrial Repolarization: A Timeline
- Why is Atrial Repolarization Obscured on the ECG?
- Inferring Atrial Repolarization: Clues from the ECG
- Clinical Significance of Atrial Repolarization
- Advanced ECG Interpretation and Research: Unmasking Atrial Repolarization
- Conclusion: The Hidden Significance of a Hidden Wave
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
At What Point Are the Atria Repolarizing? Understanding Atrial Repolarization in the ECG
The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a cornerstone of cardiac diagnostics, providing a window into the electrical activity of the heart. While much attention is focused on the readily visible QRS complex (ventricular depolarization) and the prominent T wave (ventricular repolarization), the repolarization of the atria is often less discussed, yet equally important in understanding the complete cardiac cycle. This article delves into the intricacies of atrial repolarization, exploring its timing, its subtle manifestation on the ECG, and its clinical significance.
The Cardiac Cycle and Atrial Repolarization: A Timeline
To understand when atrial repolarization occurs, it's crucial to visualize the entire cardiac cycle. The heart's electrical activity follows a precise sequence:
-
Atrial Depolarization: Initiated by the sinoatrial (SA) node, this process spreads across the atria, causing them to contract and pump blood into the ventricles. This is represented by the P wave on the ECG.
-
Atrioventricular (AV) Node Delay: A brief delay occurs at the AV node, allowing the ventricles to fill completely before contracting.
-
Ventricular Depolarization: The electrical impulse travels down the bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers, causing ventricular contraction. This is depicted by the QRS complex on the ECG. This is significantly larger than the P wave because of the greater muscle mass of the ventricles.
-
Ventricular Repolarization: After ventricular contraction, the ventricles relax and repolarize, preparing for the next cycle. This is represented by the T wave on the ECG.
-
Atrial Repolarization: This process, the focus of this article, occurs simultaneously with the QRS complex. The electrical activity of atrial repolarization is masked by the much larger electrical forces generated during ventricular depolarization. This is why atrial repolarization is not typically a distinct wave on a standard ECG.
Why is Atrial Repolarization Obscured on the ECG?
The relatively small mass of atrial muscle compared to the ventricles results in a low-amplitude electrical signal during repolarization. This, combined with the near-simultaneous occurrence with the large QRS complex, effectively obscures the atrial repolarization wave on the standard ECG. The strong electrical forces of ventricular depolarization overshadow the weaker atrial repolarization, preventing its clear visualization.
Inferring Atrial Repolarization: Clues from the ECG
While not directly visible, subtle indicators of atrial repolarization can sometimes be gleaned from a careful analysis of the ECG:
-
The ST Segment: Some argue that subtle changes in the ST segment can reflect atrial repolarization. However, this is often confounded by other factors, making it unreliable as a primary indicator.
-
The TP Segment: The TP segment, the isoelectric line between the T wave and the next P wave, theoretically represents the period of atrial repolarization. Any significant deviation from the baseline within this segment should be carefully evaluated.
-
Advanced ECG Techniques: More sophisticated ECG techniques, such as the use of higher-gain settings or specialized leads, might offer a glimpse into atrial repolarization. However, these are not routinely used in standard clinical practice.
Clinical Significance of Atrial Repolarization
Although its direct visualization is challenging, understanding atrial repolarization is crucial for several clinical reasons:
-
Arrhythmias: Disturbances in atrial repolarization can contribute to atrial arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or flutter. These arrhythmias can lead to hemodynamic compromise, stroke, and heart failure. Although not directly visible, changes in atrial repolarization might be implicated in the genesis of these arrhythmias.
-
Electrolyte Imbalances: Electrolyte abnormalities, particularly potassium and magnesium imbalances, can significantly impact atrial repolarization. Changes in the shape or duration of the P wave, while subtle, may hint at such imbalances. While not directly observing the repolarization, the changes in the P wave can be an early indicator of underlying electrolyte issues.
-
Drug Effects: Certain medications can alter atrial repolarization. These effects may not be readily apparent on a standard ECG but could be investigated through more advanced techniques or by correlating ECG findings with clinical symptoms.
-
Ischemic Heart Disease: While not primarily affecting atrial repolarization, severe coronary artery disease can indirectly influence atrial function and potentially affect the subtle electrical events during atrial repolarization.
-
Cardiac Surgery and Interventions: Cardiac surgery or interventions like ablation procedures might alter atrial electrical activity, impacting repolarization. Monitoring for subtle changes in atrial function and rhythm is critical post-intervention.
Advanced ECG Interpretation and Research: Unmasking Atrial Repolarization
Ongoing research explores advanced ECG techniques and signal processing algorithms to better understand and visualize atrial repolarization. This may include:
-
Signal Averaging: Techniques to filter out the noise and enhance the visualization of smaller signals are currently under investigation and might improve the identification of atrial repolarization.
-
Body Surface Potential Mapping: This technique uses multiple electrodes to create a comprehensive map of the heart's electrical activity, potentially revealing more detailed information about atrial repolarization.
-
Computerized ECG Analysis: Advanced software can analyze ECG data to detect subtle changes that might be missed by the naked eye, possibly detecting patterns related to atrial repolarization disturbances.
Conclusion: The Hidden Significance of a Hidden Wave
Although atrial repolarization isn't a prominent feature of a standard ECG, its understanding is crucial for a comprehensive appreciation of cardiac electrophysiology. While the wave itself remains masked by the QRS complex, its effects are potentially significant. Subtle changes in the P wave morphology, the ST segment, or the TP segment, when correlated with clinical symptoms, can offer valuable clues about underlying cardiac issues. The ongoing advancements in ECG technology and analytical techniques promise to provide a clearer picture of this often-overlooked aspect of the cardiac cycle, contributing to better diagnosis and management of cardiac arrhythmias and other related conditions. As our understanding improves, the clinical significance of atrial repolarization will likely become even more apparent. Future research will undoubtedly shed more light on its precise mechanisms and clinical implications, improving patient care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select The Graph That Is Positively Skewed
Mar 31, 2025
-
Label The Structures Of The Pelvis
Mar 31, 2025
-
Water Held Behind A Dam Would Best Reflect
Mar 31, 2025
-
Per Company Policy Tools With A Purchase
Mar 31, 2025
-
When Should You Introduce Distractor Trials
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about At What Point Are The Atria Repolarizing . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
