Accounts Receivable Are Normally Reported At The
Holbox
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
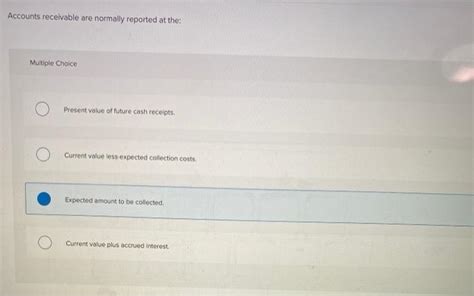
Table of Contents
Accounts Receivable are Normally Reported at Net Realizable Value
Accounts receivable (AR) represent money owed to a business by its customers for goods sold or services rendered on credit. Accurate reporting of accounts receivable is crucial for a company's financial health and the reliability of its financial statements. A key aspect of this accurate reporting is understanding how AR is valued and presented on the balance sheet. The short answer is: accounts receivable are normally reported at their net realizable value. Let's delve deeper into this concept.
Understanding Net Realizable Value
Net realizable value (NRV) represents the amount of cash a company expects to collect from its accounts receivable. It's not simply the gross amount of money owed; instead, it considers the potential for bad debts – those amounts that are unlikely to be collected. The calculation is straightforward:
Net Realizable Value = Gross Accounts Receivable - Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
-
Gross Accounts Receivable: This is the total amount owed to the company by its customers.
-
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts (AFDA): This is a contra-asset account that represents the estimated amount of uncollectible receivables. It's an estimate, and its accuracy is crucial for fair financial reporting.
Why Net Realizable Value is Used
Using net realizable value adheres to the principle of conservatism in accounting. This principle suggests that when faced with uncertainty, accountants should choose the less optimistic valuation. Since there's always a risk of some customers not paying their debts, reporting AR at the gross amount would overstate the company's assets. Using NRV provides a more realistic and prudent representation of the company's financial position.
The use of NRV also enhances the relevance and reliability of the financial statements. Investors and creditors rely on these statements to make informed decisions. Reporting AR at NRV provides a more accurate picture of the company's actual liquid assets, leading to more informed decisions.
Methods for Estimating the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Estimating the AFDA is a critical step in determining the NRV of accounts receivable. Several methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
1. Percentage of Sales Method
This method estimates bad debts based on a percentage of credit sales for a given period. The percentage is determined based on historical data, industry averages, or management's judgment. It's a relatively simple method, but it doesn't consider the age of the receivables.
Example: If a company's credit sales for the year are $1,000,000 and management estimates 2% of credit sales will be uncollectible, the AFDA would be $20,000.
Advantages: Simple and easy to implement.
Disadvantages: Doesn't consider the age of receivables; may not be accurate if credit sales fluctuate significantly.
2. Percentage of Accounts Receivable Method
This method estimates bad debts as a percentage of the existing accounts receivable balance. Similar to the percentage of sales method, the percentage is determined based on historical data, industry averages, or management's judgment. This method takes into account the current balance of receivables, providing a potentially more accurate estimate than the percentage of sales method.
Example: If a company's accounts receivable balance is $500,000 and management estimates 5% will be uncollectible, the AFDA would be $25,000.
Advantages: Considers the current balance of receivables.
Disadvantages: Doesn't consider the age of receivables; may not be accurate if the composition of receivables changes significantly.
3. Aging of Receivables Method
This is generally considered the most accurate method. It categorizes accounts receivable based on their age (e.g., 0-30 days, 31-60 days, 61-90 days, over 90 days). Each age category is assigned a percentage representing the likelihood of collection. Older receivables are typically assigned higher percentages, reflecting a greater risk of non-collection.
Example:
| Age of Receivable | Amount Outstanding | Estimated % Uncollectible | Allowance for Doubtful Accounts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-30 days | $200,000 | 1% | $2,000 |
| 31-60 days | $100,000 | 5% | $5,000 |
| 61-90 days | $50,000 | 10% | $5,000 |
| Over 90 days | $20,000 | 25% | $5,000 |
| Total | $370,000 | $17,000 |
Advantages: Considers the age of receivables, providing a more refined estimate of uncollectible amounts.
Disadvantages: More complex and time-consuming than other methods.
The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and the Income Statement
The impact of the AFDA extends beyond the balance sheet. The process of estimating and adjusting the AFDA also affects the income statement. When a company writes off a specific account receivable deemed uncollectible, it doesn't directly affect net income. Instead, it reduces the allowance for doubtful accounts and has no impact on the income statement. However, the initial estimation of the allowance for doubtful accounts is expensed on the income statement as bad debt expense.
This expense represents the company's best estimate of the receivables that will not be collected during the period. This ensures that the income statement accurately reflects the company's profitability, taking into account the potential loss from uncollectible receivables.
Factors Affecting Net Realizable Value
Several factors can impact the net realizable value of accounts receivable:
-
Economic conditions: During economic downturns, businesses may experience a higher percentage of bad debts as customers struggle to meet their financial obligations.
-
Credit policies: A company's credit policies significantly affect the quality of its receivables. Stricter credit policies can reduce the number of bad debts, while more lenient policies may increase the risk.
-
Industry norms: Certain industries are naturally more prone to bad debts than others. For example, industries with long payment cycles or volatile demand may experience higher levels of uncollectible receivables.
-
Collection efforts: Proactive collection efforts, such as sending timely reminders and following up on overdue payments, can significantly improve the collection rate and increase the NRV of accounts receivable.
-
Customer base: A company's customer base significantly influences the quality of its receivables. A customer base composed primarily of large, financially stable companies is generally associated with lower credit risk.
Importance of Accurate Reporting
Accurate reporting of accounts receivable is paramount for several reasons:
-
Financial statement reliability: Misrepresenting the NRV of AR distorts a company's financial position and performance, potentially misleading investors and creditors.
-
Creditworthiness: Accurate AR reporting contributes to a company's creditworthiness. Lenders use AR information to assess the company's ability to repay loans.
-
Internal control: Accurate AR management helps improve a company's internal control system, minimizing the risk of fraud and error.
-
Strategic decision-making: Reliable AR data enables management to make informed decisions regarding credit policies, pricing strategies, and collection efforts.
Conclusion
Accounts receivable are normally reported at net realizable value, reflecting the amount of cash a company expects to collect from its customers. Accurate estimation of the allowance for doubtful accounts is crucial for determining the NRV and ensuring the reliability of financial statements. Various methods exist for estimating the AFDA, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method depends on factors such as the company's size, industry, and the complexity of its receivables. Understanding and properly applying these concepts are vital for maintaining accurate financial records and making informed business decisions. By diligently managing and reporting accounts receivable, companies can improve their financial health and build stronger relationships with investors and creditors. The ongoing monitoring and adjustment of the AFDA, along with robust collection practices, are key components of effective accounts receivable management, ensuring the accurate reflection of the company's true financial position.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
An Account Is Said To Have A Debit Balance If
Mar 21, 2025
-
Classify The Radicals Into The Appropriate Categories
Mar 21, 2025
-
Two Spacecraft Are Following Paths In Space Given By
Mar 21, 2025
-
When Consumers Decide To Purchase A Particular Product They
Mar 21, 2025
-
Refer To Figure 4 17 At A Price Of
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Accounts Receivable Are Normally Reported At The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
