A Constraint In A Decision Is A Restriction Placed On
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 7 min read
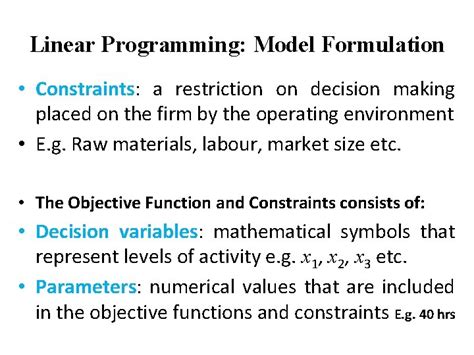
Table of Contents
A Constraint in a Decision: A Restriction Placed on Potential Choices
Constraints are an inherent part of decision-making. They represent the limitations and restrictions that shape the range of feasible options available to us. Understanding constraints is crucial for effective and rational decision-making, as ignoring them can lead to unrealistic plans and ultimately, failure. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the nature of constraints in decision-making, exploring their various types, their impact on the decision-making process, and strategies for effectively managing them.
What is a Constraint in Decision Making?
In its simplest form, a constraint in a decision is any limitation or restriction that affects the choices available to a decision-maker. These limitations can stem from various sources, internal or external, and can significantly influence the outcome of the decision-making process. Constraints are not necessarily negative; they can provide focus and structure, helping to streamline the decision-making process by eliminating infeasible options. However, understanding their nature and impact is paramount for making informed and successful choices.
Types of Constraints
Constraints can be broadly categorized into several types, each possessing unique characteristics and implications:
1. Resource Constraints: The Limits of What We Have
These are perhaps the most common type of constraint, encompassing limitations on available resources. This category includes:
-
Financial Constraints: Limited budgets significantly restrict options, particularly in business and personal finance decisions. A company may have to choose between investing in new equipment or expanding its marketing campaign due to budgetary limitations.
-
Time Constraints: Deadlines and time pressures frequently dictate decision-making. Project managers often face constraints on the time allocated to complete a project, forcing them to prioritize tasks and make trade-offs.
-
Human Resource Constraints: The availability of skilled personnel, manpower, and expertise can constrain decision-making. A company might not be able to launch a new product line if it lacks the necessary engineers or marketing specialists.
-
Material Constraints: The availability of raw materials, components, or other physical resources can limit choices. A manufacturer might have to reduce production if it experiences a shortage of a critical component.
-
Technological Constraints: Technological limitations can prevent the adoption of certain strategies or technologies. For example, a small business might not be able to implement a sophisticated CRM system due to a lack of compatible technology or expertise.
2. Legal and Regulatory Constraints: The Rules of the Game
These constraints stem from legal frameworks, regulations, and government policies. They impose restrictions on what is permissible and what is not. Examples include:
-
Environmental Regulations: Companies must adhere to environmental protection laws when making decisions about production processes and waste disposal.
-
Safety Regulations: Businesses operating in sectors like manufacturing or construction must comply with stringent safety regulations to ensure workplace safety.
-
Industry-Specific Regulations: Many industries are subject to specific regulations, such as financial regulations for banks or healthcare regulations for hospitals.
-
Contractual Obligations: Existing contracts and agreements can restrict a company's freedom to make certain decisions.
3. Ethical Constraints: The Moral Compass
Ethical considerations represent a crucial type of constraint, influencing decisions based on moral principles and values. These constraints often override purely economic or practical considerations:
-
Social Responsibility: Companies may choose to forgo profitable opportunities if they are deemed ethically questionable or harmful to society.
-
Fairness and Equity: Decisions should strive to be fair and equitable to all stakeholders involved, even if it means compromising on immediate gains.
-
Transparency and Accountability: Decisions should be transparent and accountable, ensuring that they can be justified and understood by all relevant parties.
4. Physical Constraints: The Real-World Limitations
These constraints are rooted in the physical world and represent inherent limitations in the environment or physical systems:
-
Geographic Limitations: Location plays a significant role in many decisions. A company's decision to expand operations may be constrained by the availability of suitable locations.
-
Infrastructure Limitations: The availability of adequate infrastructure, such as roads, transportation networks, and communication systems, can limit choices.
-
Capacity Constraints: The physical capacity of facilities or systems can constrain output or performance. A manufacturing plant might have a limited production capacity, restricting its ability to meet increased demand.
5. Social and Cultural Constraints: The Influence of Society
These constraints reflect the influence of societal norms, cultural values, and social expectations. They can heavily influence decisions related to marketing, product design, and human resource management:
-
Cultural Norms and Values: Marketing campaigns must be sensitive to cultural norms and values to avoid alienating potential customers.
-
Social Expectations: Businesses often face pressure to act in socially responsible ways, aligning their practices with social expectations.
-
Political Climate: The political environment can significantly influence decision-making, particularly in areas with volatile political landscapes.
The Impact of Constraints on Decision Making
Constraints play a multifaceted role in the decision-making process. While they limit options, they also:
-
Focus the Decision-Making Process: Constraints can help to streamline the decision-making process by eliminating infeasible options. By identifying constraints early on, decision-makers can focus their efforts on evaluating viable alternatives.
-
Promote Creativity and Innovation: Constraints can spur creativity and innovation by forcing decision-makers to think outside the box and find novel solutions. Limited resources can lead to the development of more efficient and effective strategies.
-
Improve Resource Allocation: By recognizing resource constraints, decision-makers can prioritize the most important tasks and allocate resources effectively.
-
Enhance Risk Management: Constraints can help to identify potential risks and challenges, allowing decision-makers to develop mitigation strategies.
-
Increase Accountability: By making constraints explicit, decision-makers can be held accountable for their choices and their adherence to predefined limitations.
Strategies for Managing Constraints
Effective management of constraints is crucial for successful decision-making. Here are some strategies for dealing with constraints:
-
Identify and Analyze Constraints: The first step is to systematically identify and analyze all relevant constraints, considering their nature, impact, and potential interactions. This involves brainstorming, gathering data, and consulting with relevant stakeholders.
-
Prioritize Constraints: Once identified, prioritize constraints based on their severity and impact on the decision. Focus on addressing the most critical constraints first.
-
Negotiate or Redefine Constraints: In some cases, it may be possible to negotiate or redefine constraints. For example, a company might be able to secure additional funding or renegotiate contracts to alleviate resource constraints.
-
Seek Creative Solutions: Constraints can spur innovation and creativity. Explore alternative approaches, challenge assumptions, and look for innovative solutions to overcome limitations.
-
Develop Contingency Plans: Develop contingency plans to address potential challenges and disruptions arising from constraints. This will help to mitigate risks and ensure that the decision-making process remains robust.
-
Utilize Decision-Making Tools: Various tools and techniques can assist in managing constraints, including decision trees, cost-benefit analysis, and scenario planning. These tools help visualize the implications of different choices under different constraint scenarios.
-
Embrace Flexibility and Adaptability: The ability to adapt to changing circumstances and adjust strategies is crucial when dealing with constraints. Be prepared to modify plans as needed in response to unforeseen challenges.
-
Communicate Effectively: Open and transparent communication among stakeholders is essential for effective constraint management. This ensures that everyone understands the constraints and their implications.
Conclusion: Navigating the Landscape of Constraints
Constraints are an integral part of the decision-making landscape. They are not simply obstacles to be overcome but rather forces that shape the possibilities and possibilities. By understanding their nature, appreciating their impact, and employing effective management strategies, decision-makers can navigate the complexities of constraint and arrive at well-informed, effective, and responsible choices. The ability to effectively manage constraints is a critical skill for success in any field, enabling individuals and organizations to make sound judgements, optimize resource utilization, and ultimately achieve their goals. Embracing constraints as opportunities for creativity and innovation can unlock new possibilities and lead to more resilient and successful outcomes. Remember, the art of decision-making lies not just in choosing the best option, but also in understanding and skillfully managing the constraints that define the available options in the first place.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Management Is Defined As The Pursuit Of Organizational Goals
Mar 17, 2025
-
Specialization In Production Is Economically Beneficial Primarily Because It
Mar 17, 2025
-
Movement That Tips The Soles Laterally
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Supreme Court Concept Of Suspect Classifications Suggests That
Mar 17, 2025
-
A 90 Day Note Issued On April 10 Matures On
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Constraint In A Decision Is A Restriction Placed On . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
