A Company Achieves Sustainable Competitive Advantage When
Holbox
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
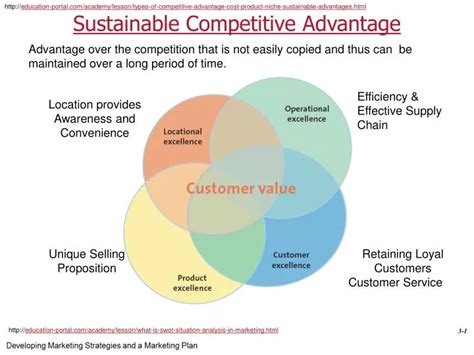
Table of Contents
A Company Achieves Sustainable Competitive Advantage When…
Achieving a sustainable competitive advantage is the holy grail for any business. It's that elusive state where a company consistently outperforms its rivals, not just for a fleeting moment, but over the long term. This isn't about luck or a single brilliant marketing campaign; it's about building a fortress of strengths that competitors struggle to replicate or overcome. So, when exactly does a company achieve this coveted status? It's a multifaceted question, and the answer lies in a confluence of factors, strategically woven together.
The Pillars of Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Sustainable competitive advantage isn't built overnight. It’s the result of a long-term strategy grounded in several key pillars:
1. Valuable and Rare Resources:
This is the cornerstone of the Resource-Based View (RBV) of strategic management. A company possesses a sustainable advantage when it controls resources that are:
-
Valuable: These resources must add value to the firm's offerings, allowing it to better meet customer needs or operate more efficiently than its competitors. Think of a proprietary technology, a unique distribution network, or a powerful brand reputation.
-
Rare: The resource must be scarce; competitors should not have easy access to it. A common resource, no matter how valuable, won't provide a sustainable advantage. If everyone has it, it's not a differentiator.
-
Inimitable: This is crucial. The resource must be difficult, if not impossible, for competitors to imitate. This could be due to its complexity, path dependency (the historical evolution of the resource), causal ambiguity (difficulty in understanding how the resource creates value), or social complexity (embeddedness in the company's culture and relationships).
-
Non-substitutable: There shouldn't be readily available substitutes that offer comparable value. If competitors can easily find alternative ways to achieve similar results, the advantage is weakened.
Example: Consider a pharmaceutical company that has a patented drug with a proven track record of effectiveness and safety. This drug is valuable (treats a significant medical condition), rare (protected by a patent), inimitable (patent protection), and non-substitutable (no equally effective alternatives). This provides a powerful sustainable competitive advantage.
2. Superior Operational Efficiency:
Efficiency is the lifeblood of profitability. A company can achieve a sustainable advantage by consistently delivering its products or services at a lower cost than its competitors while maintaining comparable quality. This advantage might stem from:
-
Economies of Scale: Producing on a larger scale lowers average costs per unit.
-
Economies of Scope: Producing multiple related products or services reduces overall costs.
-
Superior Technology and Processes: Utilizing advanced technologies or streamlining operational processes can drastically reduce expenses.
-
Efficient Supply Chain Management: Optimizing the supply chain from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product minimizes waste and delays.
Example: A fast-fashion retailer that has mastered efficient supply chain management and utilizes economies of scale in manufacturing can undercut its competitors on price, achieving a competitive advantage based on cost leadership.
3. Strong Brand and Customer Loyalty:
Brand equity and customer loyalty are invaluable intangible assets. A strong brand resonates with consumers, fostering trust and preference. This loyalty translates to:
-
Price Premium: Customers are willing to pay more for products or services associated with a trusted and desirable brand.
-
Reduced Marketing Costs: Loyal customers require less marketing investment to retain.
-
Increased Customer Lifetime Value: Long-term relationships with loyal customers generate significantly higher revenue over time.
Example: Apple has cultivated a fiercely loyal customer base through its innovative products, seamless user experience, and strong brand image. This loyalty enables Apple to command a price premium and maintain its market leadership.
4. Innovation and Continuous Improvement:
In today's dynamic business environment, stagnation is a death sentence. Sustainable competitive advantage requires a commitment to:
-
Product Innovation: Continuously developing new and improved products that meet evolving customer needs.
-
Process Innovation: Improving operational efficiency through technological advancements and streamlined processes.
-
Business Model Innovation: Rethinking the fundamental ways in which the business operates to achieve better outcomes.
Example: Tesla's commitment to electric vehicle technology and its innovative approach to battery technology, charging infrastructure, and over-the-air software updates have given it a significant competitive advantage in the automotive industry.
5. Strategic Partnerships and Alliances:
Strategic alliances can provide access to valuable resources, technologies, or markets that a company might not possess on its own. These partnerships can be:
-
Joint Ventures: Collaborating with another company on a specific project or venture.
-
Licensing Agreements: Granting or receiving rights to use intellectual property.
-
Distribution Agreements: Collaborating on distribution channels to reach new markets.
Example: A smaller technology company might form a strategic partnership with a large multinational corporation to gain access to its global distribution network, accelerating its market penetration and enhancing its competitive position.
Sustaining the Advantage: Responding to Competitive Pressures
Maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage requires vigilance and adaptability. Competitors are constantly striving to erode any advantage a company might possess. To sustain the lead, companies must:
-
Continuously innovate: Never rest on past achievements. Continuously develop new products, services, and processes to stay ahead of the curve.
-
Invest in R&D: Significant investments in research and development are essential to generate new ideas and technologies.
-
Build strong organizational capabilities: Cultivate a culture of excellence, innovation, and continuous improvement within the organization.
-
Adapt to changing market conditions: Be flexible and responsive to changing customer preferences, technological advancements, and competitive pressures.
-
Protect intellectual property: Secure patents, trademarks, and copyrights to protect valuable assets from imitation.
-
Develop strong relationships with customers and suppliers: Foster long-term partnerships to enhance loyalty and efficiency.
-
Monitor the competitive landscape: Keep a close eye on competitor activities to anticipate potential threats and opportunities.
The Danger of Complacency: When Competitive Advantage Erodes
Even the strongest competitive advantages can erode over time if a company becomes complacent. Several factors can contribute to the loss of a sustainable advantage:
-
Technological disruption: Rapid technological advancements can render existing technologies and business models obsolete.
-
Changing customer preferences: Shifts in consumer tastes and demands can weaken the value proposition of existing products or services.
-
Increased competition: New entrants or existing rivals can adopt similar strategies or develop superior alternatives.
-
Failure to innovate: A lack of investment in R&D can lead to a decline in competitiveness.
-
Poor management: Ineffective leadership and organizational weaknesses can undermine even the strongest competitive advantages.
-
Regulatory changes: New regulations or government policies can negatively impact a company's operations.
Conclusion: The Dynamic Nature of Competitive Advantage
Achieving a sustainable competitive advantage is a dynamic, ongoing process, not a destination. It requires a long-term vision, a commitment to excellence, and a continuous effort to adapt and innovate. By focusing on the key pillars outlined above—valuable and rare resources, superior operational efficiency, strong brand and customer loyalty, innovation, and strategic partnerships—companies can build a fortress of strength that enables them to outperform competitors and achieve enduring success. But the battle is never truly won; it's a constant vigilance against complacency and a relentless pursuit of improvement that defines the journey towards a truly sustainable competitive advantage. The companies that truly thrive are those who understand this dynamism and embrace the constant need to adapt and evolve.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Will Jill And Phil Are All Wheat Farmers
Mar 21, 2025
-
Managers Who Advocate Job Enrichment Focus On Creating Jobs With
Mar 21, 2025
-
A Patient Is Put On Medication At 20 Mg
Mar 21, 2025
-
An Account Is Said To Have A Debit Balance If
Mar 21, 2025
-
Classify The Radicals Into The Appropriate Categories
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Company Achieves Sustainable Competitive Advantage When . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
