You Then Ping A Website With An Ip Address
Holbox
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
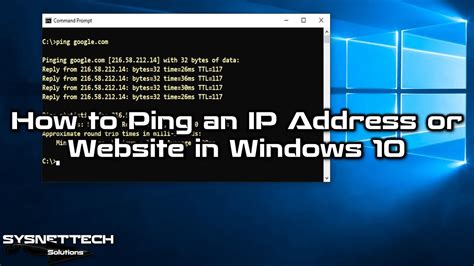
Table of Contents
- You Then Ping A Website With An Ip Address
- Table of Contents
- You Then Ping a Website with an IP Address: Understanding the Process and Implications
- What is Pinging?
- How Does it Work?
- Why Use an IP Address Instead of a Domain Name?
- Practical Applications of Pinging with an IP Address
- 1. Network Troubleshooting:
- 2. Monitoring Website Uptime:
- 3. Identifying Network Latency:
- 4. Investigating Network Connectivity Problems:
- 5. Load Balancing and Server Health Checks:
- 6. Security Auditing and Penetration Testing:
- Security Implications and Considerations
- Advanced Ping Techniques
- Finding the IP Address of a Website
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
You Then Ping a Website with an IP Address: Understanding the Process and Implications
Pinging a website using its IP address is a fundamental networking task that allows you to check the website's reachability and measure the response time. While seemingly simple, understanding the process and its implications is crucial for web developers, network administrators, and anyone interested in how the internet works. This comprehensive guide will delve into the mechanics of pinging, its uses, and potential security considerations.
What is Pinging?
Pinging, or more formally, using the ping command, is a network utility used to test the connectivity between two networked devices. It works by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to a target device (the website's IP address in this case) and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The response provides information about the round-trip time (RTT), the time it takes for a packet to travel to the destination and back. A successful ping indicates that the target device is reachable and responding to network requests. A failure typically indicates a problem with network connectivity, the target server, or a firewall blocking ICMP requests.
How Does it Work?
The ping command, available on most operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux), sends an ICMP echo request packet containing a sequence number and timestamp. This packet travels across the network to the target device, which then sends back an ICMP echo reply packet containing the same sequence number and the time it received the request. The ping utility calculates the round-trip time (RTT) based on the time difference between sending the request and receiving the reply. Multiple packets are usually sent to get a more reliable measurement of network performance and identify potential packet loss.
Why Use an IP Address Instead of a Domain Name?
While you can ping a website using its domain name (e.g., ping google.com), using the IP address offers several advantages:
- Direct Connectivity: Pinging with an IP address bypasses the Domain Name System (DNS) lookup, making the process faster and more direct. This is particularly useful when troubleshooting DNS issues.
- Identifying Multiple Servers: A single domain name can point to multiple IP addresses (e.g., through load balancing). Pinging individual IP addresses helps identify which server is responding and its performance.
- Troubleshooting Network Issues: When DNS resolution fails, using the IP address directly can help determine if the issue is with the DNS or the network connection to the server itself.
- Security Analysis: Security professionals often use IP addresses to identify potential threats and analyze network traffic patterns. Understanding the IP addresses associated with a domain can help in identifying malicious activity.
Practical Applications of Pinging with an IP Address
Pinging websites using their IP addresses has a wide range of applications, including:
1. Network Troubleshooting:
This is perhaps the most common use. When a website is unresponsive, pinging its IP address helps determine if the problem lies with your network connection, the website's server, or something in between. A successful ping suggests the problem is elsewhere (e.g., the web server itself or the website's application).
2. Monitoring Website Uptime:
System administrators regularly ping critical websites and servers to monitor their availability. Automated tools can perform continuous ping tests and send alerts if a server becomes unreachable. This proactive approach helps ensure minimal downtime and quick resolution of outages. The RTT values also provide insight into potential performance bottlenecks.
3. Identifying Network Latency:
The round-trip time (RTT) reported by the ping command indicates the latency between your computer and the website's server. High latency can result in slow loading times and poor user experience. Regularly pinging a website's IP address can help identify trends in latency and pinpoint potential network issues.
4. Investigating Network Connectivity Problems:
Pinging with an IP address can help isolate problems within a network. If you can ping a server's IP address but cannot access its website, it suggests a problem with the server's web application or configuration, rather than a general network issue.
5. Load Balancing and Server Health Checks:
In environments with multiple servers, pinging individual IP addresses helps assess the health and performance of each server. This information is crucial for load balancing algorithms to distribute traffic effectively and ensure optimal website performance.
6. Security Auditing and Penetration Testing:
Security professionals utilize pinging to identify open ports and assess the reachability of various network services. Analyzing response times and patterns can help uncover vulnerabilities and potential security risks. However, ethical considerations are paramount when performing such security assessments.
Security Implications and Considerations
While pinging is a fundamental and generally harmless network utility, it is essential to understand potential security implications:
- ICMP Flood Attacks: Malicious actors can use ICMP echo requests (ping) in denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, overwhelming a server with a flood of requests and rendering it unavailable. Well-configured firewalls and intrusion detection systems can mitigate this threat.
- Information Disclosure: Although the information returned by a ping is generally limited to RTT and packet loss, it can still provide some information about the target network's configuration.
- Network Scanning: Ping sweeps are used by attackers to identify active hosts on a network. This information can then be used in further attacks.
- Firewall Rules: Firewalls can be configured to block ICMP echo requests, preventing pinging altogether. This is a common security practice to prevent certain types of attacks.
Advanced Ping Techniques
Beyond the basic ping command, several advanced techniques exist for more detailed network analysis:
- Traceroute (tracert): Traceroute traces the path a packet takes to reach a destination, showing each hop along the way. This is helpful in identifying network bottlenecks or connectivity problems.
- Ping with Specific Options: The
pingcommand supports various options to control packet size, timeout, and the number of packets sent. These options can provide more granular control and detailed analysis. - Monitoring Tools: Various network monitoring tools offer advanced ping capabilities, including automated pinging, threshold alerts, and data visualization.
Finding the IP Address of a Website
Before you can ping a website using its IP address, you need to find the IP address. Several methods are available:
- Using the
nslookupcommand: This command queries DNS servers to resolve a domain name to its IP address. - Using the
digcommand: This command is a more powerful and versatile DNS lookup tool. - Using an online IP address lookup tool: Many websites provide tools to look up a domain name's IP address.
- Viewing the website's source code: Sometimes, the IP address might be embedded in the website's HTML or JavaScript code, although this is not a reliable method.
Conclusion
Pinging a website with its IP address is a fundamental networking task with various applications ranging from simple connectivity checks to advanced network troubleshooting and security analysis. Understanding the mechanics, implications, and advanced techniques related to pinging is crucial for anyone working with networks or web technologies. While generally harmless, being aware of potential security risks and implementing appropriate security measures is crucial to prevent abuse and maintain network security. Remember always to respect network boundaries and adhere to ethical guidelines when using network tools like ping. Properly utilizing the ping command and related tools can be an invaluable asset in maintaining a healthy and secure online environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Phenomenon Is Reduced By Oil Immersion Microscopy
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Liability For Cash Dividends Is Recorded
Apr 01, 2025
-
You Can Recognize The Process Of Pinocytosis When
Apr 01, 2025
-
Draw The Correct Product For The Given Diels Alder Reaction
Apr 01, 2025
-
Match Each Example Below To The Correct Cost Type
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about You Then Ping A Website With An Ip Address . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
