Why Must A Marketing Manager Consider Pricing Objectives And Constraints
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 7 min read
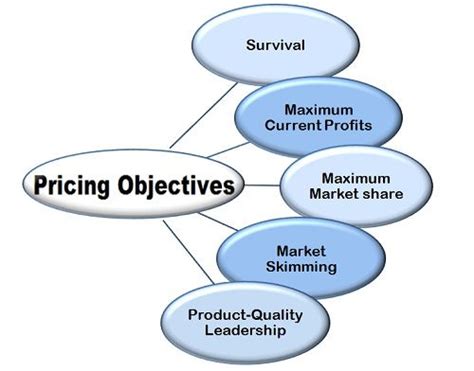
Table of Contents
- Why Must A Marketing Manager Consider Pricing Objectives And Constraints
- Table of Contents
- Why Marketing Managers Must Consider Pricing Objectives and Constraints
- Defining Pricing Objectives and Constraints
- Pricing Objectives: The Desired Outcomes
- Pricing Constraints: The Limiting Factors
- Why Pricing Objectives and Constraints Matter: The Critical Role for Marketing Managers
- 1. Profitability & Financial Performance: The Bottom Line
- 2. Market Share & Competitive Advantage: Staying Ahead
- 3. Brand Perception & Positioning: Shaping the Image
- 4. Customer Value & Satisfaction: Meeting Expectations
- 5. Adaptability & Flexibility: Navigating Market Changes
- 6. Legal Compliance & Ethical Considerations: Avoiding Pitfalls
- Integrating Pricing Objectives and Constraints: A Strategic Approach
- Case Studies: Illustrating the Importance
- Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Pricing
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Why Marketing Managers Must Consider Pricing Objectives and Constraints
Pricing is a pivotal element in the marketing mix, directly impacting profitability, market share, and brand perception. For a marketing manager, understanding and meticulously addressing pricing objectives and constraints is not merely advisable – it's absolutely crucial for success. Neglecting this aspect can lead to missed opportunities, reduced profitability, and ultimately, business failure. This article delves deep into the reasons why a marketing manager must prioritize pricing objectives and constraints, exploring the various facets of this critical decision-making process.
Defining Pricing Objectives and Constraints
Before delving into the why, let's first clarify the what.
Pricing Objectives: The Desired Outcomes
Pricing objectives are the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals a company aims to achieve through its pricing strategies. These objectives vary depending on the company's overall strategic goals and market position. Common pricing objectives include:
-
Profit Maximization: This classic objective focuses on setting prices to generate the highest possible profit margin. While seemingly straightforward, it requires careful consideration of demand elasticity and competitive pressures.
-
Market Share Growth: This objective prioritizes gaining a larger slice of the market, often achieved through competitive pricing strategies like penetration pricing (setting low prices initially to attract customers) or value pricing (offering a strong value proposition at a competitive price).
-
Brand Positioning: Pricing can significantly influence brand perception. Premium pricing, for example, positions a brand as luxurious and high-quality, while value pricing might target a more budget-conscious consumer base.
-
Survival: In highly competitive or challenging markets, the primary pricing objective might simply be survival. This often involves reducing prices to maintain sales and cash flow, even if it means lower profit margins in the short term.
-
Meeting Competition: This objective focuses on matching or slightly undercutting competitor pricing, aiming to maintain market share and avoid price wars.
Pricing Constraints: The Limiting Factors
Pricing constraints represent the external and internal limitations that restrict a company's ability to set prices freely. These can be:
-
Costs: Production costs, marketing costs, and distribution costs significantly influence the minimum price a company can charge and still remain profitable. Analyzing cost structures, including fixed and variable costs, is crucial.
-
Competition: The actions and pricing strategies of competitors directly influence a company's pricing decisions. Understanding the competitive landscape, including pricing levels, competitive advantages, and potential reactions, is essential.
-
Demand: The level of consumer demand for a product or service heavily influences pricing. Inelastic demand (where price changes don't significantly affect demand) allows for higher prices, while elastic demand (where price changes significantly affect demand) necessitates more careful price setting.
-
Government Regulations: Laws and regulations, such as anti-trust laws and price controls, can impose restrictions on pricing practices.
-
Economic Conditions: Economic factors such as inflation, recession, and consumer spending habits can significantly impact pricing strategies. A recession, for instance, might necessitate price reductions to maintain sales.
-
Internal Factors: Internal constraints include the company's financial position, resources, and overall marketing strategy. A company with limited resources might have less flexibility in setting prices compared to a larger, well-funded company.
Why Pricing Objectives and Constraints Matter: The Critical Role for Marketing Managers
The importance of considering both objectives and constraints cannot be overstated. Ignoring either aspect can have severe consequences:
1. Profitability & Financial Performance: The Bottom Line
Setting prices without a clear understanding of cost structures and profit margins is a recipe for disaster. Failing to factor in costs leads to unprofitable pricing, potentially pushing the company towards financial instability. Similarly, ignoring competitive pricing can lead to lost sales and reduced profitability. A well-defined pricing objective, aligned with cost analysis, is essential for maximizing profitability.
2. Market Share & Competitive Advantage: Staying Ahead
Pricing directly impacts market share. A strong understanding of competitor pricing and market demand enables a marketing manager to develop effective pricing strategies, whether it's aggressive penetration pricing to capture market share quickly or premium pricing to establish a strong brand image and command higher margins. Ignoring competitive dynamics can lead to lost market share and a weakened competitive position.
3. Brand Perception & Positioning: Shaping the Image
Pricing plays a crucial role in shaping brand perception. Setting prices too high might alienate potential customers, while pricing too low might damage brand credibility and perceived value. A coherent pricing strategy aligned with the overall brand positioning and target market is key to building a strong and successful brand.
4. Customer Value & Satisfaction: Meeting Expectations
Customers evaluate value based on the perceived benefits relative to the price. Ignoring customer perception and simply focusing on profit maximization can lead to dissatisfaction and decreased customer loyalty. Pricing strategies need to consider customer value and expectations, finding the right balance between price and perceived value.
5. Adaptability & Flexibility: Navigating Market Changes
Market conditions are constantly evolving. Economic downturns, changes in consumer preferences, and new competitor entries all necessitate adaptive pricing strategies. A marketing manager needs to monitor the market closely and adjust pricing accordingly, reflecting the dynamic interplay of objectives and constraints.
6. Legal Compliance & Ethical Considerations: Avoiding Pitfalls
Pricing strategies must adhere to all applicable laws and regulations. Understanding anti-trust laws, price control measures, and ethical considerations is vital to avoid legal repercussions and maintain brand reputation.
Integrating Pricing Objectives and Constraints: A Strategic Approach
Effectively integrating pricing objectives and constraints requires a systematic approach:
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand customer demand, competitor pricing, and market trends.
-
Cost Analysis: Perform a detailed cost analysis to determine production costs, marketing costs, and distribution costs.
-
Competitive Analysis: Analyze competitor pricing strategies, strengths, and weaknesses.
-
Pricing Strategy Development: Develop multiple pricing strategies based on the defined objectives and constraints, considering various options like cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, or competitive pricing.
-
Testing & Optimization: Test different pricing strategies in the market and continuously optimize based on performance data and market feedback.
-
Monitoring & Adjustment: Regularly monitor market conditions, competitor actions, and sales performance to adapt pricing strategies as needed.
Case Studies: Illustrating the Importance
Let’s examine hypothetical scenarios to demonstrate the impact of neglecting pricing objectives and constraints:
Scenario 1: Ignoring Costs
A startup launches a product with innovative features, setting a high price based solely on perceived value. However, they underestimate production costs, leading to significant losses despite strong initial sales. They haven't considered the crucial constraint of production cost, directly impacting profitability and potentially leading to business failure.
Scenario 2: Ignoring Competition
A company introduces a new product with a premium price, ignoring the fact that a competitor offers a similar product at a significantly lower price. This leads to low sales and lost market share. Not considering competitive pressure as a constraint resulted in a pricing strategy that failed to achieve the market share objective.
Scenario 3: Ignoring Customer Perception
A company sets a high price for a product based solely on profit maximization, without considering the perceived value by the customer. Customers find the product overpriced compared to alternatives, leading to low sales and a negative brand perception. Ignoring customer perception as a constraint led to the failure to achieve the objective of maximizing sales volume.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Pricing
Pricing is far more than just a number; it's a strategic lever that profoundly impacts a company's success. Marketing managers who understand and meticulously address pricing objectives and constraints are far better equipped to navigate the complexities of the market, achieve their business goals, and build a thriving and profitable enterprise. Ignoring this vital aspect of the marketing mix is simply not an option for sustained success in today's competitive business landscape. By rigorously considering both the desired outcomes and the limiting factors, marketing managers can craft pricing strategies that drive profitability, build strong brands, and secure a sustainable competitive advantage.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Give The Iupac Names Of The Following Compounds
Mar 30, 2025
-
Apply The Fill White Outline Gold Accent Color 2
Mar 30, 2025
-
Tebeaux And Dragga Formal Report Format
Mar 30, 2025
-
Researchers At Deloitte University Suggested That Blockchain Could
Mar 30, 2025
-
Calcium Is Involved In All Of The Following Functions Except
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Must A Marketing Manager Consider Pricing Objectives And Constraints . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
