Which Two Neurotransmitters Have Roles In Appetite Suppression
Holbox
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
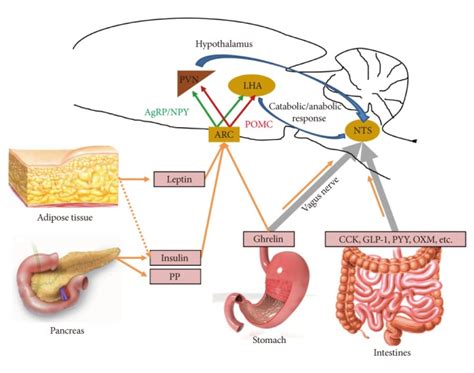
Table of Contents
- Which Two Neurotransmitters Have Roles In Appetite Suppression
- Table of Contents
- Which Two Neurotransmitters Have Roles in Appetite Suppression?
- Serotonin: The Satiety Signal
- Serotonin's Mechanisms of Action in Appetite Suppression
- Dietary Sources and Serotonin Production
- Norepinephrine: The Energy Expenditure Enhancer
- Norepinephrine's Mechanisms of Action in Appetite Regulation
- Lifestyle Factors Influencing Norepinephrine Levels
- The Interplay Between Serotonin and Norepinephrine in Appetite Regulation
- Implications for Weight Management and Treatment Strategies
- Pharmacologic Interventions
- Lifestyle Interventions
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Two Neurotransmitters Have Roles in Appetite Suppression?
The intricate dance of hunger and satiety is orchestrated by a complex interplay of hormones and neurotransmitters within the brain. While numerous factors influence our appetite, two neurotransmitters stand out for their significant roles in appetite suppression: serotonin and norepinephrine. Understanding their mechanisms of action offers valuable insights into weight management strategies and the development of potential treatments for obesity and eating disorders.
Serotonin: The Satiety Signal
Serotonin, a crucial neurotransmitter affecting mood, sleep, and cognitive function, also plays a pivotal role in regulating food intake. Its impact on appetite is primarily characterized by its satiety-promoting effects. This means that increased serotonin levels generally lead to feelings of fullness and reduced desire to eat.
Serotonin's Mechanisms of Action in Appetite Suppression
Serotonin's influence on appetite is multifaceted and involves several key pathways:
-
Activation of 5-HT2C Receptors: The 5-HT2C receptor, a subtype of serotonin receptors, is strategically located in the hypothalamus, a brain region crucial for regulating energy balance. Activation of these receptors inhibits the release of neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP), two potent appetite stimulants. By suppressing these orexigenic (appetite-increasing) peptides, serotonin effectively reduces hunger.
-
Stimulation of Vagus Nerve: Serotonin also interacts with the vagus nerve, a critical component of the gut-brain axis. The vagus nerve transmits signals from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain, providing information about nutrient intake and satiety. Serotonin's influence on the vagus nerve enhances these satiety signals, contributing to feelings of fullness.
-
Interaction with other neurotransmitters: Serotonin doesn't operate in isolation. It interacts with other neurotransmitters involved in appetite regulation, influencing their activity and ultimately contributing to a balanced regulation of food intake. For example, it can modulate the activity of dopamine, another neurotransmitter that plays a role in reward and pleasure associated with food consumption.
Dietary Sources and Serotonin Production
While serotonin itself doesn't cross the blood-brain barrier, the precursor to serotonin, tryptophan, does. Tryptophan is an essential amino acid, meaning the body cannot produce it and must obtain it through dietary sources. Foods rich in tryptophan include:
- Turkey: Often cited for its tryptophan content, though many other foods contain comparable amounts.
- Chicken: A good source of tryptophan, offering a lean protein option.
- Salmon: Provides tryptophan alongside omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial for overall health.
- Eggs: A complete protein source containing all essential amino acids, including tryptophan.
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt offer a good source of tryptophan.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are plant-based sources of tryptophan.
- Nuts and seeds: Various nuts and seeds provide tryptophan and other essential nutrients.
Important Note: While consuming tryptophan-rich foods can contribute to serotonin production, the relationship isn't straightforward. Other factors, such as carbohydrate intake and the balance of other amino acids, also influence tryptophan's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and be converted to serotonin. Therefore, simply consuming large quantities of tryptophan-rich foods doesn't guarantee significant increases in brain serotonin levels.
Norepinephrine: The Energy Expenditure Enhancer
Norepinephrine, another neurotransmitter, plays a less direct but still significant role in appetite suppression. Unlike serotonin, which primarily acts on satiety signals, norepinephrine's impact is more associated with increased energy expenditure and thermogenesis. This means that norepinephrine can indirectly reduce appetite by increasing the body's metabolic rate and burning more calories.
Norepinephrine's Mechanisms of Action in Appetite Regulation
Norepinephrine exerts its influence on appetite regulation through several pathways:
-
Stimulation of Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT): Norepinephrine is a key activator of brown adipose tissue (BAT), a type of fat tissue that generates heat by burning calories. Increased norepinephrine activity stimulates BAT activity, leading to higher energy expenditure and a potential reduction in appetite. This effect is particularly relevant in cold environments where the body increases norepinephrine levels to generate heat.
-
Modulation of Sympathetic Nervous System: Norepinephrine is a crucial neurotransmitter in the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the "fight-or-flight" response. Activation of this system leads to an increase in metabolic rate, heart rate, and blood pressure, all contributing to increased energy expenditure and potential appetite suppression.
-
Interaction with other appetite regulating hormones: Norepinephrine's influence on appetite is not limited to its direct effects on metabolic processes. It interacts with several hormones involved in appetite regulation, including leptin and insulin, and modifies their influence on the hypothalamus, indirectly impacting the sensation of hunger.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Norepinephrine Levels
Unlike serotonin, the direct dietary manipulation of norepinephrine levels is not feasible. However, several lifestyle factors significantly influence norepinephrine activity:
-
Exercise: Physical activity, particularly cardiovascular exercise, stimulates the release of norepinephrine, leading to increased energy expenditure and a potential reduction in appetite.
-
Stress: While acute stress can initially increase norepinephrine levels, chronic stress can disrupt the body's hormonal balance, potentially leading to increased appetite and weight gain. Managing stress through techniques like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance.
-
Sleep: Sufficient sleep is essential for maintaining optimal hormonal balance, including norepinephrine levels. Sleep deprivation can disrupt the body's natural rhythms and influence appetite regulation.
-
Cold Exposure: Exposure to cold temperatures stimulates norepinephrine release, leading to increased BAT activity and thermogenesis.
The Interplay Between Serotonin and Norepinephrine in Appetite Regulation
It's crucial to understand that serotonin and norepinephrine don't operate in isolation. Their actions are interconnected and influence each other's effects on appetite regulation. For example, increased serotonin levels can positively influence norepinephrine activity, leading to a synergistic effect on appetite suppression. Conversely, imbalances in either neurotransmitter can disrupt the delicate equilibrium of appetite control.
Implications for Weight Management and Treatment Strategies
The roles of serotonin and norepinephrine in appetite regulation have significant implications for weight management strategies and the development of treatments for obesity and related disorders.
Pharmacologic Interventions
Several medications aim to influence serotonin and norepinephrine levels to manage appetite and weight. However, it's crucial to remember that these medications should only be used under the strict guidance of a healthcare professional. The potential side effects and risks must be carefully weighed against potential benefits.
Lifestyle Interventions
While medication can play a role in certain cases, lifestyle modifications remain crucial for managing appetite and weight. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains provides essential nutrients, including tryptophan, and supports optimal serotonin production. Regular exercise boosts norepinephrine levels and improves overall metabolic health. Stress management techniques promote hormonal balance and healthy appetite regulation. Finally, sufficient sleep contributes to optimal functioning of the body's regulatory systems.
Conclusion
Serotonin and norepinephrine are two critical neurotransmitters that play significant roles in appetite suppression, although through different mechanisms. Serotonin primarily acts by promoting satiety, while norepinephrine influences energy expenditure and thermogenesis. Understanding their individual actions and their interplay is crucial for developing effective strategies for weight management and treating obesity and eating disorders. A holistic approach that integrates dietary modifications, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, alongside medical supervision when necessary, offers the best chance for long-term success in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Further research continues to unveil the intricate details of this complex regulatory system, leading to the development of more targeted and effective interventions in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Period Of The Voltage Source
Mar 26, 2025
-
True False Genetic Drift Can Change Allele Frequencies In A Population
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Challenges Does Generative Face With Respect To Data
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which One Of The Following Is True
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Exemplifies Extrinsically Motivated Behavior
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Two Neurotransmitters Have Roles In Appetite Suppression . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
