Which Of The Following Reactions Produces Acetyl Chloride
Holbox
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
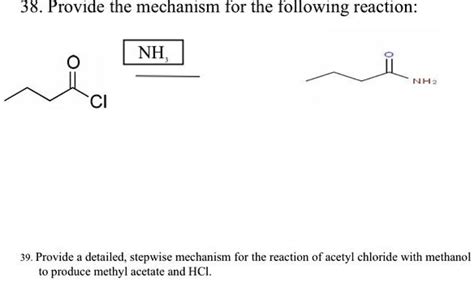
Table of Contents
- Which Of The Following Reactions Produces Acetyl Chloride
- Table of Contents
- Which of the Following Reactions Produces Acetyl Chloride? A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Acetyl Chloride and its Synthesis
- Common Methods for Acetyl Chloride Synthesis
- 1. Reaction of Acetic Acid with Thionyl Chloride (SOCl₂)
- 2. Reaction of Acetic Acid with Phosphorus Trichloride (PCl₃) or Phosphorus Pentachloride (PCl₅)
- 3. Reaction of Acetic Anhydride with Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
- 4. Reaction of Acetyl Bromide with Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
- Comparing the Methods: Efficiency and Practicality
- Safety Precautions
- Conclusion: Choosing the Best Method
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which of the Following Reactions Produces Acetyl Chloride? A Comprehensive Guide
Acetyl chloride (CH₃COCl), a crucial reagent in organic chemistry, finds wide applications in the synthesis of various compounds. Understanding its preparation is fundamental for any aspiring chemist. This comprehensive guide delves into the various reactions capable of producing acetyl chloride, exploring their mechanisms, advantages, disadvantages, and comparing their overall effectiveness. We’ll examine different approaches, focusing on practicality and yield.
Understanding Acetyl Chloride and its Synthesis
Acetyl chloride is a highly reactive acyl chloride, characterized by its pungent odor and its susceptibility to hydrolysis. Its reactivity stems from the highly electrophilic carbonyl carbon, making it a versatile reagent for nucleophilic acyl substitution. The synthesis of acetyl chloride often involves the reaction of acetic acid or its derivatives with a chlorinating agent. The choice of method depends on factors like availability of starting materials, desired purity, and scale of production.
Common Methods for Acetyl Chloride Synthesis
Several methods exist for producing acetyl chloride, each possessing unique characteristics:
1. Reaction of Acetic Acid with Thionyl Chloride (SOCl₂)
This is arguably the most common and preferred method for preparing acetyl chloride in the laboratory. Thionyl chloride is a powerful chlorinating agent that reacts with carboxylic acids to produce acyl chlorides. The reaction proceeds through a series of steps involving nucleophilic attack and elimination:
Reaction: CH₃COOH + SOCl₂ → CH₃COCl + SO₂ + HCl
Mechanism:
- Nucleophilic attack: The oxygen of the carboxylic acid attacks the sulfur atom of SOCl₂, forming an intermediate.
- Elimination of SO₂: Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) is eliminated, leaving behind an unstable intermediate.
- Chloride ion attack: A chloride ion attacks the carbonyl carbon, leading to the formation of acetyl chloride.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) formation: Hydrochloric acid is also produced as a byproduct.
Advantages:
- High yield: This method generally offers good yields of acetyl chloride.
- Relatively easy to perform: The reaction is straightforward and doesn't require complex apparatus.
- Byproducts are gaseous: The byproducts, SO₂ and HCl, are gases, making purification relatively simple.
Disadvantages:
- Formation of HCl: HCl is corrosive and requires careful handling. Appropriate safety measures are essential.
- SO₂ is toxic: Sulfur dioxide is a toxic gas, demanding a well-ventilated environment.
2. Reaction of Acetic Acid with Phosphorus Trichloride (PCl₃) or Phosphorus Pentachloride (PCl₅)
Phosphorus chlorides, both PCl₃ and PCl₅, can also be used to convert acetic acid into acetyl chloride. The reactions are analogous to the thionyl chloride method, involving nucleophilic attack and subsequent elimination.
Reaction with PCl₃: 3CH₃COOH + PCl₃ → 3CH₃COCl + H₃PO₃
Reaction with PCl₅: CH₃COOH + PCl₅ → CH₃COCl + POCl₃ + HCl
Advantages:
- Relatively inexpensive reagents: Phosphorus chlorides are often less expensive than thionyl chloride.
Disadvantages:
- Lower yields compared to SOCl₂: These methods typically yield less acetyl chloride than the thionyl chloride method.
- More difficult purification: The byproducts are not gaseous, requiring additional purification steps.
- PCl₃ is highly toxic: Phosphorus trichloride is toxic and requires cautious handling.
- PCl₅ reacts violently with water: Phosphorus pentachloride is highly reactive with water and requires stringent anhydrous conditions.
3. Reaction of Acetic Anhydride with Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
Acetic anhydride can react with hydrogen chloride to produce acetyl chloride and acetic acid. This method isn't as widely used as the previous ones due to the requirement of anhydrous conditions and the less favorable equilibrium.
Reaction: (CH₃CO)₂O + HCl ⇌ CH₃COCl + CH₃COOH
Advantages:
- Avoids the use of toxic gases: This approach avoids the use of toxic gases like SO₂ and HCl is used as a reagent.
Disadvantages:
- Lower yield and reversible reaction: The reaction is reversible and generally has a lower yield.
- Requires anhydrous conditions: Careful control of moisture is crucial for the reaction to proceed efficiently.
4. Reaction of Acetyl Bromide with Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
Similar to the previous method, a halogen exchange is possible.
Reaction: CH₃COBr + HCl ⇌ CH₃COCl + HBr
Advantages:
- Can lead to better yield of Acetyl Chloride if other reactants are removed.
- HBr can be easier to remove than other reactants.
Disadvantages:
- Requires anhydrous conditions: Moisture is the enemy.
- Reversible reaction: Maintaining the equilibrium towards acetyl chloride formation is critical.
- Relatively low yield.
Comparing the Methods: Efficiency and Practicality
While several methods exist for synthesizing acetyl chloride, the reaction of acetic acid with thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) stands out as the most efficient and practical method for laboratory-scale synthesis. Its high yield, relatively simple procedure, and ease of purification due to gaseous byproducts make it the preferred choice. The use of phosphorus chlorides offers an alternative, but the lower yields and more complex purification steps make them less attractive. The reactions involving acetic anhydride or acetyl bromide, while potentially feasible, often suffer from lower yields and require stringent reaction conditions.
Safety Precautions
Working with acetyl chloride and the reagents involved in its synthesis requires rigorous adherence to safety protocols. Acetyl chloride is highly corrosive and reactive, while thionyl chloride, phosphorus chlorides, and hydrogen chloride are toxic and/or corrosive. Always work under a well-ventilated fume hood, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Consult the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for each chemical before handling.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Method
The synthesis of acetyl chloride offers various approaches, each with its strengths and limitations. For most laboratory applications, the reaction of acetic acid with thionyl chloride emerges as the most practical and efficient method due to its high yield, relatively simple procedure, and easy purification. However, other methods might be suitable depending on the specific needs and availability of reagents. Remember to always prioritize safety and handle chemicals with utmost care. Proper understanding of the reaction mechanisms and associated safety measures are crucial for successful and safe acetyl chloride synthesis. This detailed analysis aids in selecting the optimal method based on individual requirements and considerations. Careful planning and execution are key to achieving a high yield and minimizing safety risks.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Name Of The Following
Mar 27, 2025
-
The Rate At Which Energy Is Used Is Called
Mar 27, 2025
-
Accepting A Special Order Will Improve
Mar 27, 2025
-
Finding Inputs And Outputs In A Story Context
Mar 27, 2025
-
University Of Colorado Phet Concentration Exercise
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Reactions Produces Acetyl Chloride . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
