Which Of The Following Is An Effect Of Myelination
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
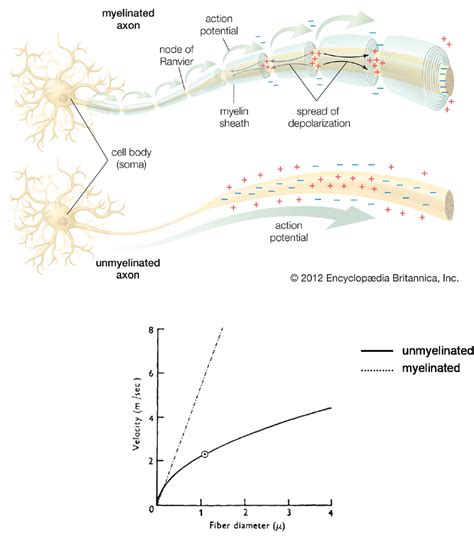
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is an Effect of Myelination? A Deep Dive into the Myelin Sheath's Impact on the Nervous System
Myelin, a fatty white substance, forms a crucial insulating layer around nerve fibers, significantly impacting the speed and efficiency of nerve impulse transmission. Understanding the effects of myelination is fundamental to comprehending the complexities of the nervous system and neurological function. This article will explore the various effects of myelination, addressing its role in speed of conduction, saltatory conduction, energy efficiency, signal fidelity, and the consequences of demyelination. We’ll also delve into the developmental aspects of myelination and its implications for neurological diseases.
The Speed of Nerve Impulse Transmission: A Myelin-Driven Phenomenon
One of the most significant effects of myelination is the dramatic increase in the speed of nerve impulse transmission. Without myelin, nerve impulses travel relatively slowly, akin to a message carried by a single runner. However, the presence of myelin acts like a high-speed railway, enabling rapid transmission of information across long distances within the nervous system. This accelerated speed is essential for various physiological processes, from simple reflexes to complex cognitive functions.
The Role of Nodes of Ranvier
Myelin doesn't form a continuous sheath around the axon; instead, it’s interrupted at regular intervals by gaps called Nodes of Ranvier. These nodes play a crucial role in facilitating rapid signal transmission through a process called saltatory conduction. Instead of the impulse travelling continuously down the axon, it "jumps" from one Node of Ranvier to the next, significantly increasing the speed of conduction. Imagine it as a train skipping between stations instead of constantly moving at a slower pace.
Saltatory Conduction: The Efficient Leap of Nerve Impulses
Saltatory conduction, facilitated by the myelin sheath and Nodes of Ranvier, is a crucial mechanism that underpins the speed advantage offered by myelination. The concentrated ion channels at the Nodes of Ranvier allow for rapid depolarization and repolarization, effectively propelling the nerve impulse forward in a series of jumps. This mechanism is far more energy-efficient than continuous conduction, as fewer ions need to be transported across the axon membrane.
Energy Efficiency: Myelin's Economic Impact on Nerve Function
Myelination not only increases the speed of nerve impulse transmission but also enhances its energy efficiency. As mentioned above, the saltatory conduction mechanism reduces the amount of energy required to propagate an impulse. Without myelin, the continuous influx and efflux of ions along the entire axon length would demand considerably more energy from the neuron. This energy conservation is critical for maintaining the overall functionality of the nervous system, especially in the context of the brain's high energy demands.
Signal Fidelity: Maintaining the Integrity of Neural Messages
Myelin sheaths also play a crucial role in maintaining the fidelity of neural signals. They act as insulators, preventing the leakage of ions across the axon membrane and thus minimizing signal degradation over long distances. This ensures that the signal arrives at its destination with minimal distortion, crucial for accurate transmission of information throughout the nervous system. Without myelin, the signal would weaken and become distorted, leading to errors in neural communication.
Demyelination: The Consequences of Myelin Loss
The consequences of demyelination, the loss or damage to the myelin sheath, highlight the importance of myelin's protective and functional roles. Demyelinating diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), cause a range of neurological symptoms, including:
- Slowed nerve conduction: The loss of myelin significantly reduces the speed of nerve impulse transmission, leading to impaired motor function, sensory deficits, and cognitive impairment.
- Distorted signals: The compromised insulation provided by damaged myelin can lead to signal distortion and interference, further impacting neural communication and causing various neurological symptoms.
- Fatigue: The increased energy demands associated with demyelination can lead to profound fatigue, as the nervous system struggles to maintain its function.
- Muscle weakness and spasticity: Impaired motor control resulting from demyelination can manifest as muscle weakness, involuntary muscle spasms, and difficulties with coordination.
- Sensory disturbances: Sensory deficits, such as numbness, tingling, and impaired vision, are common consequences of demyelination, reflecting disruptions in sensory nerve function.
- Cognitive impairment: Demyelination can affect cognitive function, leading to difficulties with memory, attention, and executive functions, primarily affecting regions of the brain critical for these processes.
Developmental Aspects of Myelination: A Gradual Process
Myelination is not a static process; it's a dynamic developmental process that occurs throughout childhood and adolescence, and to a lesser extent into adulthood. Different regions of the nervous system myelinate at different rates, reflecting the progressive maturation of various neural circuits. This developmental timeline is important for understanding the neurological milestones achieved during different stages of life, and helps explain why certain neurological functions mature at different ages.
Myelination and Brain Development
The myelination of the brain is particularly crucial for cognitive development. The progressive myelination of brain regions associated with higher-order cognitive functions, such as the prefrontal cortex, contributes significantly to the development of executive functions, working memory, and complex problem-solving abilities. Delay or impairment in brain myelination can have far-reaching effects on cognitive abilities throughout life.
Myelin and Neurological Diseases: A Focus on Demyelination
Several neurological diseases are directly linked to damage or loss of myelin. Understanding these diseases provides further insight into the crucial role of myelin in maintaining healthy neurological function. Some key examples include:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and demyelination of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS): An acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy affecting the peripheral nervous system.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT): A group of inherited neurological disorders affecting the peripheral nerves, often due to genetic mutations affecting myelin production or structure.
- Leukodystrophies: A group of inherited metabolic disorders that affect the myelin sheath in the brain and spinal cord.
Conclusion: Myelin's Profound Impact
Myelination plays a crucial role in facilitating efficient and effective neural communication. Its impact on the speed of nerve impulse transmission, energy efficiency, signal fidelity, and the overall health of the nervous system is undeniable. The consequences of demyelination highlight the critical importance of maintaining the integrity of the myelin sheath. Understanding the complexities of myelination and its role in neurological function is fundamental to advancing our understanding of neurological diseases and developing effective therapies for these debilitating conditions. Further research into the mechanisms of myelination and the pathophysiology of demyelinating diseases remains crucial for improving neurological health and quality of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A True Statement
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Formula To Determine The Materials To Be Purchased Is
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Rectangular Loop Of Wire With Sides
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Represents A Broad Match Keyword
Mar 15, 2025
-
When Evaluating A Special Order Management Should
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is An Effect Of Myelination . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
