Which Layer Is Composed Primarily Of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Holbox
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
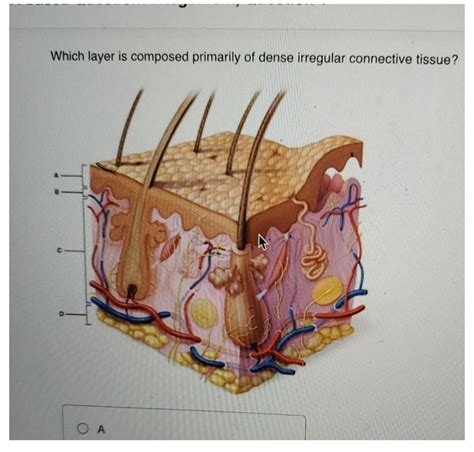
Table of Contents
- Which Layer Is Composed Primarily Of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
- Table of Contents
- Which Layer Is Composed Primarily of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue? A Deep Dive into Connective Tissues
- Understanding Connective Tissues: A Broad Overview
- The Diverse Family of Connective Tissues: A Classification
- Dense Irregular Connective Tissue: Structure and Composition
- Where is Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Found?
- Dense Irregular Connective Tissue vs. Other Connective Tissues
- Clinical Significance of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
- Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Connective Tissues
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Layer Is Composed Primarily of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue? A Deep Dive into Connective Tissues
The human body is a marvel of engineering, composed of numerous intricate systems working in perfect harmony. Understanding the building blocks of these systems – the tissues – is crucial for comprehending overall body function and health. One type of tissue, connective tissue, plays a vital role in supporting, connecting, and separating different tissues and organs. Within the diverse world of connective tissues, dense irregular connective tissue stands out for its unique structure and crucial function. This article will delve deep into the specifics of dense irregular connective tissue, exploring its composition, location, and significant roles in the body. We will also explore how its unique structure relates to its function, contrasting it with other connective tissue types.
Understanding Connective Tissues: A Broad Overview
Before focusing on dense irregular connective tissue, it's essential to establish a foundational understanding of connective tissues in general. Connective tissues are a diverse group characterized by their abundance of extracellular matrix (ECM). This ECM, composed of ground substance and protein fibers, surrounds widely dispersed cells. The properties of the ECM largely determine the characteristics and function of the specific connective tissue type. Connective tissues serve several essential roles in the body, including:
- Connecting and supporting: Binding different tissues and organs together, providing structural support to the body.
- Protection: Shielding organs and tissues from damage.
- Transportation: Facilitating the movement of substances throughout the body (e.g., blood).
- Storage: Storing energy reserves (e.g., adipose tissue) and minerals (e.g., bone).
The Diverse Family of Connective Tissues: A Classification
Connective tissues are broadly classified into several subtypes, each with distinct structural and functional properties:
- Connective Tissue Proper: This category includes loose and dense connective tissues. Loose connective tissues are further subdivided into areolar, adipose, and reticular connective tissues. Dense connective tissues are categorized into dense regular and dense irregular connective tissues.
- Specialized Connective Tissues: This group encompasses cartilage, bone, blood, and lymphatic tissues, each with unique cellular compositions and functions.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue: Structure and Composition
Now, we focus our attention on dense irregular connective tissue. This tissue type is characterized by its densely packed collagen fibers arranged in a random, interwoven pattern. This irregular arrangement is crucial for its function. Unlike dense regular connective tissue (found in tendons and ligaments), which has tightly organized parallel fibers for unidirectional strength, dense irregular connective tissue provides multidirectional strength and resistance to stress.
The main components of dense irregular connective tissue are:
- Collagen Fibers: These are the most abundant fibers, providing tensile strength and resistance to stretching and tearing. Their irregular arrangement allows the tissue to withstand forces from various directions.
- Elastic Fibers: These fibers provide elasticity, allowing the tissue to stretch and recoil. They are less abundant than collagen fibers but contribute significantly to the tissue's resilience.
- Reticular Fibers: These thin collagen fibers provide a supportive framework for the tissue. They are less prevalent than collagen fibers in dense irregular connective tissue.
- Fibroblasts: These are the primary cells of dense irregular connective tissue. They are responsible for synthesizing and maintaining the collagen and elastic fibers.
- Ground Substance: This gel-like substance fills the spaces between the fibers and cells, providing hydration and mediating nutrient exchange.
Where is Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Found?
The multidirectional strength and resilience of dense irregular connective tissue make it ideally suited for locations in the body that experience stress from various directions. Its strategic locations include:
- Dermis of the Skin: The dermis, the deeper layer of skin, contains a significant amount of dense irregular connective tissue. This provides structural support and protection against mechanical injury, abrasion, and stretching.
- Organ Capsules: Many organs are encased in a protective capsule of dense irregular connective tissue. This capsule provides structural integrity and support to the organ. Examples include the kidneys, liver, and spleen.
- Periosteum: The periosteum, the outer layer of bone, contains dense irregular connective tissue. This layer protects the bone, serves as an attachment site for tendons and ligaments, and provides a source of blood supply for bone growth and repair.
- Perichondrium: Similar to the periosteum, the perichondrium is a connective tissue sheath surrounding cartilage. This layer contains dense irregular connective tissue that protects the cartilage and provides nutrients and support.
- Submucosa of the Digestive Tract: The submucosa, a layer beneath the mucosa in the digestive system, contains dense irregular connective tissue. This provides support and flexibility to the digestive tract walls.
- Heart Valves: The structural integrity and resilience of heart valves are partially due to dense irregular connective tissue. This ensures the valves can withstand the repeated stresses of opening and closing.
- Fibrous Layer of the Capsule of the Eye: This layer provides structural support and protection for the delicate eye structures.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue vs. Other Connective Tissues
It's crucial to differentiate dense irregular connective tissue from other connective tissue types, particularly dense regular connective tissue:
| Feature | Dense Irregular Connective Tissue | Dense Regular Connective Tissue |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Arrangement | Random, interwoven | Parallel, highly organized |
| Strength | Multidirectional | Unidirectional |
| Flexibility | Less flexible than loose CT | Less flexible than loose CT |
| Location | Dermis, organ capsules, periosteum | Tendons, ligaments |
| Function | Withstands stress from various directions | Withstands unidirectional tensile stress |
Clinical Significance of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
The integrity of dense irregular connective tissue is vital for overall health. Damage to this tissue can lead to several clinical implications:
- Wound Healing: Efficient wound healing relies on the proper regeneration of dense irregular connective tissue in the dermis. Impaired healing can lead to poor scar formation and increased risk of infection.
- Organ Damage: Injury or disease affecting the organ capsules can compromise organ function.
- Bone Fractures: Damage to the periosteum can impact bone healing and stability.
- Skin Diseases: Many skin diseases involve alterations in the structure and function of the dermis's dense irregular connective tissue.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Connective Tissues
Dense irregular connective tissue, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in supporting the structural integrity and function of numerous organs and tissues throughout the body. Its unique arrangement of densely packed, randomly oriented collagen fibers enables it to withstand stresses from multiple directions. Understanding its composition, location, and clinical significance is vital for appreciating the complexity and elegance of the human body and its remarkable ability to withstand various mechanical stressors. Further research continues to unveil the intricate details of its functions, interactions with other tissues, and importance in health and disease. Its unique characteristics make it an essential component of our complex biological system, working tirelessly to maintain our structural integrity and overall well-being. The next time you think about the strength and resilience of your body, remember the unsung hero, the dense irregular connective tissue, working hard behind the scenes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Received Sales Return Request No R8034
Mar 28, 2025
-
Companies Must Ensure That They Are Reporting Their Inventory At
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Type Of Stress Is Shown In The Image
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Constant Cost Industry Is An Industry In Which
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Regal Cycle Company Manufactures Three Types Of Bicycles
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Layer Is Composed Primarily Of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
