Which Definition Best Describes The Term Molar Mass
Holbox
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
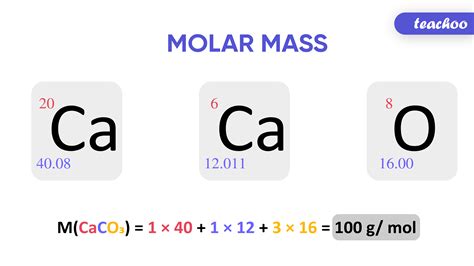
Table of Contents
- Which Definition Best Describes The Term Molar Mass
- Table of Contents
- Which Definition Best Describes the Term Molar Mass?
- Understanding the Building Blocks: Atoms and Moles
- Atoms: The Fundamental Units of Matter
- Moles: A Chemist's Dozen
- Defining Molar Mass: The Mass of a Mole
- Different Ways to Express Molar Mass
- Calculating Molar Mass: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The Significance of Molar Mass in Chemistry
- Stoichiometry: Predicting Reaction Yields
- Solution Chemistry: Determining Concentration
- Gas Laws: Relating Volume to Moles
- Addressing Common Misconceptions
- Conclusion: The Cornerstone of Quantitative Chemistry
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Which Definition Best Describes the Term Molar Mass?
The term "molar mass" is fundamental in chemistry, yet its precise meaning can sometimes be elusive, particularly for those new to the subject. Understanding molar mass is crucial for performing stoichiometric calculations, predicting reaction yields, and generally grasping the quantitative aspects of chemical reactions. This article will delve deeply into the definition of molar mass, exploring various interpretations and clarifying any potential ambiguities. We'll also explore related concepts and demonstrate its practical application through examples.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Atoms and Moles
Before diving into molar mass, we need to establish a firm understanding of its constituent parts: atoms and moles.
Atoms: The Fundamental Units of Matter
Atoms are the basic units of matter. Each element is composed of atoms with a unique number of protons in their nucleus, defining their atomic number. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons, resulting in isotopes, which affect the atomic mass.
Moles: A Chemist's Dozen
A mole (mol) is a unit representing a specific number of particles, whether atoms, molecules, ions, or other entities. This number, known as Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10²³), is a constant used to relate the macroscopic world of grams and kilograms to the microscopic world of atoms and molecules. Essentially, a mole provides a convenient way to count incredibly large numbers of tiny particles.
Defining Molar Mass: The Mass of a Mole
Now, we can tackle the core concept: molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. This seemingly simple definition encompasses several key aspects:
-
Substance: This refers to any chemical species – an element, a compound, or even a mixture, although molar mass is most commonly used for pure substances.
-
One Mole: This is crucial. The mass isn't just the mass of a single atom or molecule, but the mass of 6.022 x 10²³ of them. This allows for practical measurements in the lab.
-
Mass: This is the weight of the substance, usually expressed in grams (g). While other units can be used, grams are the most common and convenient for molar mass calculations.
Different Ways to Express Molar Mass
The definition of molar mass might be presented in slightly different ways, depending on the context:
-
The mass in grams of one mole of a substance: This is the most straightforward and widely accepted definition. It emphasizes the practical aspect of measuring the mass of a macroscopic sample.
-
The mass of Avogadro's number of particles of a substance: This definition highlights the connection between the macroscopic world (grams) and the microscopic world (atoms and molecules) through Avogadro's number.
-
The average atomic mass (for elements) expressed in grams per mole: For elements with multiple isotopes, the molar mass represents the weighted average of the masses of these isotopes, taking into account their natural abundances.
Calculating Molar Mass: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating molar mass is a fundamental skill in chemistry. The process involves utilizing the atomic masses of the constituent elements, which are typically found on the periodic table.
For elements: The molar mass of an element is numerically equal to its atomic mass, but the units are grams per mole (g/mol). For example, the atomic mass of carbon (C) is approximately 12.01 amu, so its molar mass is 12.01 g/mol.
For compounds: The molar mass of a compound is calculated by summing the molar masses of all the atoms present in its chemical formula. For example, to calculate the molar mass of water (H₂O):
-
Determine the molar mass of each element:
- Hydrogen (H): 1.01 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
-
Multiply the molar mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the formula:
- Hydrogen: 2 atoms x 1.01 g/mol = 2.02 g/mol
- Oxygen: 1 atom x 16.00 g/mol = 16.00 g/mol
-
Add the results:
- 2.02 g/mol + 16.00 g/mol = 18.02 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of water is 18.02 g/mol.
The Significance of Molar Mass in Chemistry
Molar mass is not just a theoretical concept; it's a crucial tool used extensively in various chemical calculations:
Stoichiometry: Predicting Reaction Yields
Stoichiometry deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Molar mass is essential for converting between mass and moles, allowing chemists to predict the amount of product formed or reactant consumed in a reaction. It bridges the gap between the theoretical quantities in a balanced chemical equation and the actual amounts used or produced in a lab setting.
Solution Chemistry: Determining Concentration
Molarity, a common unit of concentration in solution chemistry, is defined as moles of solute per liter of solution. Calculating molarity requires knowing the molar mass of the solute to convert mass to moles. Similarly, other concentration units, such as molality, also rely on molar mass for calculations.
Gas Laws: Relating Volume to Moles
The ideal gas law (PV = nRT) relates pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), temperature (T), and the ideal gas constant (R). Molar mass allows for the conversion between the mass of a gas and the number of moles, enabling calculations involving gas volumes.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
A few common misunderstandings about molar mass need clarification:
-
Molar mass is not the same as atomic mass: While numerically related for elements, the units differ. Atomic mass is expressed in atomic mass units (amu), while molar mass is in grams per mole (g/mol).
-
Molar mass is an average for elements with isotopes: The molar mass of an element reflects the weighted average of the masses of its isotopes, considering their natural abundances. It's not the mass of a single atom.
-
Molar mass is not always a whole number: Due to the presence of isotopes and their different abundances, molar masses are often non-integer values.
Conclusion: The Cornerstone of Quantitative Chemistry
In summary, the most accurate and comprehensive definition of molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole. This definition encompasses the crucial connection between the microscopic world of atoms and molecules and the macroscopic world of laboratory measurements. Understanding molar mass is paramount for performing accurate stoichiometric calculations, determining solution concentrations, applying gas laws, and making many other essential computations in chemistry. Its widespread application underscores its fundamental role as a cornerstone of quantitative chemistry. By mastering the concept of molar mass, students and professionals alike gain a robust understanding of the quantitative relationships underpinning the field.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Correct
Mar 26, 2025
-
Dna Replication Is Called Semiconservative Because
Mar 26, 2025
-
Rank The Following Quantities In Order Of Decreasing Distance
Mar 26, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Muscles Of The Leg
Mar 26, 2025
-
Gathering The Information Needed And Then Setting Departmental Goals
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Definition Best Describes The Term Molar Mass . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
