What Is 58 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius
Holbox
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
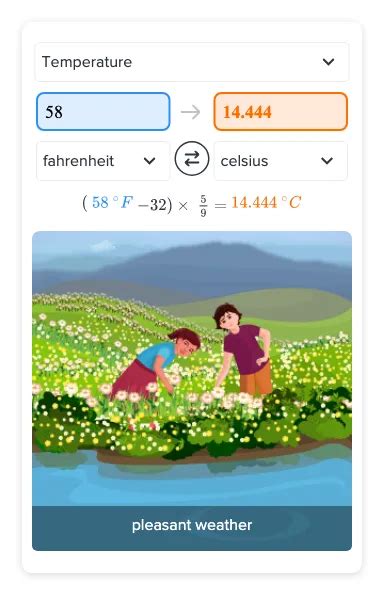
Table of Contents
What is 58 Degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius? A Comprehensive Guide
Knowing how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a valuable skill, especially in our increasingly interconnected world. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "What is 58 degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius?" but also delve deep into the intricacies of temperature conversion, exploring the history, formulas, and practical applications of both scales. We'll also examine scenarios where this conversion might be useful and provide additional resources to further enhance your understanding.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before we dive into the conversion, let's understand the two temperature scales involved:
Fahrenheit (°F)
The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, is a temperature scale where the freezing point of water is 32 degrees (°F) and the boiling point is 212 °F, both at standard atmospheric pressure. This scale is still predominantly used in the United States, a few Caribbean islands, and some other parts of the world. However, its use is diminishing globally in favor of the Celsius scale.
Celsius (°C)
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a temperature scale where the freezing point of water is 0 degrees (°C) and the boiling point is 100 °C, also at standard atmospheric pressure. This scale is widely used internationally and is the preferred temperature scale in scientific contexts and most parts of the world. Its simplicity and logical increments make it easier to understand and use than the Fahrenheit scale.
Converting 58°F to Celsius
Now, let's address the main question: What is 58 degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius?
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Plugging in 58°F into the formula:
°C = (58 - 32) × 5/9 = 26 × 5/9 = 130/9 ≈ 14.4°C
Therefore, 58 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately equal to 14.4 degrees Celsius.
Beyond the Conversion: A Deeper Dive into Temperature Scales
While the simple conversion is straightforward, understanding the underlying principles of these scales provides a richer understanding of temperature measurement.
The History of Temperature Scales
The development of reliable temperature scales was a crucial step in scientific advancement. Fahrenheit's scale, initially based on three fixed points (the freezing point of a brine solution, the freezing point of water, and human body temperature), evolved over time. Celsius, originally created by Anders Celsius, initially defined 0°C as the boiling point of water and 100°C as its freezing point – the opposite of the modern scale. This inversion was later corrected. The differences in these scales highlight the historical context of scientific measurement.
Kelvin (K) – The Absolute Temperature Scale
Beyond Fahrenheit and Celsius, the Kelvin scale is another crucial temperature scale used extensively in science and engineering. Unlike Fahrenheit and Celsius, which are relative scales, the Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale. This means that 0 Kelvin (0 K) represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. The Kelvin scale is related to Celsius by the following equation:
K = °C + 273.15
Therefore, 14.4°C is equivalent to approximately 287.55 K. The Kelvin scale is essential for calculations involving thermodynamics and other scientific disciplines.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various practical scenarios:
Everyday Life:
- Cooking and Baking: Many recipes use either Fahrenheit or Celsius, depending on the origin and intended audience. Accurate conversions are crucial for consistent results.
- Weather Forecasting: International weather reports often use Celsius, while those within the United States frequently use Fahrenheit. Converting between the two is essential for a comprehensive understanding of weather conditions.
- Travel: Knowing how to convert temperature units is essential when planning international trips, helping you pack appropriately for the expected weather.
- Healthcare: Body temperature is often measured in either Fahrenheit or Celsius, depending on the region and device. Converting these units is essential for accurate medical record-keeping and diagnosis.
Scientific and Engineering Applications:
- Material Science: Many material properties, such as melting points and boiling points, are often provided in both Fahrenheit and Celsius. Accurate conversion is crucial for correct application and process design.
- Chemical Engineering: Chemical processes are often temperature-sensitive, and precise conversions are needed for accurate calculations and process control.
- Meteorology: Understanding temperatures at various atmospheric levels necessitates accurate conversions between different units of measurement.
- Environmental Science: Analyzing climate change data often involves working with temperature measurements in both Fahrenheit and Celsius.
Other Applications:
- Automotive Industry: Engine performance and cooling systems depend on precise temperature control and measurements, requiring accurate conversions between units.
- Aerospace Engineering: Aircraft design and operation necessitate meticulous temperature control and monitoring, highlighting the importance of consistent unit conversions.
Expanding Your Knowledge: Resources and Further Learning
To further enhance your understanding of temperature scales and conversions, you can explore several resources:
- Online Converters: Numerous websites offer free online tools for converting between Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin. These tools provide instant conversions and can be useful for quick calculations.
- Scientific Textbooks and Journals: For a deeper understanding of the underlying physics and history of temperature scales, consult relevant scientific texts.
- Educational Websites: Many educational websites provide comprehensive information on temperature conversion and related topics.
Conclusion
Understanding temperature conversion is not merely a matter of calculation but also a valuable skill that bridges cultural and scientific differences. The conversion of 58°F to approximately 14.4°C is just one example of the broader significance of understanding temperature scales. By mastering these conversions and appreciating their historical and practical applications, you can enhance your understanding of the world around you and navigate a variety of situations with greater confidence and accuracy. The ability to seamlessly transition between Fahrenheit and Celsius demonstrates a versatile skillset applicable across many disciplines. Remember that while the formula provides a precise mathematical conversion, appreciating the context of the units themselves adds depth to your understanding. By further exploring the resources mentioned above, you can enhance your knowledge and contribute to a more accurate and globally connected understanding of temperature measurements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Life Cycle Of A Sea Turtle
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Do Toucans Need To Survive
Mar 10, 2025
-
Light Source Of A Microscope Function
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Heart Chambers Do Frogs Have
Mar 10, 2025
-
Viscosity Of Water At 25 C
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 58 Degrees Fahrenheit In Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
