What Do Sutures Gomphoses And Syndesmoses Have In Common
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
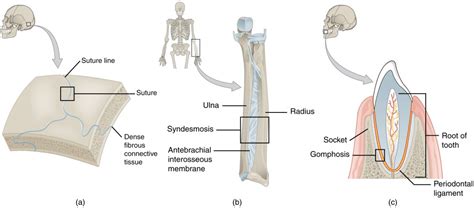
Table of Contents
What Do Sutures, Gomphoses, and Syndesmoses Have in Common? A Deep Dive into Fibrous Joints
Understanding the intricacies of the human skeletal system requires a detailed examination of its various components. One crucial aspect is the classification and characteristics of joints, the points where two or more bones meet. While synovial joints, characterized by their fluid-filled cavities, are often the focus of attention, a significant group of joints—fibrous joints—play a crucial role in providing stability and structure. This article delves into the shared characteristics of three specific types of fibrous joints: sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses. We will explore their similarities, highlighting their unique features and emphasizing their collective contribution to the overall skeletal framework.
The Unifying Feature: Fibrous Connective Tissue
The fundamental characteristic that unites sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses is their reliance on fibrous connective tissue for connection. Unlike synovial joints with their synovial fluid-filled cavities, these joints are characterized by a lack of a synovial cavity. Instead, the bones are held together by dense fibrous connective tissue, composed primarily of collagen fibers. This dense fibrous tissue provides strong, yet often inflexible, connections between the bones. The amount and arrangement of this connective tissue dictate the specific type of fibrous joint and its degree of movement.
Sutures: The Intricate Joints of the Skull
Sutures are a unique type of fibrous joint found exclusively in the skull. These joints are characterized by their interlocking, irregular edges, creating a strong, interlocking connection between the cranial bones. The fibrous connective tissue within sutures is exceptionally dense and tightly interwoven, allowing for minimal movement. This immobility is crucial for protecting the brain and maintaining the structural integrity of the skull.
Types of Sutures: A Closer Look
Different types of sutures exist, reflecting the variations in the interlocking patterns of the cranial bones. These include:
- Serrate sutures: These sutures exhibit saw-toothed interlocking edges, providing maximal interdigitation and stability, as seen in the sagittal suture.
- Squamous sutures: These sutures feature overlapping edges, resulting in a smoother, less interlocking connection, as exemplified by the squamous suture between the temporal and parietal bones.
- Plane sutures: These sutures exhibit relatively straight, non-overlapping edges, offering a simpler, yet still strong, connection.
The Significance of Sutures in Development
Sutures play a vital role in skull development and growth. During infancy and childhood, these joints allow for some degree of movement, accommodating the growing brain. As the skull reaches maturity, the sutures gradually fuse, resulting in a rigid and immobile structure. This process of fusion, known as synostosis, is essential for protecting the brain and providing the skull with its characteristic shape. Premature fusion of sutures can lead to craniosynostosis, a condition that can cause abnormal skull shape and potential neurological complications.
Gomphoses: The Peg-in-Socket Joints
Gomphoses represent another type of fibrous joint, distinguished by their unique peg-in-socket structure. The most prominent example of a gomphosis is the articulation between the teeth and the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible. The peg, represented by the root of the tooth, fits snugly into the socket, the alveolar process. This connection is secured by a type of fibrous connective tissue called the periodontal ligament.
The Periodontal Ligament: A Specialized Connective Tissue
The periodontal ligament is not merely a passive connector; it plays a crucial role in absorbing forces during mastication, protecting the tooth and its supporting structures from excessive stress. It also facilitates slight movement, allowing the teeth to accommodate during chewing and preventing damage. While this movement is minimal, it distinguishes gomphoses from the completely immobile sutures.
Syndesmoses: The Fibrous Joints with Variable Movement
Syndesmoses are fibrous joints in which the bones are connected by a significant amount of fibrous connective tissue, typically a ligament or an interosseous membrane. Unlike sutures and gomphoses, syndesmoses allow for a degree of movement, depending on the length and structure of the connecting fibrous tissue.
Examples of Syndesmoses: A Spectrum of Movement
The range of movement in syndesmoses varies considerably. Some syndesmoses, like the connection between the tibia and fibula in the lower leg, allow for a limited amount of rotation and gliding. This articulation is strengthened by the interosseous membrane, a sheet of dense fibrous connective tissue. Other syndesmoses, characterized by shorter and thicker ligaments, allow for even less movement.
The Interosseous Membrane: A Versatile Connector
The interosseous membrane, a key feature of many syndesmoses, is a broad sheet of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects parallel bones. This membrane not only provides stability but also serves as an attachment site for muscles. Its flexibility and strength are crucial for supporting weight-bearing activities and facilitating subtle movements.
Shared Characteristics and Key Differences: A Comparative Overview
While sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses share the defining characteristic of being fibrous joints connected by dense connective tissue, they exhibit distinct differences in their structure, location, and degree of movement.
| Feature | Sutures | Gomphoses | Syndesmoses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Skull | Teeth and alveolar processes | Between various long bones |
| Connective Tissue | Dense fibrous connective tissue | Periodontal ligament | Ligaments, interosseous membranes |
| Movement | Immobile (synarthroses) | Minimal movement | Variable (amphiarthroses) |
| Structure | Interlocking, irregular edges | Peg-in-socket | Bones connected by ligaments or membranes |
Clinical Significance: Implications of Dysfunction
Dysfunction in fibrous joints can have significant clinical implications. For instance, premature fusion of sutures (craniosynostosis) can lead to abnormal skull shape and potential neurological complications. Damage to the periodontal ligament can result in tooth loosening and loss. Injury to syndesmoses, such as a high ankle sprain involving the syndesmosis between the tibia and fibula, can cause pain, instability, and impaired function.
Conclusion: The Unsung Heroes of Skeletal Stability
Sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses, though often overshadowed by the more mobile synovial joints, play a pivotal role in providing structural support and stability to the skeleton. Their shared reliance on dense fibrous connective tissue underlies their function, while their individual variations in structure and degree of movement reflect their specialized roles within the body. Understanding the similarities and differences between these fibrous joints offers valuable insights into the overall mechanics and complexities of the human skeletal system and its potential vulnerabilities. Further research into the specific properties of the connective tissues and the biomechanics of these joint types will continue to unravel their intricate roles in maintaining overall skeletal health and function. The strength and stability they provide are crucial for protecting vital organs and enabling coordinated movement throughout life. Appreciating the complexities of these seemingly simple joints enriches our understanding of the marvels of human anatomy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Conceptual Physics Practice Page Chapter 14 Gases Gas Pressure Answers
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Core Assumption Underpins The Coaching Relationship
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Materiality Constraint As Applied To Bad Debts
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Structure Is Common To Both Gymnosperms And Angiosperms
Mar 19, 2025
-
Two Blocks Are Connected By A Massless Rope
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Do Sutures Gomphoses And Syndesmoses Have In Common . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
